Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
Critical comments on the genus Propachynolophus Lemoine, 1891 (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Equoidea)
|
|
S.I. Data |

|
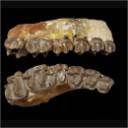
A new species of Propalaeotherium (Palaeotheriidae, Perissodactyla, Mammalia) from the Middle Eocene locality of Aumelas (Hérault, France).Jean-Albert Remy, Gabriel Krasovec and Bernard MarandatKeywords: Eocene; new species; Palaeotheriidae; Propalaeotheriumdoi: 10.18563/pv.40.2.e1 Abstract A new Propalaeotherium species, clearly distinct from the genus Eurohippus, is described. It is characterized by having a similar size as P. voigti from the German Geiseltal localities (MP 11 to MP 13 reference-level), but differs in several features suggesting a slighty more derived morphology. It presents indeed less brachyodont crowns with less prominent and less elevated cingula, slightly larger relative surface of premolars, and a more marked metaconid splitting on cheek teeth. This new species is unknown from other European localities except the nearby Saint-Martin de Londres locality which has been considered older than the MP 13 level. Article infos Published in Vol.40-2 (2016) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
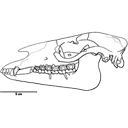
Les Périssodactyles (Mammalia) du gisement Bartonien supérieur de Robiac (Éocène moyen du Gard, Sud de la France)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Chasmotherium; new species; Palaeotheriidae; paleoenvironmentsdoi: 10.18563/pv.39.1.e3 Abstract We present here a new updated counting of the perissodactyls of Robiac, the type locality of the MP 16 level of the biochronological scale of paleogene mammals and that of the Robiacian stage of Eocene Land Mammals Ages in Western Europe. Article infos Published in Vol.39-1 (2015) |
|
|
|
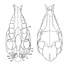
Révision systématique des Anchilophini (Palaeotheriidae, Perissodactyla, Mammalia).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Anchilophus; Eocene; new genus; new species; Palaeotheriidae; Paranchilophus; Perissodactyla; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.37.1-3.1-165 Abstract The knowledge of the Anchilophini has been lately renewed by the discovery of a rather large amount of new material still largely unpublished. This new material offers the opportunity of a systematic revision of this tribe gathering those of European Eocene Equoidea which bear no mesostyle on upper check teeth and display a heavy trend to the molarization of premolars. Article infos Published in Vol. 37, Fasc. 1-3 (2012) |
|
|

|
Le genre Plagiolophus (Palaeotheriidae, Perissodactyla, Mammalia): révision systématique, morphologie et histologie dentaires, anatomie crânienne, essai d'interprétation fonctionnelleJean-Albert RemyKeywords: New taxa; Paléogène; perissodactyls; skull anatomy; tooth histologyAbstract The genus Plagiolophus is documented, almost solely in Western Europe, from the middle Eocene up to the mid Oligocene (MP 12 to MP 25), i.e. more than for 15 MY. Seventeen species are now recorded whose two of them are new, P. ringeadei nov. sp. and P. mamertensis nov. sp. Some anatomical variations and the deflection of certain evolutionary trends justify the distinction of three subgenera, Paloplotherium, Fraasiolophus nov. and Plagiolophus s.s. The genus displays a wide range in size and weight (between 10 and 150 kg). The detailed description of the skull of several species is here given for the first time. Article infos Published in Vol. 33, Fasc. 1-4 (2004) |
|
|

|
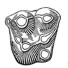
Un nouveau genre de ?Palaeotheriidae (Perissodactyla, Mammalia) décelé dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Eocène supérieur ou Oligocène) d'après un arrière crâne sans dents.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: endocranial cast; Epitympanic sinus; Palaeotheriidae; Paléogène; Quercy Phosphorites; skull anatomyAbstract A rear skull from the Quercy Phosphorites is described. It documents a new perissodactyl genus, likely assignable to the family Palaeotheriidae and probably paleogene of age. Owing to the lack of any tooth, this family assignment remains however somewhat hypothetical. The specimen is firstly characterised by the presence of a wide epitympanic sinus swelling and hollowing the squamosal shell and the post-glenoid process. This cavity might make up a peculiar pattern of improvement for the hearing apparatus by carrying out a kind of drum near the middle ear, whereas the bony tympanic remains barely bulged and forms but a few developed auditory bulla. This pattern appears an outcome of a trend observed with many palaeotheriids, such as Plagiolophus. Furthermore, the endocranial cast shows a rather high degree of gyrencephaly for a paleogene mammal. The prominent lambdoidal crest points out a powerful nape musculature and a lowered head bearing. Consequently, it is assumed that such an animal was probably living in somewhat open places, at the expense of rather tough vegetables. It might have been accordingly provided with a semi-hypsodont, cement covered, "plagiolophoid" dentition. Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|
|
Le genre Leptolophus (Perissodactyla, Mammalia): morphologie et histologie dentaires, anatomie cranienne, implications fonctionnelles.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: dental histology; Eocene; functional anatomy; Palaeotheriidae; skull anatomy; Southern France; SystematicsAbstract A strong lophodonty, an extreme heterodonty, some hypsodonty and regular overlayings of coronal cement are prominent features of the genus Leptolophus (Palaeotheriinae = Palaeotheriidae s.s.). The histological pattern of the teeth unusually joins type II enamel prisms, characteristic of advanced ungulates, together with archaic features, such as an almost complete lack of Hunter-Schreger zonation and a weak expanse of peritubular dentine. The skull is narrow and slender, with an elongated ante-orbital facial region, a moderately notched nasal aperture, a rather elongated post-canine diastem, parallel zygornatic arches and a fairly dorsally located squamoso-mandibular joint.The functional analysis brings to light "ectolophodont" masticatory cycles with two phases, in which maximum power was applied, contrary to equíds, on hindmost teeth; likewise, skull accomodations to increasing height of the teeth are quite different. This study leads to the assumption that Leptolophus may have been light mammals, living in rather open surroundings, browsing on herbaceous plants or leaves cropped close to the ground. Moreover, it appears that it could have been some inadequacy of dental structures to the dietary, which leaded to quick wear of the teeth and to many enamel notches, but had been somewhat balanced by the early increase of hypsodonty, not induced in such a case by a biotop deterioration (as it will happen at the end of the Eocene). This ínadaptation might account for the short duration of the genus Leptolophus, whose the 3 species, L. stehlini, L. nouletí and L. magnus n. sp. are indeed confined in the level MP 16. Its geographical spreading (as far as known, South of western Europe) and the morphological pattern of its dentition suggest that this genus would have been related to early upper Eocene endemic spanish forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 1-2 (1998) |
|
|

|
Une faunule de vertébrés sous la base de grès de Celas (Eocène supérieur) à ST Dresery (Gard)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Artiodactyla; Biostratigraphy; Eocene; MammalsAbstract The St-Dézéry local fauna (3 reptile-, 4 mammal species) is approximately of the same age as the La Débruge or the Ste-Néboule faunas. It conduces to a better dating of the limestones underlying the Célas sandstones. A large part of a mandible of Amphimeryx was found there, which documents the record of this family of small artiodactyls Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
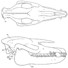
Observations sur l'anatomie crânienne du genre Palaeotherium (Perissodactyla, Mammalia): mise en évidence d'un nouveau sous-genre, FranzenitheriumJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Palaeotherium; Paléogène; Perissodactyla; skull anatomy; SystematicsAbstract The skull remains referred to the genus Palaeotherium are recorded and described. Biometrical tests are made to elucidate intrageneric allometric relationships and to allow comparisons with various other perissodactyls. Apart from the well known shortness of post canine diastems and deepness of the narial opening, the genus is characterized by a great lengthening of the splanchnocranium, owing to a spreading of the post-orbital facial region, by a reduced area of the eye-socket and by the prevalence of the temporal muscle with regard to the masseter; this original shape of the masticatory apparatus needs to be related to the morphology of the jugal teeth and particularly to their asymmetrical semi-hypsodonty. Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Fasc. 3-4 (1992) |
|
|
|
Une faune du niveau d'Egerkinger (MP 14; Bartonien inférieur) dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Sud de la France)Jean Sudre, Bernard Sigé, Jean-Albert Remy, Bernard Marandat, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Marc Godinot and Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Biochronology; Early Bartonian; Eocene; evolution; Mammals; New taxa; QuercyAbstract The Laprade fauna is chronologically situated between those from Egerkingen and Lissieu and consequently, is close to the MP 14 reference-level of the European mammalian biochronological scale (Symposium of Mainz, 1987). Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 1 (1990) |
|
|

|
Saturnin Garimond (1914-1987)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: biographyAbstract Biographie et liste des publications de S. Garimond. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 3 (1987) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 10 - Paléothérides (Perissodactyles).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract La poche à phosphorite de Sainte-Néboule (Lot) a livré au cours des récentes campagnes de fouilles effectuées dans le cadre de la Rep 311 une douzaine de dents ou fragments de dents de paléothéridés à rapporter à 3 taxons. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. IntroductionBernard Gèze, Jean-Claude Rage, Colette Vergnaud-Grazzini, France de Broin, Eric Buffetaut, Cécile Mourer-Chauviré, Jean-Yves Crochet, Bernard Sigé, Jean Sudre, Jean-Albert Remy, Brigitte Lange-Badré, Louis de Bonis, Jean-Louis Hartenberger and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Le Quercy est aujourd 'hui un vaste plateau calcaire, parcouru par un réseau karstique actif, profondément View editorial Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Observations sur des remaniements structuraux post-mortem dans des dents de mammifères fossiles provenant des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Quercy Phosphorites; rearrangements; TeethAbstract Deux types de remaniements post mortem me paraissent caractéristiques de l'état de conservation des dents de mammifères fossiles dans les Phosphorites du Quercy : Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
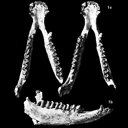
Etude du crâne de Pachynolophus lavocati n. sp. (Perissodactyla, Palaeotheriidae) des Phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Perissodactyla; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.5.2.45-78 Abstract The genus Pachynolophus, one of the poorest known of the Palaeotheriidae, includes the brachyodont forms with reduced and non-molariform premolars and with upper molars lacking a mesostyle. Quantitative characters (divers surface indications and elongation of the teeth), while demonstrating a close relationship to Hyracotherium, permit a better differentiation of the genus, confirm its specific splitting, and permit the distinction of three lineages. The skull from Memerlein is taken as the type of a new species, P. Iavocati, of which the dentition is extremely characterized by its lophiodonty, the strong reduction of the premolars and the reduction of the cingula. This characterization testifies to a late age which extends the existence of the genus quite near to the Eocene-Oligocene limit. Compared with the only two skulls known of related species (Hyracotheríum vulpiceps and Pachynolophus Iivinierensis), that from Memerlein is distinguished by progressive characters affecting diferent regions but most particularly the braincase; it is not possible, however, to isolate within this evolution the part which leads to a systematic differentiation. Modernization is translated by a considerable increase in size of the braincase, principally in the frontal region, a development of the facial region with anterior displacement of the dental series and a greater specialization of the masticatory apparatus. This evolution parallels the history of the Equidae of the North American early Tertiary, but certain particularities, the form of the alisphenoid, the presence of an anterior frontal foramen, and the structure of the paroccipital apophysis, testifies to the independance of the European forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 2 (1972) |
|
|
|
Les Palaeotheridae (Perissodactyla) de la faune de Mammifères de Fons 1 (Eocène supérieur).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Anchilophus; Eocene; Pachynolophus; Palaeotheriidae; Perissodactyladoi: 10.18563/pv.1.1.1-46 Abstract The locality of Fons 1, one of the fossiliferous outcrops in the late Eocene limestones of Fons-outre-Gardon (Gard), has yielded varied remains of mammals. The specimens were prepared by dilute acetic acid attack on the rock and by impregnation with an acrylic resin. Article infos Published in Vol. 01, Fasc. 1 (1967) |
|