Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
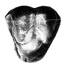
Neolicaphrium recens Frenguelli,1921,the only surviving proterotheriidae (Litopterna, Mammalia) into the south american Pleistocene.Mariano Bond, Daniel Perea, Martin Ubilla and Adan TauberKeywords: Litopterna; Neolicaphrium recens; Pleistocene; Proterotheriidae; South AmericaAbstract The litoptem Proterotheriidae are extinct endemic South American ungulates frequently used as an example of evolutionary convergence with the horses. They were considered to be exclusively Tertiary representatives with the youngest record being in the late Pliocene, before the appearence of the equids and cervids during the Great American Interchange. Two undoubted Pleistocene records in Argentina and the specimen here described from Uruguay, confirm the persistence of the proterotherids into that period. In the Quaternary, these ungulates are found outside the typical pampean region and probably were confined to a few northern and warmer more forested relictual microhabitats. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|
|
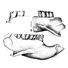
Carolocoutoia ferigoloi nov. and sp. (Protodidelphidae), a new Paleocene "opossum-like" marsupial from Brazil.Francisco J. Goin, Edison V. Oliveira and Adriana M. CandelaKeywords: Brazil; Didelphimorphia; Itaborai; Marsupialia; New taxa; Paleocene; Protodidelphidae; South AmericaAbstract Carolocoutoia ferigoloi gen. et sp. nov. is the largest of protodidelphid marsupials, known from Middle Paleocene levels at Itaboraí Formation, southeastern Brazil. It differs from other members of this family in having molars with low cusps which are basally inflated, rounded crests without cutting edges, and a thick enamel layer which is wrinkled, specially at the labial half. A comparative analysis among representatives of this family led us to recognize only three genera undoubtely assignable to it: Protodidelphis PAULA COUTO, 1952, Robertbutleria MARSHALL, 1987, and Carolocoutoia gen. nov. Protodidelphids lack the basic derived features diagnostic of Polydolopimorphian marsupials, while most of its derived features agree with its belonging to the Didelphimorphia. Protodidelphids comprise a specialized clade of opossum-like marsupials adapted to frugivorous or frugivore-omnivorous feeding habits. They differ from other didelphimorphians in having very large, spire-like entoconids, reduced and antero-posteriorly compressed paraconids, absence of stylar cusp C and of para- and metaconules, large stylar cusps B and D which are proximate to each other, short postmetacristae, eccentric protocones, and molars that increase rapidly in size from M/ml to M/m3. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 3-4 (1998) |
|
|
|
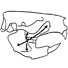
Octodontid-like Echimyidae (Rodentia) : an upper Miocene episode in the radiation of the familyDiego H. Verzi, Maria G. Vucetich and Claudia I. MontalvoKeywords: Argentina; Echimyidae; Miocene; New taxa; Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract Reigechimys octodontiformis gen. et sp. novo and R. plesiodon sp. novo are described. They represent the frrst record of the family Echimyidae for the Cerro Azul Formation (Huayquerian Age, Late Upper Miocene) at La Pampa Province, central Argentina. Both species have hypsodont cheek teeth with an eight-shaped occlusal design. This dental morphology represents a noticeable case of convergence to octodontids and indicates that these echimyids inhabited open environments. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Schmelzmikrostruktur in den inzisiven alt-und neuweltlicher histricognather nagetiereThomas MartinKeywords: Africa; Caviomorpha; Ctenodactyloidea; Deseadan; Enamel microstructure; Hunter-Schreger bands; Hystricognathi; Incisors; Ischyromyoidea; multiserial; Paleobiogeography; pauciserial; Phiomorpha; Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract Enamel microstructure in the incisors of Old- and New World hystricognath rodents: Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Ext (1992) |
|
|

|
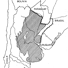
Analysis of changing diversity patterns in Cenozoic land mammal age faunas, South AmericaLarry G. Marshall and Richard L. CifelliKeywords: Cenozoic; Chronofaunas; diversity; Equilibrium theory; Extinction; Land mammal faunas; Origination; South AmericaAbstract Comparison of various measurements of taxonomic evolution using stratigraphic range data for orders, families and genera of land mammals indicates several means by which deficiencies of the South American fossil record (e.g., presence of hiatuses, unequal temporal and geographic representation of ages, unequal systematic treatment) may be normalized, thus permitting a less distorted appreciation of diversity pattern and trend. Initial radiation of native taxa resulted in a relative equilibrium by early Eocene time. Subsequent increases in absolute diversity were apparently induced by immigration at the family level and by environmental factors at the generic level. Miocene through Pleistocene phases of faunal stability, herein characterized as chronofaunas, are punctuated by rapid turnover events resulting from a complex of factors, including adaptive radiation of immigrant taxa into unoccupied eco-space; environmental and concomitant habitat change induced by orogenic events of the Andes; and biotic interactions between native and immigrant taxa, including competition and prey naivete. The first two factors account for major faunal transitions in the South American middle and late Tertiary; immigration-induced turnover may have been of greater importance in shaping the character of the fauna upon the Great American Interchange and the arrival of man in the Neotropics Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 4 (1990) |
|
|
|
Mammals and stratigraphy of the continental mammal-bearing Quarternary of South AmericaLarry G. Marshall, Annalisa Berta, Robert Hoffstetter, Rosendo Pascual, Osvaldo A. Reig, Miguel Bombin and Alvaro MonesKeywords: Geochronology; Mammalia; Quaternary; South America; StratigraphyAbstract Previous chronological arrangements of South American Quaternary land mammal faunas are appraised on the basis of current geological and paleontological data. Three South American late Pliocene-Pleistocene land mammal ages are conventionally recognized, from oldest to youngest, the Uquian, Ensenadan, and Lujanian ; all are defined on Argentine faunas. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Ext (1984) |
|
|
|
Mammals and stratigraphy : Geochronology of the continental mammal-bearing Tertiary of south America.Larry G. Marshall, Robert Hoffstetter and Rosendo PascualKeywords: Cenozoic; Geochronology; Mammalia; South America; Stratigraphy; TertiaryAbstract The principles and practices employed in establishment and recognition of South American land mammal ages are reviewed along with previous and present concepts of distinguishing time, rock, and faunal units. Previous chronological arrangements of South American Tertiary land mammal faunas are appraised on the basis of recent geological and paleontological data. Twelve South American Tertiary land mammal ages are here recognized [from oldest to youngest, Riochican (middle to late Paleocene); Casamayoran (early Eocene); Mustersan (middle Eocene); Divisaderan (late Eocene); Deseadan (early [to middle?] Oligocene); Colhuehuapian (late Oligocene); Santacrucian (early Miocene); Friasan (middle Miocene); Chasicoan (late Miocene); Huayquerian (latest Miocene); Montehermosan (early to middle Pliocene); and Chapadmalalan (late Pliocene)]. As all except the Friasian were originally defined on the basis of Argentine faunas, these are discussed first and at length, and each is reviewed with discussion of type locality, stratigraphy, type fauna, and faunal correlations. Non-Argentine faunas are then discussed country by country in alphabetical order. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Ext (1983) |
|
|
|
Description des restes d'Elasmobranches (Pisces) du Dévonien moyen de BoliviePhilippe JanvierKeywords: South AmericaAbstract Some fragmentary remains of spines and endoskeletal elements, referred here to as ctenacanthid like elasmobranchs, are recorded in the Middle Devonian of Bolivia. These specimens, and some others from the Eodevonian of Brasil represent the only Devonian fish remains hitherto known from South America and indicate that further discoveries may be made in their original localities respectively. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 4 (1977) |
|
|

|
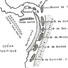
Rongeurs caviomorphes de l'Oligocène de Bolivie. 1 Introduction au deseadien de BolivieRobert HoffstetterKeywords: Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract The Tertiary of the Salla-Luribay basin consists of red beds affected by the second period of the andine compression, of Miocene ending age. The Tertiary layers are exposed at an approximate elevation of 3.500 to 4.000 meters. Two stratigraphic units can be distinguished in them: the Luribay conglomerates, in which vertical clifts result from erosion, and the Salla layers consisting mostly of consolidated clays. These clays are very fossiliferous and have furnished a rich vertebrate fauna which gave to R. Hoffstetter the possibility to establish the Oligocene age of these beds. Sediments of same age has been reported to be present in several other places of Bolivia, particularly near Lacayani, where have been collected highly hypsodont Rodents, different from those found in Salla-Luribay basin. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 3 (1976) |
|
|
|
Les vertébrés fossiles de Colombie et les problèmes posés par l'isolement du Continent sud-Américain.Jaime de PortaKeywords: Columbia; Cretaceous; Fauna; Quaternary; South Americadoi: 10.18563/pv.2.2.77-94 Abstract A general view is given of the vertebrate faunas, Cretaceous to Quaternary of age, found in Columbia and of their principal characteristics. This view leads to the discussion of the isolation of the South American continent and of the role played by the Bolivar syncline with respect to North American immigrants during the Oligocene. The absence of marine deposits of Oligocene age in the north and northwest of Columbia suggests the possibility of a communication with Central America. This communication would have permitted the passage of hystricomorph rodents, of platyrrhine monkeys, and of colubrids. The non-occupation, until then, of the ecologie niches of these groups would have favored their installation beside the indigenous fauna. In this hypothesis it would no longer be necessary to admit that these vertebrates arrived as «island hoppers ››. The eco-biologic conditions would explain the absence of large-sized forms of North American origin. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 2 (1969) |
|