Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Eocene otoliths (Clinchfield Formation), Georgia
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
Welcome
Since 1967, Palaeovertebrata has published original research on all aspects of vertebrate paleontology, including taxonomy, phylogeny, paleobiogeography, functional anatomy, biostratigraphy, paleoecology, and taphonomy. |
Submit an article |

|
Pterosaurs (Pterosauria) from the Cerro del Pueblo Formation (Late Campanian) of Coahuila, MexicoHector Rivera-Sylva, David Hone, Martha Aguillón-Martínez, Rubén Guzmán-Gutiérrez, David Morales-Flores, Iván Sánchez-Uribe, José Flores-Ventura and Rafael Vivas-GonzálezKeywords: Azhdarchoidea; Coahuila; Mexico; Pterodactyloidea; Pterosauriadoi: 10.18563/pv.48.2.e1 Abstract The Late Campanian Cerro del Pueblo Formation, located in southeastern Coahuila, Mexico, has produced a diverse array of vertebrate fossils. However, pterosaur remains from this unit are notably scarce. In this study, we describe new pterosaur material from the formation. The specimens include a fragmentary vertebra identified as belonging to an indeterminate, but derived pterodactyloid, along with the distal condyle of a left metacarpal, referable to an azhdarchoid pterosaur, and a left manus print. While these specimens provide additional evidence of pterosaur presence in the region during the Late Cretaceous, their fragmentary nature limits precise taxonomic and ichnotaxonomic identification. Nevertheless, they highlight the potential for future discoveries that could refine our understanding of the diversity and distribution of pterosaurs in Mexico. Article infos |
|
|

|
Lissamphibians from Dams (Quercy, SW France): Taxonomic identification and evolution across the Eocene-Oligocene transitionAlfred Lemierre and Maeva J. OrliacKeywords: Eocene-Oligocene; Grande Coupure; Lissamphibia; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.48.1.e3 Abstract The locality of Dams (Quercy, southwestern France) has yielded two fossil assemblages, one from the late Eocene and another from the early Oligocene, making it one of the few localities with infillings across the Eocene-Oligocene transition. At least 24 taxa (13 mammals, 11 snakes) have been identified in this locality. Study of the lissamphibian remains from Dams yields an Eocene and an Oligocene assemblage, with a total of eight taxa. The Eocene assemblage includes two unnamed salamandrine species, one unnamed pelobatid species and one pyxicephalid species (Thaumastosaurus). The Oligocene assemblage includes two unnamed pleurodeline species, one salamandrine species (Salamandra sansaniensis) and an unnamed pelobatid species. Among the eight taxa from Dams, one Eocene salamandrine and one Oligocene pleurodeline are identified for the first time in the Quercy. A review of the lissamphibians from the Quercy area identifies eleven taxa for the Late Eocene (MP19) and eight taxa for Early Oligocene (MP22), with a major turnover at the Eocene-Oligocene transition. This turnover occurs in a time of major climatic changes, with a significant decrease in temperature and precipitation and concurrent increase in seasonality in Europe, likely affecting specialized taxa. Article infos |
|
|

|
Revision of the historical collections of Pliocene-Pleistocene large mammals from Le Riège and Saint-Palais localities, near Pézenas (Southern France)Federica Mulè, Luca Pandolfi, Anne-Lise Charruault, Jean-Yves Crochet, Jérôme Ivorra, Fabrice Lihoreau, Laurent Marivaux, Mehdi Mouana, Félix Nesme, Céline Robinet, Philippe Münch and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: Hérault; Mammalia; Montpellier; Neogene; Quaternarydoi: 10.18563/pv.48.1.e2 Abstract Numerous “Quaternary” large-mammal fossils have been collected since the 1830s along the Le Riège stream, near Pézenas (Southern France). More than 120 specimens are stored in the collections of the Université de Montpellier (UM) under the name “Le Riège”. A major operation aiming at relocating the palaeontological collections of the University has made it possible to group together all the specimens of interest and launch their systematic revision for the first time. The fossils belong to the Reboul (1839; 51 samples) and de Christol (1865; 18 samples) Collections and 17 samples compose the Crochet & Ivorra Collection (1998). The remaining 38 samples have no mention about the exact time and location of their finding. We provide a critical inventory with literal transcription of inscriptions on specimens and historical labels. This revision confirms the presence of two distinct faunal assemblages under the name of “Le Riège”: Saint-Palais (Early Pliocene, MN14–15) and Le Riège sensu stricto (late Early Pleistocene, most likely MNQ19). The former assemblage, with coastal affinities, is composed of the ruminants Alephis sp. and Procapreolus cf. pyrenaicus, the rhinocerotid Pliorhinus megarhinus, the gomphotheriid Anancus arvernensis and marine mammals, all emblematic taxa for the Early Pliocene of Montpellier and Perpignan. The latter assemblage documents a late Early Pleistocene fluvio-volcanic sequence, yielding the bovid Bison (Eobison) spp., the cervid Eucladoceros cf. giulii, the hippopotamid Hippopotamus antiquus, the rhinocerotid Stephanorhinus etruscus, the equid Equus cf. altidens, and the elephantid Mammuthus cf. meridionalis, plus a few specimens of uncertain taxonomic affinities. This revision underscores the interest of revisiting historical collections and further provides a starting point for future research. Article infos |
|
S.I. Data |

|
Book of Abstracts of the XXII Annual Meeting of the European Association of Vertebrate Palaeontologists, 30 June–5 July 2025, Kraków, PolandGeorgios L. Georgalis, Tomasz Sulej, Matteo Belvedere and Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra (Eds.)Keywords:doi: 10.18563/pv.eavp2025 Abstract xx Article infos |
|
|

|
A partial skeleton of Metaxytherium medium from the middle Miocene of La Morfassière quarry (Indre-et-Loire, France)
|
|
|

|
Preliminary report on the fishes (Chondrichthyes & Teleostei) from the lower Oligocene (Rupelian) Red Bluff Clay at site AMo-9, Monroe County, Alabama, USAJun A. Ebersole, David J. Cicimurri, Lindsey M. Stallworth and Andrew D. GentryKeywords: Batomorphii; Elasmobranchii; Galeomorphi; Gulf Coastal Plain; Vicksburg Groupdoi: 10.18563/pv.47.2.e2 Abstract Herein we describe a small but relatively diverse assemblage of fossil fishes derived from the lower Oligocene (Rupelian) Red Bluff Clay at site AMo-9 in Monroe County, Alabama, USA. Identified amongst the remains are 15 unequivocal taxa representing 11 families within five orders, and one additional taxon represents an unknown order and family. Taxa identified include Eostegostoma sp., Otodus (Carcharocles) sp., Mitsukurinidae/Carchariidae indet., Macrorhizodus praecursor, Galeorhinus sp., Negaprion gilmorei, Physogaleus sp., “Sphyrna” sp., Galeocerdo sp., cf. “Aetobatus” sp., Sphyraena sp., Xiphiorhynchus kimblalocki, Xiphiorhynchus sp., Cylindracanthus ornatus, and C. rectus. Several additional fossils could not be identified beyond Lamniformes, Carcharhiniformes, and Teleostei, but they likely belong to one of the identified taxa within this paleofauna. All of the fishes previously reported from the Red Bluff Clay within the entirety of the Gulf Coastal Plain of the USA are otolith-based, and each of the 15 unequivocal taxa reported herein are important new records for this lithostratigraphic unit. In particular, the Eostegostoma sp. and Xiphiorhynchus spp. specimens represent the first occurrences of these taxa in Alabama. The specimens of C. ornatus, Eostegostoma sp., and X. kimblalocki are stratigraphic and temporal range extensions from the middle and late Eocene into the Rupelian Stage of the Oligocene. Other described taxa may represent transitional forms between those described from the late Eocene and late Oligocene within the region. This study provides a tantalizing preliminary view into faunal transitions that occurred amongst marine fishes across the Eocene/Oligocene boundary within the Gulf Coastal Plain of the USA. Article infos |
|
|
|
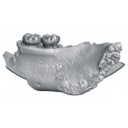
Enigmatic rodents from Lavergne, a late middle Eocene (MP 16) fissure-filling of the Quercy Phosphorites (Southwest France)
|
|
|
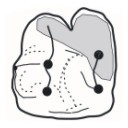
A late Eocene palaeoamasiine embrithopod (Mammalia, Afrotheria) from the Adriatic realm (Island of Rab, Croatia)Fabrice Lihoreau, Ljerka Marjanac, Tihomir Marjanac, Ozan Erdal and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: Balkanatolia; Grande Coupure; Great Adria; Paleobiogeography; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.47.1.e1 Abstract A cheek tooth recently unearthed in the Lopar Sandstone unit, of late Eocene age, in the northern part of Rab Island, Croatia, is one of the very few Eocene mammalian remains found in the Adriatic area. Thorough comparison of this tooth with those of Old-World Palaeogene mammalian orders suggests that it is a M3 belonging to an embrithopod afrothere. The specimen is referred to as Palaeoamasia sp. This genus was formerly known only in Eocene deposits of Anatolia but with close relatives in Romania among Palaeoamasiinae. The geographical distribution of this subfamily perfectly matches the recently-named Balkanatolian landmass, which experienced in-situ evolution of endemic mammals prior to the Grande Coupure event that occurred around the Eocene–Oligocene transition. This last event is characterised by massive Asian immigration in Western Europe and the supposed extinction of many endemic Central and Western European mammals, including Palaeoamasiinae. Article infos |
|
|
|
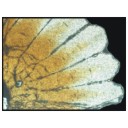
First report of Cylindracanthus (Osteichthyes) from the Eocene of IndiaPankal Kumar, Rajeev Patnaik, Deepak Choudhary, Rohit Kumar and Wasim Abass WazirKeywords: Cylindracanthus; Eocene; histology; rostrum; Umarsar mine.doi: 10.18563/pv.47.1.e2 Abstract Fossils of the endangered sturgeons and peddlefishes are widely distributed. We here report for the first time the presence of one of the extinct osteichthyes genus Cylindracanthus (Liedy 1856a) from the Early Eocene lignite-bearing successions of the Kutch Basin, India. The present well preserved rostrum is characterised by numerous wedge-shaped components encircling the central canal that runs along its length, paired at the base and each wedge contributing to the formation of a ridge. The rostrum lacks teeth. The present find extends the palaeobiogeographical distribution of Cylindracanthus considerably and supports its Eocene age as dental remnants preserved in Cylindracanthus sp. shows a decrease in remanent dentition and tooth bases from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. Cylindracanthus is an useful palaeoenvironmental indicator as it has been found associated typically with deposits of nearshore marine environments. Article infos |
|