Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Les traces de pas d'amphibiens, de dinosaures et autres reptiles du Mesozoïque Français : inventaire et interprétations.Georges Gand, Georges Demathieu and Christian MontenatKeywords: Footprints; France; Inventory; Mesozoic; palaeontology; palaeovenvironments; Stratigraphydoi: 10.18563/pv.35.1-4.1-149 Abstract Since the 19th century, thousands of footprints were observed in the geological series of the French Mesozoic. All are located in the Triassic and Jurassic. After a promising beginning, in France, it is only a few papers which will be published in the first half 20th century, unlike the USA and of others countries of Western Europe. One ought to wait about 1950 for a revival and now they are nearly 200 papers which were devoted to the ichnofossils. The literature abundance and the renewed interest of the naturalists for the palichnologic studies decided to us to write a synthesis work. This one begins with a stratigraphic inventory in which, localisation, age and paleontological contents of about 180 fossiliferous sites are specified. After having pointed out the followed methods, the footprints paleontological interpretation is then approached in detail and the results obtained are replaced in stratigraphy to deduce the fauna evolution during the Mesozoic. So, it appears that Ichnologic data, more varied and rich in the Triassic and Liassic than those relating to the bones, very rare for the considered periods, are very informative. The middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian), thus reveals Cotylosauria, Lepidosauria, Crurotarsi with Rauisuchia, Ornithosuchidae, Crocodylia and Dinosauromorpha more the "Prodinosauria": Dinosamiforme whose skeletons are known in Argentina but only in Ladinian. The rather fast domination of Dinosaurs during Norian is also as well shown. The almost exclusive presence of their footprints, up to fifty cm long, in the Lower Hettangian indicates their supremacy in the environments. Footprints characterise not very deep life places located between inter-supratidal limits and often out of water. Sedimentologic and Palaeontologic studies showed that they were great coastal spaces during Middle Triassic, flood-plain with sebkhas while Upper Triassic, and a large !!coastal marsh!! in Grands-Causses during Liassic in which, mainly, fine stromatolithic layers were deposited. During the same periad, bay beaches spread in Vendée. During the Middle Jurassic, they are also brackish to lacustrine environments and recifallagoons in- the Upper Jurassic. Numerous measurements of the footprints and trackways directions showed that the animaIs moved there in weil defined directions, for long periods. They seem due to the palaeotopography of the life environments relatively stable. Also, the discovery of vegetal radicular networks and small footprints far away from the continental borderlands has suggested that the animals continuously lived in these palaeoenvironnements, belonging to large ecosystems, where the sedimentation rate was weak. This explains that thebadies could not fossilize there but only their footprints through the cyanobacterian action in main cases. From the vertical distribution of different ichnospecies, defined with adapted statistical methods, explained in this work, a palichnostratigraphy was established for the Middle Triassic. Although the footprints are also abundant in Hettango-Sinemurian of "Grands-Causses" and the Vendée, it was not possible, up to now, to establish any zonation in this series; Probably because the palichnofauna is too little diversified there, currently reduced to a majority of Theropods II-IV tridactyl traces. Article infos Published in Vol. 35, Fasc. 1-4 (2007) |
|
|
|
Cryptomerix Schlosser, 1886, Tragulidé de l'oligocène d'Europe ; relations du genre et considérations sur l'origine des ruminants.Jean SudreKeywords: Archaic Ruminants; Paleobiogeography; Quercy Phosphorites; Systematics; TragulidsAbstract The genus Cryptomeryx SCHLOSSER, 1886, inusited during a long period, has been discovered in Lower and Middle Oligocene localities of the Quercy region (South-West France). This new material, as well as specimens from the old collections referred to Cryptomeryx, are described; their study, allows us precising the definition of the genus, and confirming its allocation to the Tragulidae family. The type species of the genus, Crypmmeryx gaudryi (= Lophiomeryx gaudryi FILHOL, 1877), occurs in several localities at the base of the Middle Oligocene (Itardies, La Plante 2, Roqueprune 2, Soulce, Herrlingen 1). The new species C. matsoui n. sp. has been defined in the older locality of Mas de Got (top of Lower Oligocene). It is possible that the species Pseudamphimeryx decedens STEHLIN, 1910 pertains to the same genus. Also to the Tragulids must be referred the monospecific genus Iberomeryx (I. parvus GABOUNIA, 1964) from Upper Oligocene of Benara (Georgie, URSS), with which Cryptomeryx is related. These genera are not direct ancestors of Miocene tragulids; their occurrence in the Western European Oligocene results from a first immigration wawe of the family. These Tragulids are one of the most archaic groups of Ruminants. They are probably derived from a primitive stock which had acquired in Asia the selenodont condition of the dentition. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 1 (1984) |
|
|
|
Les Amphibiens et les reptiles du Pliocène supérieur de Balaruc II (Herault, France)Salvador BailonKeywords: amphibians; Europe; France; Pliocene; ReptilesAbstract The late Pliocene site (MN 16) of Balaruc II (Hérault, France) has provided remains of the following amphibians and reptiles: Chelotriton pliocenicus nov. sp. and Triturus marmoratus (Salamandridae), cf. Rana (Ranidae), cf. Blanus (Amphisbaenidae), cf. Agama (Agamidae), Gekkonidae indet., Lacerta s.l. (Lacertidae), "Ophisaurus" sp. (Anguidae), Michauxophis occitanus (Aniliidae), Erycinae indet. (Boidae), Elaphe cf. E. longissima and Malpolon sp. (Colubridae), cf. Naja (Elapidae) and Vipera sp. (Viperidae). The salamandrid Chelotriton pliocenicus and the aniliid Michauxophis occitanus constitute, up to now, the only records of these groups in the European Pliocene. The fauna is indicative of a warm, dry Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|
|
Les crocodiliens paléogenes du Tilemsi (Mali): un aperçu systématiqueEric BuffetautKeywords: Crocodilians; Dyrosoridae; Eocene; Mali; PalaeoceneAbstract Abundant crocodilian fossil remains have been collected, mainly by R. Lavocat. from several levels of the Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Un gisement à mammifères dans la formation lacustre d'âge Miocène moyen du Collet Redon près de St-Cannat (Bouches-du-Rhone). Implications stratigaphiquesJean-Pierre Aguilar and G. ClauzonKeywords: France; Neogene; RodentiaAbstract The new fauna of Collet Redon (Bouches-du-Rhône, France) is dated by three rodents: Megacricetodon aff. bavaricus, Democricetodon affinis mutilus and Peridyromys cf. hamadryas. They correlate this locality with Oggenhof and Ohningen in Bavaria (Western Germany). As the radiometric age of Ohningen is estimated between 14 and 13 M.Y., these three localities are of Serravallian age. This datation brings a complete readjusment of the stratigraphy of the section of Collet Redon formerly described by Collot and Combaluzier. The marine deposits with underly the continental formation with the mammal fauna, are Burdigalian. The angular unconformity between the marine and the continental deposits gives evidence of an episode of emersion on the margin of a sedimentary basin, with deformation and erosion. Owing to the newly discovered fauna, this geodynamical event is clearly settled within the regional geographical and chronological context. Lacustrine and continental deposits of such an age were up to now unsuspected in this area. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 5 (1979) |
|
|
|
Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp, et les relations phylogénétiques entre les kiaeraspidiens (Osteostraci) du dévonien inférieur du Spitsberg.Philippe JanvierKeywords: Devonian; kiaeraspids; Osteostraci; SpitsbergenAbstract The anatomy of Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp., a primitive kiaeraspidian from the Lower Devonian of Spitsbergen, is described on the basis of spécimens studied by grinding sections or prepared with dilute formic acid. This study yielded some new anatomical details, including the presence of a canal prolonging posteromedially the canal alloted to the facial nerve by Stensiö. This posterior prolongation of the « facial canal ›› into the posterolateral part of the labyrinth cavity is consistent with the hypothesis put forward by Allis, Lindström, Jefferies and Whiting, that this canal housed the glossopharyngeus nerve. Furthermore, in N. glacialis, the foramen usually referred to as the foramen for the œsophagus opens posteriorly into a cavity in the postbranchial wall, referred to here as the intramural cavity, and which is interpreted as having housed the heart. Consequently, the œsophagus probably accompanied the dorsal aorta through the aortic canal. Finally, the foramen generally interpreted as having transmitted the ventral afferent arterial trunk is here considered as having housed the hepatic vein, which emptied into the venous sinus of the heart. The ventral afferent arterial trunk may thus have passed through the former «œsophageal ›› foramen. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 2-3 (1981) |
|
|

|
Morphotypes dentaires actuels et fossiles des chiroptères vespertilionines. 2ème partie: implications systématique et phylogéniques.Henri MenuKeywords: Chiroptera; PHYLOGENY; Systematics; VespertilionineAbstract The first part of this study was devoted to a descriptive analysis of teeth morphologies among the vespertilionine bats. This leads now to a tentative synthesis, providing views on the systematics of the group. The results could be seen according to three distinct but closely related purposes : 1 - the sorting of the genera contents in order to conform the genera units to homogeneous taxa that could represent natural issues of evolutionary lineages ; 2 - the investigation of relationships between extant genera in order to infer the possibilities of common origin ; 3 - according to the preceeding items and to the observed evolutionary trends, a tentative phylogeny, modest and cautious. The contents of many genera are sorted : Leuconoe is removed from subgeneric to generic position, whereas Myotis becomes a subgenus of it ; the myotodont species are cleared away from the Pipistrellus genus ; Glischropus and Scotozous are synonymized within Pipistrellus ; Hypsugo is raised to the generic level ; some species previously ranged within Pipistrellus will form provisionally a collective group, Attalepharca nov. ; the Eptesicus genus is broken up, the excluded species being grouped within Nycterikaupius gen. nov. ; the Nycticeini tribe is defined again after exclusion of Otonycteris , Scotoecus, Scotophilus , and addition of Hesperoptenus ; the species la io and Pipistrellus tasmaniensis are removed to Eptesicus (n.s.) and Pipistrellus dormeri to Scotoecus. Groupings of genera are stated according to the main evolutionary trends of I1/. The relevance of these is often warranted by close morphologic similarities of other teeth. This leads to a recognition of the major evolutionary radiations which occurred in the group. The filiations schematized at the end of the work show the dental relationships observed between the extant genera, and could represent a phylogenic framework. Two major facts are to be underlined : 1- the early divergence of leuconoids ; 2 - the successives crossings to myotodonty from the nyctaloid flow. Fossil data from the literature are punctually and tentatively incorporated within phylogenic sketches. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 3 (1987) |
|
|
|
The eosimiid and amphipithecid primates (Anthropoidea) from the Oligocene of the Bugti hills (Balochistan, Pakistan): new insight into early higher primate evolution in South Asia.Laurent MarivauxKeywords: Amphipithecidae; anthropoid phylogney; Bugti Hills; Early Oligocene; Eosimiidae; PakistanAbstract Eosimiid and amphipithecid primates document a long and significant history of primate evolution throughout the Eocene in Southeast Asia. Despite the absence of a comprehensive post-Eocene fossil record, it was generally hypothesized that both families left no descendant in Asia. Recently, two new small-bodied taxa, Bugtipithecus and Phileosimias, have been recovered in early Oligocene coastal deposits from the Bugti Hills (Balochistan, central Pakistan) and referred to the families Amphipithecidae and Eosimiidae, respectively, on the basis of dental fossil remains. In this paper, we provide more exhaustive description, comparison, and discussion of these taxa. As for tarsiid and sivaladapid primates, the persistence of eosimiids and amphipithecids into the Oligocene clearly demonstrates that low latitudes of South Asia provided a continuous access to tropical refugia during the climatic deterioration characterizing the late Eocene-early Oligocene interval, which was seemingly lethal for primate communities elsewhere across the Holarctic continents. As a contribution to the ongoing phylogenetic debates regarding the position of eosimiids and amphipithecids on the primate family tree, we have performed a cladistic analysis in a high-level primate systematic context in order to assess the position and the role of these new taxa in that phylogenetic issue. Our results support the view according to which eosimiids and amphipithecids (and by extension Phileosimias and Bugtipithecus, respectively) are stem anthropoids. These fossils from Pakistan document an unsuspected Oligocene phase of the evolutionary history of anthropoid primates in southern Asia, which clearly enhances the extent of the anthropoid radiation in this province during the Paleogene. Several phylogenetic and paleobiogeographic aspects are discussed, notably the intra- and inter-relationships between Paleogene Asian and Afro-Arabian anthropoids, and the resulting potential dispersal models between both land-masses during the Paleogene. Article infos Published in Vol. 34, Fasc. 1-2 (2006) |
|
|
|
New datation of the Tafna Basin (Algeria): A combination between biochronological and magnetostratigraphical dataSalamet Mahboubi, Mouloud Benammi and Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: correlations; Late Miocene; North Africa; Rodentiadoi: 10.18563/pv.39.1.e1 Abstract The Tafna Basin corresponds to the lowlands, which are located in front of Tessala and Traras ranges, below the Tlemcen mountains, Algeria. This basin displays a complete sedimentary cycle dominated by lagoonal-fluvial and marine deposits. The continental formations located at the base of these deposits are mainly composed of alternating sandstones and clays. An early late Miocene age has been previously attributed to them, based on direct correlations with marine deposits. Search for micromammal fossils led to the discovery of three different rodent species from a single level of the Djebel Guetaf section, located at the bottom of these deposits. The rodent assemblage indicates a late Miocene age. Combined magnetostratigraphical and biostratigraphical investigations were carried out to provide a more accurate age control of these continental deposits. Sixty-four oriented rock samples were collected for a magnetostratigraphic study along a 92 meters thick section including the fossiliferous layer. Rock magnetic investigations indicate the presence of both high and low coercivity minerals. Specimens subjected to progressive thermal demagnetization procedures show that the samples exhibit a high temperature magnetization component and display a normal polarity. Based on biostratigraphic constraints, the Guetaf section is correlated with Chron C4An, indicating an age ranging from Article infos Published in Vol.39-1 (2015) |
|
|
|
Premier signalement du Monachinae (Phocidae, Mammalia) dans le Sahélien (Miocène supérieur) d'Oran (Algérie)Christian de MuizonKeywords: Algeria; Late Miocene; PhocidaeAbstract Messiphoca mauretanica nov. gen., nov. sp. représente le premier Phocidae fossile recensé en Afrique du Nord. Provenant du gisement sahélien (Miocène supérieur) de Raz-el-Aïn (Algérie), il est connu par quelques os du membre antérieur (humérus, radius, ulna), quelques vertèbres dorsales et un crâne très fragmentaire. La description de cette forme nouvelle amène à considérer Messiphoca mauretanica comme un Monachinae archaïque proche de l'origine du groupe Pliophoca - Monachus. L'incidence de cette interprétation d'un Phocidae «pré-Messinien ›› sur la crise de salinité du Messinien est aussi envisagée. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 5 (1981) |
|
|

|
Rongeurs du Miocène supérieur de Chorora, Ethiopie: Murinae, Dendromurinae et conclusions.Denis GeraadsKeywords: Ethiopia; Late Miocene; Muridae; RodentiaAbstract The subfamilies Murinae and "Dendromurinae" both include 4 species at Chorora. Among the former, while Preacomys nov. gen. seems to be a forerunner of Acomys, the affinities of the remaining, poorly known taxa, are more difficult to evaluate. The bulk of the fauna, remarkably, consists of Dendromurines. Their similarities with those of Ngorora tends to pull the site back in time, but the large size and diversity of Murines fit better an age more recent than the very beginning of the Late Miocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|
|
The Quaternary avifauna of Crete, Greece.Peter D. WeesieKeywords: Avifauna; Crete; Quaternary; SystematicsAbstract Pleistocene bird fossils have been studied from nine localities on Crete. Part of this material was described earlier by the author (Weesie, 1982) and will not be treated here in extenso, the results will be incorporated. More than one third of the over 10,000 fossil bird bones available could be identified ; they were found to represent at least 65 bird species. The following species of the Pleistocene Cretan avifauna are new to the fauna of Crete : Branta ruficollis, Haliaeetus albicilla, Gyps melitensis, Aquila chrysaetos simurgh n. ssp., Ketupa zeylomensis, Aegolius funereus, Dendrocopos leucotos, Zoothera dauma, Turdus iliacus and Pyrrhula pyrrhula. The Pleistocene Cretan avifauna differs less from comparable mainland avifaunas than (fossil) avifaunas from oceanic islands do. Still, the Pleistocene Cretan avifauna has two qualities that are characteristic of island avifaunas : the almost complete absence of a group of birds (the Galliformes) and the presence of two endemic (sub)species : the giant eagle Aquila chrysaetos simurgh n. ssp. and the long-legged owl Athene cretensis (Weesie, 1982). The new subspecies is described in the present study. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 1 (1988) |
|
|

|
Préface au mémoire jubilaire en hommage à René LavocatJacques MichauxKeywords: EditorialAbstract Monsieur René Lavocat, Directeur du Laboratoire de Paléontologie des Vertébrés de la troisième section de l'Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes, quittait le service actif en l'année 1979. View editorial Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Terrestrial vertebrate paleocommunities from the Cerro del Pueblo Formation (Late Cretaceous; Late Campanian) at Las Aguilas, Coahuila, MexicoHéctor E. Rivera-Sylva, Eberhard Frey, Wolfgang . Stinnesbeck, Natalia Amezcua Torres and Diana Flores HuertaKeywords: Campanian; Coahuila; dinosaurs; Mexico.; Vertebratesdoi: 10.18563/pv.42.2.e1 Abstract The Las Águilas site near Porvenir de Jalpa, Coahuila, Mexico, is extremely rich in tetrapod remains comprising both bones and trackways of several dinosaur taxa of late Campanian age. Within a 50 m thick section we identified at least nine layers with dinosaur bone assemblages. In one of these the dinosaur bones are associated with remnants of eusuchian crocodilians, turtles, plesiosaurs, pterosaurs, tyrannosaurids, dromaeosaurids, parksosaurid, hadrosaurids, ceratopsids, and ankylosaurs. This layer is also rich in coprolites of turtles, crocodilians and likely theropods, thus providing evidence for the wealth of Late Cretaceous vertebrate life in the area. Article infos Published in Vol 42-2 (2019) |
|
|
|
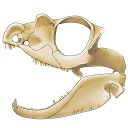
The skull of Tetraceratops insignis (Synapsida, Sphenacodontia)Frederik SpindlerKeywords: cranium; pelycosaur; Permian; therapsid originsdoi: 10.18563/pv.43.1.e1 Abstract Tetraceratops insignis is known from a single, crushed skull from the Lower Permian of Texas. Its unique proportions and osteological details gained central meaning in the question of the origins of Therapsida since this early synapsid has been determined as the oldest and less derived therapsid. Apart from Tetraceratops, the ‘mammal-like’ Therapsida and their sister, the pelycosaur-grade Sphenacodontidae, are separated by one of the longest ghost lineages in tetrapod fossil record. However, the minor, though well justified critique faced insistent publication regarding the therapsid hypothesis. A carefull re-evaluation of the holotypic skull reveals that therapsid traits cannot be supported, including a rejection of the formerly supposed adductor shelf in the temporal fenestra. Increased understanding of ‘pelycosaur’ character variation underlines a haptodontine-grade or, less likely, sphenacodontid position for Tetraceratops. Article infos Published in Vol 43-1 (2020) |
|
|
|
Les gangas (Aves, Columbiformes, Pteroclidae) du Paléocène et du Miocène inférieur de France.Cécile Mourer-ChauviréKeywords: Birds; evolution; Lower Miocene; New taxa; Oligocene; Paleoecology; Paulhiac; Quercy Phosphorites; Saint-Gérand-Ie-Puy; Sandgrouse; Upper EoceneAbstract The two species of Sandgrouse from Quercy, Pterocles validus MILNE-EDWARDS and P. larvatus MILNE-EDWARDS, are ascribed to the genus Archaeoganga MOURER-CI-IAUVIRÉ which includes a third, very large species, A. pinguis. The sandgrouse of Saint-Gérand-le-Puy, Pterocles sepultus MILNE-EDWARDS, is ascribed to a new genus, Lepzoganga. This form appears in the Upper Oligocene of Quercy, in Pech Desse and Pech du Fraysse localities, and is still present in the Lower Miocene of Saint-Gérand-le-Puy and Paulhiac. Recent sandgrouse live in semidesert or desert areas. The indications provided by mammal and bird faunas in the localities where sandgrouse were found, confirm that the paleoenvironment was open and arid. The morphological study of these fossils indicates that, in the Upper Eocene, the Pteroclidae were already completely individualized with respect to Charadriiformes. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|

|
Les sélaciens du Miocène de la région de MontpellierHenri CappettaKeywords: Ichtyofauna; Miocene; Montpellierdoi: 10.18563/pv.3.ext.1-139 Abstract The utilization of screen-washing and attack by dilute acetic acid has permitted the collecting, in the Miocene of the department of Hérault (France), of a very rich ichthyofauna. This fauna is presently comprised of about 60 studied species, of which 11 are new, and represents, in the present state of knowledge, the most varied Miocene selachian fauna described in the world. Article infos Published in Vol. 3, Ext (1970) |
|
|
|
Un crane de Chalicothere (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) du Miocène supérieur de Macédoine (Grèce) : remarque sur la phylogénie des ChalicotheiinaeLouis de Bonis, Geneviève Bouvrain, George D. Koufos and Pascal TassyKeywords: Chalicotheriidae; Cladistics; Greece; Miocene; Perissodactyla; PHYLOGENYAbstract The discovery in the Turolian (Late Miocene) of Dytiko 3 (Macedonia, Greece) of a complete skull with mandibles and cervical vertebrae, atlas and epistropheus, is a very important contribution to the knowledge of the subfarnily Chalicotheríinae. After the description, the comparison with other specimens of Miocene chalicotheres permits the revival of the generic name Macrotherium with a new species M. macedonicum. This genus is mainly characterized by a short snout and an inflated cerebral skull. It coexists during the Miocene with Chalicotherium. A cladistic analysis leads to conclusion that the species which has been described from the Early Middle Miocene of Rusinga must be identified as the type-species of a new genus: Butleria. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|

|
Equus caballus antunesi, nouvelle sous-espèce Quaternaire du PortugalJoao L. Cardoso and Véra EisenmannKeywords: Equidae; Equus caballus; new subspecies; Perissodactyla; Portugal; WürmAbstract Equus caballus antunesi, nova subspecies, was a hypsodont, slender, and rather small horse (around 141cm at the withers), with narrow hooves and protocones longer on P3/-P4/ than on M1/-M2/. It does not fit in any of the different "types" of Pleistocene caballine horses previously recognized but may be related to the horse from the Acheulean of Solana del Zamborino. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 2 (1989) |
|
|
|
On the genus Dikkomys (Geomyoidea, Mammalia)Morton Green and Philip R. BjorkKeywords: Dikkomys; Geomyoidae; North AmericaAbstract The geomyoid genus Dikkomys is well represented in a sample from the Black Bear Quarry Il local fauna of Early Hemingfordian age in Bennett County, South Dakota. Isolated unworn P/4's of Dikkomys matthewi WOOD have a prominent median cristid (sagicristid) with a connection to the metaconid and the hypolophid. With wear, P/4 does not become as molariform as P/4 because of this cristid. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|