Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Rodent paleocommunities from Ulantatal
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp, et les relations phylogénétiques entre les kiaeraspidiens (Osteostraci) du dévonien inférieur du Spitsberg.Philippe JanvierKeywords: Devonian; kiaeraspids; Osteostraci; SpitsbergenAbstract The anatomy of Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp., a primitive kiaeraspidian from the Lower Devonian of Spitsbergen, is described on the basis of spécimens studied by grinding sections or prepared with dilute formic acid. This study yielded some new anatomical details, including the presence of a canal prolonging posteromedially the canal alloted to the facial nerve by Stensiö. This posterior prolongation of the « facial canal ›› into the posterolateral part of the labyrinth cavity is consistent with the hypothesis put forward by Allis, Lindström, Jefferies and Whiting, that this canal housed the glossopharyngeus nerve. Furthermore, in N. glacialis, the foramen usually referred to as the foramen for the œsophagus opens posteriorly into a cavity in the postbranchial wall, referred to here as the intramural cavity, and which is interpreted as having housed the heart. Consequently, the œsophagus probably accompanied the dorsal aorta through the aortic canal. Finally, the foramen generally interpreted as having transmitted the ventral afferent arterial trunk is here considered as having housed the hepatic vein, which emptied into the venous sinus of the heart. The ventral afferent arterial trunk may thus have passed through the former «œsophageal ›› foramen. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 2-3 (1981) |
|
|
|
Les pantolestidés (Mammalia, Pantolesta) de l'Eocène inférieur de Prémontré (Aisne, France).Richard SmithKeywords: France; Mammals; Pantolestids; YpresianAbstract Study of pantolestid mammals from the late Ypresian locality of Prémontré (reference level MP 10) allows the recognition of three genera: Palaeosinopa. Pantolestes and Premontrelestes n. gen. Pantolestes, up to now only recorded from North America, is represented by P. sabatieri n. sp. Premontrelestes n. gen., represented by the type species P. duchaussoisi n. sp., is compared with Pantolestes and Buxolestes. The latter, known from middle Eocene sites in Europe, has not been recognized at Prémontré. Two other taxa, the first of which is close to Pantolestes and the second of Premontrelestes n. gen. are left in open nomenclature. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|
|
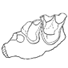
Un crane de Chalicothere (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) du Miocène supérieur de Macédoine (Grèce) : remarque sur la phylogénie des ChalicotheiinaeLouis de Bonis, Geneviève Bouvrain, George D. Koufos and Pascal TassyKeywords: Chalicotheriidae; Cladistics; Greece; Miocene; Perissodactyla; PHYLOGENYAbstract The discovery in the Turolian (Late Miocene) of Dytiko 3 (Macedonia, Greece) of a complete skull with mandibles and cervical vertebrae, atlas and epistropheus, is a very important contribution to the knowledge of the subfarnily Chalicotheríinae. After the description, the comparison with other specimens of Miocene chalicotheres permits the revival of the generic name Macrotherium with a new species M. macedonicum. This genus is mainly characterized by a short snout and an inflated cerebral skull. It coexists during the Miocene with Chalicotherium. A cladistic analysis leads to conclusion that the species which has been described from the Early Middle Miocene of Rusinga must be identified as the type-species of a new genus: Butleria. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
Mammifères de l'Ilerdien Moyen (Eocène inférieur) des Corbières et du Minervois (Bas-Languedoc, France). Systématique, Biostratigraphie, Corrélations.Bernard MarandatKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Corbières; correlations; Early Eocene; Ilerdian; Mammalia; Minervois; Paleobiogeography; Southern FranceAbstract Mammal-bearing localities have been discovered in the marine and lacustrine series of the middle Ilerdian (Lowermost Eocene) from Southem France (Minervois and Corbières). In the localities of Fordones, Monze, Fournès, and La Gasque, thirty mammal species have been identified. Among others, they include ischyromyid rodents (Microparamys and Pseudoparamys), paromomyid and adapid primates (Arcius and Donrussellia), new insectivores, condylarths, and a dyspternine pantolestid. These faunas provide new informations on the early Eocene Mesogean faunas of Rians and Palette. The assemblages of primates and rodents from Fordones support good correlations with Palette which was recently placed near the standard-level of Dormaal (MP 7). In fact, Palette and Fordones could be even older than Dormaal. Consequently, there seems to be a relatively important temporal gap between the late Paleocene of Cernay and the Sparnacian of Dormaal. This gap could be partly filled with the Mesogean faunas of Palette, Fordones, and Silveirinha. On the basis of these new mammal faunas the marine middle Ilerdian is proved to be older than the Cuisian stage of the Paris Basin. With regards to the position of the Fordones fauna at the top of the NP 10 calcareous nannoplankton biozone, the westem European paleomammalogists Paleocene/Eocene boundary could be situated between the NP 9 and NP 10 biozones. Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 2-3 (1991) |
|
|

|
Un gisement à mammifères dans la formation lacustre d'âge Miocène moyen du Collet Redon près de St-Cannat (Bouches-du-Rhone). Implications stratigaphiquesJean-Pierre Aguilar and G. ClauzonKeywords: France; Neogene; RodentiaAbstract The new fauna of Collet Redon (Bouches-du-Rhône, France) is dated by three rodents: Megacricetodon aff. bavaricus, Democricetodon affinis mutilus and Peridyromys cf. hamadryas. They correlate this locality with Oggenhof and Ohningen in Bavaria (Western Germany). As the radiometric age of Ohningen is estimated between 14 and 13 M.Y., these three localities are of Serravallian age. This datation brings a complete readjusment of the stratigraphy of the section of Collet Redon formerly described by Collot and Combaluzier. The marine deposits with underly the continental formation with the mammal fauna, are Burdigalian. The angular unconformity between the marine and the continental deposits gives evidence of an episode of emersion on the margin of a sedimentary basin, with deformation and erosion. Owing to the newly discovered fauna, this geodynamical event is clearly settled within the regional geographical and chronological context. Lacustrine and continental deposits of such an age were up to now unsuspected in this area. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 5 (1979) |
|
|
|
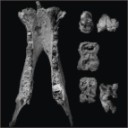
A new species of hippopotamine (Cetartiodactyla, Hippopotamidae) from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation, Abu Dhabi, United Arab EmiratesJean-Renaud Boisserie, Mathieu Schuster, Mark J. Beech, Andrew Hill and Faysal BibiKeywords: Arab Peninsula; Hippopotamidae; Hippopotamine event; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.41.1.e2 Abstract The discovery of new hippopotamid material from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation (Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates) has prompted the revision of the existing material of this as yet unnamed fossil taxon. The Baynunah hippopotamid appears to be distinct from all other contemporary and later species in having a relatively more elongate symphysis, a feature similar to the earlier (and more primitive) Kenyapotamus. Yet, the Baynunah hippopotamid presents a dentition typical of the Hippopotaminae. It is therefore a distinct species attributed to the later subfamily, described and named in this contribution. This species provides further evidence for a ca. 8 Ma evolutionary event (termed “Hippopotamine Event”) that initiated the spread and ecological significance of the Hippopotaminae into wet habitats across Africa and Eurasia. The morphological affinities of the new species from Abu Dhabi suggest that the Arabian Peninsula was not a dispersal route from Africa toward southern Asia for the Hippopotamidae at ca. 7.5 Ma to 6.5 Ma. Article infos Published in Vol 41-1 (2018) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
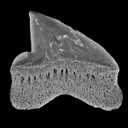
New Squalicorax species (Neoselachii: Lamniformes) from the Lower Maastrichtian of Ganntour phosphate deposit, MoroccoHenri Cappetta, Sylvain Adnet, Driss Akkrim and Mohammed AmalikKeywords: Anacoracidae; Chondrichthyes; Maastrichtian; Morocco; New taxadoi: 10.18563/pv.38.2.e3 Abstract Two new Squalicorax species, S. benguerirensis nov. sp. and S. microserratus nov. sp. are described from the Lower Maastrichtian of the Benguérir phosphate open mine, Ganntour deposit, Morocco. The species S. benguerirensis nov. sp. was classically assigned to S. yangaensis since Arambourg (1952) and has been also recognized in coeval deposits from eastern USA to Mid-East. The species S. microserratus nov. sp. correspond to the lateral teeth of S. kaupi as reported by Arambourg (1952) and which is now referred in fact to S. bassanii. The comparison of these two new species with other Anacoracids, known in Moroccan or elsewhere, allows highlighting the great taxonomic and ecological diversities of this family during the Cretaceous. Article infos Published in Vol.38-2 (2014) |
|
|
|
Un nouveau chiroptère vespertilionide de l'Oligocène d'EuropeBernard Sigé and Henri MenuKeywords: bats; Europe; nov. sp.; Oligocene; VespertilionidAbstract A fossil species of the extant genus Leuconoe, L. lavocati n. sp. from Le Garouillas Oligocene locality, Quercy phosphorites, SW-France, is established in nomenclatural standards. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|
|

|
Etude du crâne de Pachynolophus lavocati n. sp. (Perissodactyla, Palaeotheriidae) des Phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Perissodactyla; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.5.2.45-78 Abstract The genus Pachynolophus, one of the poorest known of the Palaeotheriidae, includes the brachyodont forms with reduced and non-molariform premolars and with upper molars lacking a mesostyle. Quantitative characters (divers surface indications and elongation of the teeth), while demonstrating a close relationship to Hyracotherium, permit a better differentiation of the genus, confirm its specific splitting, and permit the distinction of three lineages. The skull from Memerlein is taken as the type of a new species, P. Iavocati, of which the dentition is extremely characterized by its lophiodonty, the strong reduction of the premolars and the reduction of the cingula. This characterization testifies to a late age which extends the existence of the genus quite near to the Eocene-Oligocene limit. Compared with the only two skulls known of related species (Hyracotheríum vulpiceps and Pachynolophus Iivinierensis), that from Memerlein is distinguished by progressive characters affecting diferent regions but most particularly the braincase; it is not possible, however, to isolate within this evolution the part which leads to a systematic differentiation. Modernization is translated by a considerable increase in size of the braincase, principally in the frontal region, a development of the facial region with anterior displacement of the dental series and a greater specialization of the masticatory apparatus. This evolution parallels the history of the Equidae of the North American early Tertiary, but certain particularities, the form of the alisphenoid, the presence of an anterior frontal foramen, and the structure of the paroccipital apophysis, testifies to the independance of the European forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 2 (1972) |
|
|

|
Evolution de la lignée Megacricetodon collongensis-Megacricetotodon roussillonensis (Cricetidae, Rodentia, mammalia) au cours du Midocène inférieur et moyen dans le Sud de la France.Jean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Cricetids rodents; Evolutionary lineage; Lower and Middle Miocene; Mammalian biochronology; Megacricetodon new species; Southern FranceAbstract New populations of the genus Megacricetodon have recently been discovered in Southern France.Two new species are defined: M. lemartineli n. sp. and M. fournasi n. sp., their stages of evolution are intermediate between those of M. gersii and M. roussillonensis. Morphological and biometrical analysis indicate the presence of only one lineage: M. collongensis--M. collongensis-gersii--M. gersii--M.lemartineli nov. sp.--M. fournasi nov. sp. and M. roussillonensis. This observation allows to refine the chronology based on rodents, for the Late Early Miocene and the Middle Miocene in the Southern France. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
Les Tayassuidés des phosphorites du QuercyLéonard GinsburgKeywords: Quercy Phosphorites; TayassuidaeAbstract Revision of the Tayassuidae from the old collections of the Quercy leads to interesting facts about taxonomic and phylogenetic problems. It could not have been well done without constant comparison with contemporaneous Tayassuidae from stratified series, as well as with European Miocene Tayassuidae and Hyotheriinae. The result is that only three species are present in the Phosphorites of Quercy: Doliochoerus quercyi FiLHOL (represented by two sub-species: the older, D. quercyi quercyi and the more recent, D. quercyi aquensis), Palaeochoerus gergorianus CROIZET et BLAINVILLE and Palaeochoerus purillus nov. sp. The two former species disappeared with Stampian time, while the third is the direct ancestor of the Aquitanian Palaeochoerus typus POMEL, which became extinct before the beginning of Burdigalian. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|
|
Les vertébrés fossiles de Colombie et les problèmes posés par l'isolement du Continent sud-Américain.Jaime de PortaKeywords: Columbia; Cretaceous; Fauna; Quaternary; South Americadoi: 10.18563/pv.2.2.77-94 Abstract A general view is given of the vertebrate faunas, Cretaceous to Quaternary of age, found in Columbia and of their principal characteristics. This view leads to the discussion of the isolation of the South American continent and of the role played by the Bolivar syncline with respect to North American immigrants during the Oligocene. The absence of marine deposits of Oligocene age in the north and northwest of Columbia suggests the possibility of a communication with Central America. This communication would have permitted the passage of hystricomorph rodents, of platyrrhine monkeys, and of colubrids. The non-occupation, until then, of the ecologie niches of these groups would have favored their installation beside the indigenous fauna. In this hypothesis it would no longer be necessary to admit that these vertebrates arrived as «island hoppers ››. The eco-biologic conditions would explain the absence of large-sized forms of North American origin. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 2 (1969) |
|
|
|
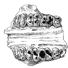
A pangolin (Manidae, Pholidota, Mammalia) from the French Quercy phosphorites (Pech du Fraysse, Saint-Projet, Tarn-et-Garonne, late Oligocene, MP 28)Jean-Yves Crochet, Lionel Hautier and Thomas LehmannKeywords: Oligocene; Pangolin; Pech du Fraysse; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e4 Abstract Pangolins have never shown a high taxic diversity and their fossil record is scarce. We report here the first discovery of a partial humerus from late Oligocene deposits in Pech du Fraysse (MP28, France). The new specimen from Pech du Fraysse is described and compared to various extant and extinct species of pangolins. It shows a suite of morphological features very similar to the humeri discovered in Saint-André (MP 26), Solnhofen (Burdigalien), and Saulcet (Aquitanian), attributed here to Necromanis franconica. The description of the specimen from Pech du Fraysse allowed us to discuss the systematics of Paleogene and Neogene pholidotans. The differences between PFY 4051 and N. franconica on the one side, and N. quercyi on the other side, might be sufficiently important to justify a generic distinction. A comparison with extant species showed that N. franconica was likely terrestrial and fossorial based on its humeral morphology. Related dataset Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|
|
Les rongeurs de l' Eocène inférieur et moyen d'Europe Occidentale; Systématique, phylogénie, biochronologie et paléobiogéographie des niveaux-repères MP 7 à MP 14.Gilles EscarguelKeywords: Biochronology; Early and Middle Eocene; Gliridae; Ischyromyidae; Mammalia; MP Scale; New Genus and Species; Palaeogeography; PHYLOGENY; Rodents; Theridomyidae; Western EuropeAbstract Fourteen distinct phyletical lineages which belong at least in three families: Ischyromyidae ALSTON, 1876, Gliridae THOMAS, 1896 and Theridomyidae ALSTON, 1876, have been identified after the study of more than 3600 rodent dental remains from about twenty Early and Middle Eocene european localities. A systematical and phylogenetical revision of these rodents has been achieved. Nearly all the specific and generic diagnosis are emended. Several new combinations and synonymies are proposed. Four new species and two new genera, Euromys nov. (Ailuravinae) and Hartenbergeromys nov. (Microparamyini), are named and described. Euromys nov. gen. is known by three distinctive ypresian (MP 7 to MP 10 european reference levels) chronospecies. This new lineage is thought to be the direct ancestor of Meldimys MICHAUX, 1968 and Ailuravus RUTIMEYER, 1891. A new species of the genus Plesiarctomys BRAVARD, 1850, Pl. lapicidinarum from Condé-en-Brie (MP 8-9 reference level), allows to relate the Plesiarctomys lineage to the Pseudoparamys MICHAUX, 1964 one. The taxa Sparnacomys HARTENBERGER, 1971, Pantrogna HARTENBERGER, 1971, and Corbarimys MARANDAT, 1989 are erected to genus rank; the last one is not thought to be an Ischyromyidae. A new chronospecies of Pantrogna, P. marandati nov. sp. from the locality of Prémontré (MP 10 reference level), is described. This lineage is at the origin of two others, namely Masillamys TOBIEN, 1954, including M. mattaueri (HARTENBERGER, 1975) nov. comb. (MP 10 reference level), and Hartenbergeromys nov. gen., known from MP 10 (H. hautefeuillei nov. sp.) and MP 11 (H. parvus TOBIEN, 1954) reference levels. The phylogenetical position of Hartenbergeromys nov. gen., at the origin of the european family Theridomyidae, is discussed. The systematical and phylogenetical status of two probable Paramyinae, "Paramys" woodi MICHAUX, 1964 and an unnamed genus and species, are discussed. New populations of the primitive Gliridae Eogliravus HARTENBERGER, 1971 and of the primitive Theridomyidae Protadelomys HARTENBERGER, 1968, are described and assigned to previously known species. Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 2-4 (1999) |
|
|

|
Observations sur des remaniements structuraux post-mortem dans des dents de mammifères fossiles provenant des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Quercy Phosphorites; rearrangements; TeethAbstract Deux types de remaniements post mortem me paraissent caractéristiques de l'état de conservation des dents de mammifères fossiles dans les Phosphorites du Quercy : Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
La plus ancienne faune de mammifères du Quercy : Le BretouJean-Louis Hartenberger, Bernard Sigé and Jean SudreKeywords: Le Bretou; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
On the genus Dikkomys (Geomyoidea, Mammalia)Morton Green and Philip R. BjorkKeywords: Dikkomys; Geomyoidae; North AmericaAbstract The geomyoid genus Dikkomys is well represented in a sample from the Black Bear Quarry Il local fauna of Early Hemingfordian age in Bennett County, South Dakota. Isolated unworn P/4's of Dikkomys matthewi WOOD have a prominent median cristid (sagicristid) with a connection to the metaconid and the hypolophid. With wear, P/4 does not become as molariform as P/4 because of this cristid. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Les Otolithes de téléostéens du Miocène de Montpeyroux (Herault),France).Dirk Nolf and Henri CappettaKeywords: Miocene; Montpeyroux; Otolithes; teleostean fishAbstract Sieving and washing of about 700 kg of sediment from the miocene site at Montpeyroux produced otoliths of 34 teleost species, of which four still occur in the present day fauna or are near to extant species. Among the fossil species, eight are new : Ilisha lerichei, «genus Clupeidarum ›› orbiculatus, Dipulus mediterraneus, Morone cornuta, Chanda nelsoni, Pomadasys steurbauti, «genus Sciaenidarum ›› barthassadensis and Paraplagusia roseni. The fauna found is typical for a tropical or subtropical very littoral, probably even estuarine environment; it was living in a period near the boundary between Lower and Middle Miocene, perhaps somewhat earlier. Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 1 (1980) |
|
|
|
Mode de vie et affinités de Paschatherium (Condylarthra, Hyopsopontidae) d'après ses os du tarseMarc Godinot, Thierry Smith and Richard SmithKeywords: Astragalus; Calcaneum; Condylarthra; Eocene; Functional morphology; Paschatherium; PHYLOGENYAbstract Tarsals that can be confidently attributed to Paschatheríum dolloi from Dormaal (Belgium) are described. The astragalus is short; its broad neck is set at an angle of 30 degrees to the trochlea. The trochlea is pulley-shaped and proximally extended. There is no astragalar foramen. The medial tibial facet extends distally in a cup deeply excavated in the neck and buttressed. The sustentacular facet extends toward the navicular facet but is not fully confluent with it. The calcaneum bears a proximo-distally extended proximal facet for the astragalus. A relatively large peroneal tubercle projects from the body, and is situated distally. Functionally, the trochlea indicates extensive flexion-extension movements of the foot. Calcaneo-astragalar facets indicate sliding and rotation between the two tarsals. The inclination of the navicular facet suggests frequent foot inversion. The peroneal tubercle reflects good muscular capacities for foot rotation. Overall morphology is interpreted as a scansorial adaptation similar to that of sciurids.Comparisons are made with the tarsals of Macrocranion vandebroeki from Dormaal and Hyopsodus paulus from the Bridgerian of Wyoming. Some similarities between the astragali of Paschatherium and Macrocraníon (trochlea) are interpreted as convergences for rapid locomotion. However absence of mobility at the lower ankle and midtarsal joints in M. vandebroekzi suggests that this species was cursorial, as is known for M. tenerum from Messel. Similarities in the calcanea of Paschatherium and Hyopsodus are probably the result of close phylogenetic relations, and confirm the placement of Paschatherium in the hyopsodontids. The differences in the calcanea of Paschatherium and Macrocranion underline that Paschatherium is distinct from erinaceomorph insectivores. The differences in astragalar morphology between Paschatherium and Hyopsodus show that a marked adaptive divergence separates the two genera. We speculate about the common occurrence of a deep tibial cup (“cotylar fossa”) and a pulley-shaped trochlea in Paschatherium and hyracoids, suggesting that an adaptive scenario similar to that having led to Paschatherium (scansoriality) might explain the acquisition of the peculiar hyracoid tarsal characters; such a scenario contradicts the concept of Pantomesaxonia. Other peculiar characters of Hyopsodus suggest that hyopsodontids might be given more consideration in the search for hyracoid (and tethythere) origins. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Nouvelles faunes de rongeurs de la fin Miocène inférieur en Provence. Implications géologiques et Paléogéographiques.Dominique LalaïKeywords: Biogeographic province; Biozonation; Correlation; Miocene; Palaeogeography; RodentiaAbstract Rodents from the new localities of Châteauredon (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence) and La Denise (Bouches-du-Rhône) show more similarities with the rodents known from the Czecho-Slovak locality of Franzenbad than with the species found in contemporaneous Lower Miocene faunas located westward of the present Rhône Valley. This is another data wich support the existance of several biogeographical provinces in Southern France during Lower Miocene. The correlations which have been settled down allow new datations of several formations in Provence and give new information on the Aquitanian and Burdigalian paleogeographies of this region. More precise stratigraphical allocations are given to some other localities of Central Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 2 (1986) |
|