Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
Les rongeurs du Miocène moyen et supérieur du MaghrebJean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Neogene; North Africa; RodentiaAbstract The Faunas of Rodents from seven north-african fossiliferous beds distributed from the Middle up to the Uppest Miocene are studied. One genus, seventeen species, one subspecies described are new. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 1 (1977) |
|
|
|
Les vertébres dévoniens de la Montagne Noire (Sud de la France) et leur apport à la phylogénie des pachyosteomorphes (Placodermes Arthrodires).Hervé Lelièvre, Raimund Feist, Daniel Goujet and Alain BlieckKeywords: Devonian; Montagne Noire; New taxon; PHYLOGENY; Placoderms; Stratigraphy; VertebrateAbstract Several different taxa of jawed vertebrates are reported for the first time from the Devonian of south-eastern Montagne Noire, France. Besides some undeterminable fragments of placoderm fishes from the Pragian and Lower Emsian, the material from the Upper Devonian is mainly represented by Melanosteus occitanus gen. and sp. nov. (Frasnian) and Thoralodus cabrieri LEHMAN, 1952 ("Famennian"). The good state of preservation of Melanosteus allows a detailed anatomical study leading to a phylogenetic analysis of the selenosteid pachyosteomorphs. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 1 (1987) |
|
|

|
Les nouvelles faunes de rongeurs proches de la limite mio-pliocène en Roussillon. Implications biostratigraphiques et biogéographiquesJean-Pierre Aguilar, Jacques Michaux, Bernadette Bachelet, Marc Calvet and Jean-Pierre FaillatKeywords: Arvicolidae; Cricetidae; Gliridae; Miocene; Muridae; Pliocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract Three new fossiliferous localities, two of karstic origin, Castelnou 3 and Font Estramar, respectively Late Upper Miocene and Lower Pliocene, and one of lacustrine origin, Thuir, Lower Pliocene, add data about the transition between Miocene and Pliocene faunas of rodents in southern France. An unexpected association of taxa was present in the late Upper Miocene, including between others, Myocricetodon, Hispanomys, Ruscinomys, Cricetus barrierei, Promimomys and a new species of Stephanomys, S. dubari nov. sp. Myocricetodon is still known in the Lower Pliocene. It is shown that the large field-mice known since the Late Upper Miocene belong to two different lineages, on one side, A. jeanteti, on the other side, A. gudrunae followed by A. gorafensis. Biochronological and biogeographical implications are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 4 (1991) |
|
|

|
Révision des Chiroptères Lutériens de Messel (Hesse, Allemagne).Donald E. Russell and Bernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Lutetian; Messeldoi: 10.18563/pv.3.4.83-182 Abstract The revision of the Lutetian chiropterans from Messel, first described by Revilliod in 1917, is based on the anatomy of the teeth and the skeleton. A figuration or refiguration of thematerial utilized accompanies the new description, which goes beyond that of the original monograph. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 4 (1970) |
|
|

|
Revision der Equoidea aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bel Halle (DDR).Jens L. Franzen and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Eocene; Europe; Mammalia; Perissodactyla; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The dentitions as well as one complete and several partial skeletons of Equoids from the Eocene lignite beds of the Geiseltal locality are revised. Instead of 13 species distinguished up to now 3 chronoclines with 5 species and 3 separate species are recognized (text. fig. 1). Propalaeotherium hassiacum HAUPT, 1925 is evolving into Propalaeotherium isselanum (CUVIER, 1824) between the levels of the « obere Unterkohle ›› and the « untere Mittelkohle ›› of the Geiseltal section. Propalaeotherium argentonicum GERVAIS, 1849 is shown to be present in the « untere Unterkohle ››, whereas Lophiotherium pygmaeum (DEPERET,1901) occurs in the « obere Mittelkohle ›› and in the « oberes Hauptmittel ››. Plagiolophus cartieri STEHLIN, 1904 appears during the transition from the « Mittelkohle ›› into the « Oberkohle ›› as the earliest true Palaeothere. Therefore the « Oberkohle ›› is already regarded as Upper Eocene. This is corroborated by the occurrence of a phyletic descendant of Propalaeatherium parvulum (Propalaeotherium n.sp.) in the middle and upper "Oberkohle " because this species appears otherwise for the first time at the mammal level of Lissieu. On the other hand Propachynolophus gaudryz (LEMOINE, 1878) described by Matthes (1977) from the « untere Unterkohle ›› turns out te be in fact a Phenacodont. Thus the decisive argument for classifying the « untere Unterkohle ›› as Lower Eocene has to be dropped. Biostratigraphically the « Unterkohle ›› and the «Basishauptrnittel ›› correspond with the lower Middle Eocene (mammal level of Messel), whereas the «unteres Hauptmittel ›› and the « untere Mittelkohle ›› are equivalent to the middle part of the middle Eocene (mammal level of lssel), and the « obere Mittelkohle ›› together with the « oberes Hauptmittel ›› coincide with the upper Middle Eocene (mammal level of Bouxwiller). Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
Evolution des Aplodontidae Oligocènes EuropéensNorbert Schmidt-Kittler and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Aplodontidae; Europe; OligoceneAbstract Until now Aplodontidae of the European Oligocene have been documented by four species only. The phylogenetic relations remained obscure. as the distribution of only one species has been known in some detail. New material made it possible to define the stratigraphic range of two of the already existing species (Plesispermophilus angustidens, Sciurodon cadurcense) and to follow their development during the Oligocene beginning with the event of the « Grande Coupure ››. Sciurodon remained nearly without change until the end of the Middle Oligocene. Plesispermophilus angustidens split into two distinct phyletic lines, one of which (P. macrodon n. sp.) reaching considerable size, is represented till the beginning of the Upper Oligocene (Pech de Fraysse, Gaimersheim). The other line leads to Plesispermophilus ernii (basal Upper Oligocene of Burgmagerbein 1. terminal Upper Oligocene of Coderet). Besides the already known forms a new small-sized species (P. atavus n. sp.) is described, which by its primitive features closely resembles the genus Plesispermophilus. Two other small-sized species already known from the Upper Oligocene (? P. argoviensis) and Lower Miocene (? P. descedens) seem to be closely related to the new species. It cannot be decided whether they are descendents of this line or have developed independently, because of their poor fossil record. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 2 (1979) |
|
|
|
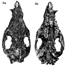
Ein neuer condylarthre und ein tillodontier (Mammalia) aus dem Mitteleozän des Geiseltales.Jens L. Franzen and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Condylarthra; Eocene; Europe; Mammalia; taxonomy; TillodontiaAbstract In the course of a revision of the Equoidea numerous dentitions as well as a partial skeleton of a Phenaeodont were discovered from the Middle Eocene lignite beds of the Geiseltal locality. These fossils are recognized as a new genus and species of Phenacodontidae : HaIlensia matthesi n.g. n.sp.. The species is present in the « untere und obere Unterkohle ›› (uUK, oUK = the lower and upper part of the Lower Coal Seam) as well as in the « obere Mittelkohle ›› (oMK = the upper part of the Middle Coal Seam). Two fragmentary upper jaws described and figured by Matthes (1977) as Propachynolophus gaudryi are also belonging to Hallensia matthesi. Thus the decisive argument for classifying the " Unterkohle " of the Geiseltal section as Lower Eocene has to be dropped. Another relict form of the Geiseltal is Esthonyx tardus n. sp. documented by a fragmentary mandible coming from the « untere Unterkohle ››. This is the latest Tillodont from Europe. Contrasting to E. munieri from the european Lower Eocene the dentition of E. tardus is morphologically more progressive. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
First Neogene Otonycteris (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from Ukraine: its biostratigraphic and paleogeographic significance.Valentina V. RosinaKeywords: bats; East Europe; Gritsev; Late Miocene; Mammaliadoi: 10.18563/pv.39.1.e2 Abstract A new species, Otonycteris rummeli nov. sp., is described from the Late Miocene site Gritsev (MN 9) in the Ukraine. Otonycteris rummeli nov. sp. differs from those of most vespertilionids, except recent Otonycteris, Antrozous and Early Miocene Karstala silva, in having a well-developed entocingulid at the foot of the trigonid valley in the lower molars. The morphological resemblance of Otonycteris, Antrozous and Karstala is apparently a case of convergence in the evolution of the Old and New Worlds bat faunas. From at least the Middle Miocene the range of Otonycteris distribution spread to the whole of Central Europe and such a situation continued during the whole Late Miocene. This indicates a more arid climate in Europe during the Upper Miocene compared to the Quaternary. The reduction of the distribution range of Otonycteris and its extinction in most of the territory of Europe could have been caused by the global climatic cooling and increasing glacial cycle amplitude during the onset of the Quaternary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-1 (2015) |
|
|

|
Problems of classification as applied to the RodentiaAlbert E. WoodKeywords:Abstract A classification should be both usable and useful,not too complex either in the amount of splitting or in the number of hierarchies involved, and not so simple as to give a false assurance of knowledge of relationships. Classifications are only possible because we do not have complete knowledge of the evolution of the organisms concerned because gaps in the record are necessary to allow the separation of the various taxa. Rodent classification is complicated by the large number of organisms involved and by the geat amount of parallelism that has taken place in the evolution of any and all features. If several independent features are characteristic of a certain taxon, should an effort be made to define the group on the basis of all the features, or should only one be selected as the determinant ? Unless the evolution of the several features was closely linked, the former solution will sooner or later lead to insurmountable problems. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
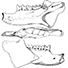
Artiodactyla aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bei Halle (DDR)Jorg Erfurt and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Artiodactyles; Eocene; Europe; Paleoecology; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The present study of Artiodactyla from the Middle Eocene of the Geiseltal lignite beds concems systematics, biostratigraphy, and palaeoecology on the basis of 174 specimens: isolated remains to more complete skeletons. Instead of the formerly known five species of two families are now recognized 14 species of the Diacodexeidae, Dichobunidae, Cebochoeridae, and Haplobunodontidae. New species are Aumelasia maniai, Anthracobunodon neumarkensis, Masillabune franzeni. Four species of the Geiseltalfauna are definitely known from elswere, and five species are closely related to those from other European localities. Evidently the faunal situation of artiodactyls during the Middle Eocene of Europe was largely uniform. The distribution of artiodactyls within the sequence of the Geiseltal strata corroborates the biostratigraphical concept of the land mammal age Geiseltalian (Franzen & Haubold l986b) as well as the mammalian reference levels MP 11-13 (Franzen 1987). Reconstructions of the skulls and skeletons allow conclusions on the functional morphology and palaeoecology of the artiodactyls of the European Middle Eocene Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|

|
Evolution et extinction des reptiles marins au cours du Mésozoïque.Nathalie BardetKeywords: Crocodiles; evolution; Extinctions; faunal assemblages; Helveticosaurs; Hupehsuchians; Ichthyoaurs; lizards; Marine Reptiles; Mesozoic; Nothosaurs; Pachypleurosaurs; Placodonts; Plesiosaurs; Snakes; Thalattosaurs; Turnovers; TurtlesAbstract An interpretation of the marine reptile fossil record, based on the existing litterature and complemented by the review of ancient collections and the study of new material, permits a better understanding of Mesozoic marine ecosystems. An inventory of the marine reptiles known from the Lower Triassic to the Paleocene is presented: 46 families, about 200 genera and 400 species have been recorded. This data base includes commentaries about systematics, stratigraphical ranges and geographical distribution of taxa. Marine reptiles include a mosaic of not necessarily closely related groups: ichthyosaurs, thalattosaurs, hupehsuchians, pachypleurosaurs, placodonts, nothosaurs, plesiosaurs, pliosaurs but also crocodiles, lizards, snakes, turtles. The diversity studies reveal that the fossil record of marine reptiles has been punctuated by two mass extinctions, during the Middle-Upper Triassic transition and at the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. The Jurassic-Cretaceous and Cenomanian-Turonian boundaries (the latter marked by the disappearance of ichthyosaurs) are potential crisis periods, but current data are not sufficient to reach conclusions. The Ladinian-Carnian transition is characterized by the disappearance of 64 % of families and affects essentially coastal forms. This extinction coincides with an important regressive phase. During the Upper Triassic, a faunal reorganisation within marine reptiles leads to the progressive disappearance of near-shore forms and to the development of pelagic groups. During the Maastrichtian-Danian crisis, 36% of families died out. Large-sized pelagic forms such as mosasaurs and elasmosaurs were the most affected and their extinction seems to have been rather sudden. On the other hand, pliosaurs and protostegid turtles became extinct, but were already declining. The survivors were near-shore forms such as crocodiles, snakes and some turtles and they may have taken refuge in freshwater environments. A break in the food chain based on phytoplankton is proposed as an extinction scenario for pelagic forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 3-4 (1995) |
|
|

|
Relations phylétiques de Bachitherium filhol, ruminant de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Denis Geraads, Geneviève Bouvrain and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Bachitherium; Cladistic analysis; France; Mammalia; Oligocene; RuminantiaAbstract A detailed comparative study of a complete skeleton of Bachitherium and a cladistic analysis of the sub-order Neoselenodontia lead us to propose a cladogram and a new classification of this group. The Tylopoda are the sister-group of the Ruminantia, which are chiefly defined by the fusion of the cuboid and navicular. Within this infra-order, Amphimeryx is the sister genus of a tetraselenodont group, in which the Hypertragulidae are well-separated group from a monophyletic group defined by the loss of trapezium, fusion of capitatum and trapezoid, and the isolation of the hypoconid on lower molars. The most primitive genera of this group, Lophiomeryx and Iberomeryx still have an open trigonid on the lower molars, but this is lingually closed in Archaeomeryx, sister-genus of the higher Ruminantia which have fused metatarsals and more evolved milk teeth. We divide them into two pan/orders : Tragulina (including the recent and miocene Tragulidae, and the North-American Leptomerycidae), and Pecora, with reduced lateral metacarpals and a new crest (telocristid) on the lower premolars. Within the Pecora, the upper molars of Gelocus are more primitive than those of Bachitherium (a genus with many autapomorphies in the dentition) itself more primitive than the group Prodremotherium + Eupecora, with fused metacarpals. We consider the Eupecora (including several genera without frontal appendages) to be monophyletic. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 2 (1987) |
|
|

|
Designating a lectotype for Mesacanthus pusillus (Gnathostomata: Acanthodii)Matthew Baron and Kevin SeymourKeywords: acanthodians; Chordata; Devonian; Midland Valley; Orcadian Basindoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e2 Abstract The early gnathostome genus Mesacanthus is well represented in both Lower Old Red Sandstone and Middle Old Red Sandstone assemblages of northern and central Scotland. This ‘acanthodian’ taxon is currently thought to comprise two valid species: M. mitchelli and M. pusillus. Although the whereabouts of the holotype of M. mitchelli (NHMUK PV P560) is known, the syntype material for M. pusillus has long been thought lost. Here we identify at least one specimen that formed part of the original syntype material for M. pusillus, albeit in a slightly different condition than when it was originally figured. This specimen is ROM 25872, which is here designated as the lectotype. A second specimen – ELGNM 1978.191.1 – could represent another of the syntype specimens, but poor preservation quality makes it impossible to be certain. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
S.I. Data |

|
Une faunule de vertébrés sous la base de grès de Celas (Eocène supérieur) à ST Dresery (Gard)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Artiodactyla; Biostratigraphy; Eocene; MammalsAbstract The St-Dézéry local fauna (3 reptile-, 4 mammal species) is approximately of the same age as the La Débruge or the Ste-Néboule faunas. It conduces to a better dating of the limestones underlying the Célas sandstones. A large part of a mandible of Amphimeryx was found there, which documents the record of this family of small artiodactyls Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Un giraffidae dans le pliocène de Montpellier ?Claude GuérinKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Giraffidae; Mammalia; Montpellier; RuscinianAbstract An upper giraffid premolar without any indication about its origin is preserved at the Montpellier University among numerous fossils from the ruscinian formation of Montpellier. It can be related to Samotherium, of the Upper Miocene in Eastern Europe, North Africa and Asia, or more probably to Bramatherium or Hydaspitherium of the Pliocene of South East Asia. The sedimentological study of the matrix shows a calcareous background, which may indicate that this tooth does not come from the Montpellier formation. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|

|
Contribution à la classification des Pistes de Vertébrés du Trias : les types du Stormberg d'Afrique du Sud (2 ème Partie: le Stormberg supérieur - 1. Le biome de la zone B/1 ou niveau de Moyeni: ses biocénoses).Paul EllenbergerKeywords: biocenosis; Footprints; South Africa; Stormberg; TriasAbstract Les Pistes de Vertébrés du Stormberg Supérieur ("Trias terminal à Rhétien"), ou Quthingien Article infos Published in Vol. 6, Ext (1974) |
|
|
|
Critical comments on the genus Propachynolophus Lemoine, 1891 (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Equoidea)
|
|
S.I. Data |
|
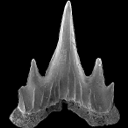
Two new scyliorhinid shark species (Elasmobranchii, Carcharhiniformes, Scyliorhinidae), from the Sülstorf Beds (Chattian, Late Oligocene) of the southeastern North Sea Basin, northern Germany.Thomas ReineckeKeywords: Chattian; Elasmobranchii; North Sea Basin; Scyliorhinidae; Scyliorhinusdoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e1 Abstract Based on isolated teeth two new scyliorhinid shark species, Scyliorhinus biformis nov. sp. and Scyliorhinus suelstorfensis nov. sp., are described from the Sülstorf Beds, early-middle Chattian, of Mecklenburg, northeastern Germany. They form part of a speciose assemblage of necto-benthic sharks and batoids which populated the warm-temperate to subtropical upper shelf sea of the south-eastern North Sea Basin. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|
|
|
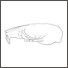
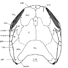
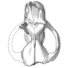
A new Ardynomys (Rodentia,Cylindrodontidae) from the Eocene of the eastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia.Demberelyin DashzevegKeywords: Ardynomys; Eocene; Mongolia; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract A partial skull of Ardynomys russelli sp. nov. (Rodentia, Cylindrodontidae) is described. This was collected in the late Eocene of Alag Tsab locality in the eastem Gobi Desert, Mongolia. Ardynomys russelli sp. nov. is characterized by small size, brachyodont molars, and retention of P3. It represents the earliest record of the genus Ardynomys MATTHEW & GRANGER, 1925, in Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
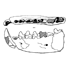
Pantolestidae nouveaux (Mammalia, Insectivora) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller (Alsace).Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Bouxwiller; Insectivora; Mammalia; Middle Eocene; Pantolestidaedoi: 10.18563/pv.3.3.63-82 Abstract The Pantolestidae from the middle eocene of Bouxwiller are the subject of a detailed study. Buxolestes hammeli (n. g., n. sp.) is not closely related to any other European or North American form described until now; it presents, however, some characters in common with Pantolestes, a form of the same age from North America. A parallel evolution from a common ancestral form could explain this ressemblance. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 3 (1970) |
|