Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
A partial skeleton of Metaxytherium medium from the middle Miocene of La Morfassière quarry (Indre-et-Loire, France)
|
|
|

|
A reassessment of the giant birds Liornis floweri Ameghino, 1895 and Callornis giganteus Ameghino, 1895, from the Santacrucian (late Early Miocene) of Argentina.Eric BuffetautKeywords: Argentina; Aves; Callornis; Liornis; Miocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.40.2.e3 Abstract The status of the giant bird taxa Liornis floweri and Callornis giganteus from the Santa Cruz Formation (late Early Miocene) of Patagonia, first described by Ameghino (1895) is reassessed on the basis of a re-examination of the type material at the Natural History Museum, London. Liornis floweri, which lacks a Pons supratendineus on the tibiotarsus and has an unbifurcated Canalis interosseus distalis on the tarsometatarsus, is clearly a brontornithid and is considered as a junior synonym of Brontornis burmeisteri. Ameghino’s replacement of Callornis by Eucallornis is unjustified. Callornis giganteus is a chimera based on a phorusrhacid tarsometatarsus (probably belonging to Phorusrhacos longissimus) and a brontornithid tibiotarsus. The latter can be considered as the lectotype of Callornis giganteus, which may represent a small morph of Brontornis burmeisteri or a distinct taxon. It is referred to here as Brontornithidae indet. The tarsometatarsus described by Dolgopol de Saez (1927a,b) as Liornis minor and considered by her as a gracile brontornithid apparently has a bifurcated Canalis interosseus distalis and should therefore be placed among the Phorusrhacidae. Article infos Published in Vol.40-2 (2016) |
|
|

|
The new Algerian locality of Bir el Ater 3: validity of Libycosaurus algeriensis (Mammalia, Hippopotamoidea) and the age of the Nementcha FormationFabrice Lihoreau, Lionel Hautier and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Dispersal event; Miocene; North Africa; Tetralophodondoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e1 Abstract The description of original material of anthracothere and proboscidean in the new locality of Bir el Ater 3 from East Algeria, and a thorough review of early Libycosaurus remains of Bir el Ater 2 allows us validating L. algeriensis as the smallest and earliest species of Libycosaurus and probably the earliest migrant of the genus from Asia. The presence of a Tetralophodon in the Neogene Nementcha formation might represent the earliest occurrence of the genus in Africa. These original fossil remains allow us to discuss the age of the Neogene part of the Nementcha formation close to the Serravalian/Tortonian boundary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|

|
The evolution of the molar pattern of the Erethizontidae (Rodentia,Hystricognathi) and the validity of Parasteiromys Ameghino, 1904.Adriana M. CandelaKeywords: Argentina; Erethizontidae; Hystricognathi; Miocene; Molar evolution; Porcupines; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract The genus Parasteiromys AMEGHINO, 1904 is revalidated, and P. friantae sp. nov. (Hystricognathi, Erethizontidae) from Colhuehuapian (early Miocene) sediments of the southern cliff of Colhue-Huapi Lake (Province of Chubut, Argentina), is described. The molar morphology of these taxa and of living porcupines adds new elements to understand the dental evolution of the Erethizontidae, and to propose the hypothetical ancestral molar pattern for this family. This pattern does not correspond to any of the morphologies traditionally proposed as ancestral for South American hystricognathous rodents. The proposed pattern is characterized by a metaloph disconnected from the posteroloph and oriented towards the hypocone, and the third loph incompletely developed with the lingual portion homologous to the mesolophule of Baluchimyinae (Chapattimyidae) from the Miocene of Pakistan. The inferred steps of the molar evolution of erethizontids towards the pentalophodont condition, considered derived for the family, are illustrated. This study strengthens the hypothesis placing erethizontids in a basal position among rodents of the suborder Hystricognathi. Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|

|
First evidence of an early Miocene marine teleostean fish fauna (otoliths) from la Paillade.(Montpellier,France)Bettina Reichenbacher and Henri CappettaKeywords: Aquitanian; Biostratigraphy; La Paillade; marine deposits; Miocene; otoliths; Palaeoecology; Palaeogeography; Southern France; TeleosteiAbstract A fossil fish fauna, based on 5533 otoliths, from the La Paillade locality at Montpellier is described and figured. The otolith-bearing marls correlate to mammal zone MN l (Aguilar, 1982), and thus represent the earliest Miocene. The fish fauna consists of 30 taxa belonging to 20 families. Two species are new: Dussumieria sittigi and Liza gaudanti. The predominant faunal element is the Lesueurigobius vicínalis-species complex, composing 73% of all investigated otoliths. The palaeoecological analysis reveals a marine to euryhaline fish fauna living under tropical to subtropical conditions in the transition zone littoral - sublittoral. Water depth probably was more than 10 m. The scarcity of pelagic físhes suggests that the habitat was either a sheltered bay and/or far away from the open sea. Furthermore, some genera represented in the La Paillade fish fauna presently live exclusively in the Indopacific realm. Their presence strongly supports a broad connection between the Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean, and the Paratethys Seas during the Early Miocene (Aquitanian). From a palaeobiogeographical point of view, faunal relationships were found between the La Paillade fish fauna and both the Paratethys fish fauna and the fish fauna from the deposits in the Upper Rhinegraben and the Mayence and Hanau Basins (Germany). Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|

|
Stratigraphy and Oligocene-Miocene mammalian biochronology of the Aktau Moutains, Dzhungarian Alatau Range, KazakhstanElena G. Kordikova and Alexander V. MavrinKeywords: Dzhungarian Alatau; Kazakhstan; Lithologic correlation; Mammalian biochronology; Miocene; Oligocene; StratigraphyAbstract Stratigraphic studies in the Aktau Mountains bordering the Dzhungarian Alatau Range in southeastern Kazakhstan have included mapping of Tertiary lithostratigraphic units, documentation of fossiliferous deposits, correlation of sections, etc. These investigations have led in turn to revised interpretation of the Tertiary geology of the area. The Tertiary sequence in the Aktau Mountains is represented by three lithostratigraphic units (in ascending order): (1) the middle Eocene Akbulak Formation; (2) the Oligocene Aktau Formation with a lower member including white quartz sands that contain fossil mammals, and an upper member including red-colored clays and sandstones, brick red clays, an anhydrite and gypsum clayey horizon, and bright brown-red clays; and (3) the upper Oligocene-Miocene Chul'adyr Formation with a lower member of greenish and yellowish conglomerates and gritstones, a middle member including grayish and yellowish sands and gritstones, and an upper member including brown and red clays and carbonate- and anhydrite-rich clays. The Aktau and Chul”adyr Formations represent separate cycles of sedimentation. Mammalian biostratigraphy and biochronology of the three vertebrate faunas in Aktau Mountains are reviewed. The mammalian fauna from white sands of the lower Aktau Formation is small but includes Ardynia and is thought to be early Oligocene in age. The mammalian fauna from conglomerates and gritstones of the lower member of the Chul”adyr Formation is also small but includes Paraceratherium and is thought to be late Oligocene in age. The mammalian fauna from sands of the middle member of the Chul'adyr Formation is extensive, with micro- and macrofauna attributed to Neogene mammal zones MN4 to MN 6, indicating a latest early Miocene to earliest middle Miocene age (Orleanian-Astaracian). Most genera of middle Chul”adyr mammals are known from the middle Miocene Shanwang faunas of China and from the Castelnau-d”Arbieu faunal assemblage (MN4-MN6) of southwestern France. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Systematic revision of Ctenodactylidae (Mammalia, Rodentia) from theMiocene of Pakistan.J.A. BaskinKeywords: Ctenodactylidae; Miocene; Prosayimys; Rodents; Sayimys; SiwalikAbstract Extensive sampling of the Siwalik deposits of the Potwar Plateau of northem Pakistan and from the Zinda Pir dome of central Pakistan has produced a fossil record of Miocene ctenodactylids that can be correlated with the paleomagnetic time scale. The early Miocene Prosayimys flynni (n. gen., n. sp.) is recognized as the first ctenodactylid in the Indian subcontinent. Prosayimys is ancestral to Sayimys. From the late early Miocene to the early late Miocene, there is an anagenetic succession of three species of Sayimys: S. cf. S. intermedius, S. sivalensis, and S. chinjiensis (n. sp.). Sayimys chinjiensis gave rise to the late late Miocene S. perplexus. A second lineage is represented by Sayimys minor, S. sp. A, and S. sp. B. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 1 (1996) |
|
|
|
Un crane de Chalicothere (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) du Miocène supérieur de Macédoine (Grèce) : remarque sur la phylogénie des ChalicotheiinaeLouis de Bonis, Geneviève Bouvrain, George D. Koufos and Pascal TassyKeywords: Chalicotheriidae; Cladistics; Greece; Miocene; Perissodactyla; PHYLOGENYAbstract The discovery in the Turolian (Late Miocene) of Dytiko 3 (Macedonia, Greece) of a complete skull with mandibles and cervical vertebrae, atlas and epistropheus, is a very important contribution to the knowledge of the subfarnily Chalicotheríinae. After the description, the comparison with other specimens of Miocene chalicotheres permits the revival of the generic name Macrotherium with a new species M. macedonicum. This genus is mainly characterized by a short snout and an inflated cerebral skull. It coexists during the Miocene with Chalicotherium. A cladistic analysis leads to conclusion that the species which has been described from the Early Middle Miocene of Rusinga must be identified as the type-species of a new genus: Butleria. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|

|
The lower Miocene artiodactyls of Tagai bay, Olhon island, lake Baikal (Russia)Inesa VislobokovaKeywords: Artiodactyls; Mammals; Miocene; SiberiaAbstract The mammalian fauna of the Tagai locality of Olhon Island in Lake Baikal contains six artiodactyls: Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Octodontid-like Echimyidae (Rodentia) : an upper Miocene episode in the radiation of the familyDiego H. Verzi, Maria G. Vucetich and Claudia I. MontalvoKeywords: Argentina; Echimyidae; Miocene; New taxa; Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract Reigechimys octodontiformis gen. et sp. novo and R. plesiodon sp. novo are described. They represent the frrst record of the family Echimyidae for the Cerro Azul Formation (Huayquerian Age, Late Upper Miocene) at La Pampa Province, central Argentina. Both species have hypsodont cheek teeth with an eight-shaped occlusal design. This dental morphology represents a noticeable case of convergence to octodontids and indicates that these echimyids inhabited open environments. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Nouveaux gisements à rongeurs dans les molasses oligo-miocènes de la région toulousaineFrancis DuranthonKeywords: Cricetidae; Eomyidae; GIiridae; Miocene; Oligocene; Rodents; Sciuridae; Southern FranceAbstract The fauna from three new rodent localities (Castelmaurou, Grépiac-carrière et Grépiac-rive gauche) from Oligo-Miocene molasses of the Toulouse area is described. The one from Colomiers is completed. 11 species belonging to 4 families (Cricetidae, Eomyidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) are present. The Miocene localities of Grépiac-carrière and Colomiers are correlated with Balizac, La Brète, Lambert and Lespignan. Grépiac-rive gauche is just a little older than these sites. Castelmaurou is somewhat younger than La Milloque and belongs to Oligocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|

|
Les nouvelles faunes de rongeurs proches de la limite mio-pliocène en Roussillon. Implications biostratigraphiques et biogéographiquesJean-Pierre Aguilar, Jacques Michaux, Bernadette Bachelet, Marc Calvet and Jean-Pierre FaillatKeywords: Arvicolidae; Cricetidae; Gliridae; Miocene; Muridae; Pliocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract Three new fossiliferous localities, two of karstic origin, Castelnou 3 and Font Estramar, respectively Late Upper Miocene and Lower Pliocene, and one of lacustrine origin, Thuir, Lower Pliocene, add data about the transition between Miocene and Pliocene faunas of rodents in southern France. An unexpected association of taxa was present in the late Upper Miocene, including between others, Myocricetodon, Hispanomys, Ruscinomys, Cricetus barrierei, Promimomys and a new species of Stephanomys, S. dubari nov. sp. Myocricetodon is still known in the Lower Pliocene. It is shown that the large field-mice known since the Late Upper Miocene belong to two different lineages, on one side, A. jeanteti, on the other side, A. gudrunae followed by A. gorafensis. Biochronological and biogeographical implications are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 4 (1991) |
|
|
|
Ostéologie de la tête de Richardus excavans Lavocat,1988René LavocatKeywords: Africa; anatomy; Bathyergidae; Miocene; RodentsAbstract Remarkable association of a small infraorbital foramen, similar to that in recent Heterocephalus, and of a strong muscular print on the dorsal anterior part of the zygomatic plate and on the premaxillary. Several anatomical structures to be compared with those of Heterocephalus suggest relationships with this genus. Richardus supports the ancestrality of the hystricomorph character in the bathyergids Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 2 (1989) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 6 - Les périssodactyles RhinocerotidaeClaude GuérinKeywords: Aceratherium; anatomy; Biostratigraphy; Dicerorhinus; Miocene; Montredon; Paleoecology; Upper VallesianAbstract The Montredon site has yielded about hundred rhinoceros remains: Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Nouvelles faunes de rongeurs de la fin Miocène inférieur en Provence. Implications géologiques et Paléogéographiques.Dominique LalaïKeywords: Biogeographic province; Biozonation; Correlation; Miocene; Palaeogeography; RodentiaAbstract Rodents from the new localities of Châteauredon (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence) and La Denise (Bouches-du-Rhône) show more similarities with the rodents known from the Czecho-Slovak locality of Franzenbad than with the species found in contemporaneous Lower Miocene faunas located westward of the present Rhône Valley. This is another data wich support the existance of several biogeographical provinces in Southern France during Lower Miocene. The correlations which have been settled down allow new datations of several formations in Provence and give new information on the Aquitanian and Burdigalian paleogeographies of this region. More precise stratigraphical allocations are given to some other localities of Central Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 2 (1986) |
|
|
|
Macroscelidea, Insectivora and Chiroptera from the Miocene of east Africa.Percy M. ButlerKeywords: Chiroptera; East Africa; Insectivora; Macroscelidea; Miocene; SystematicsAbstract The East African Miocene Macroscelidea, lnsectivora and Chiroptera are revised on the basis of new material. New taxa proposed are: Miorhynchocyon, .n. gen. (Macroscelididae): Míorhynchocyon meswae, n. sp.: Pronasílío ternanensis. n. gen.. n. sp. (Macroscelididae); Hiwegicyon juvenalis, n. gen. n. sp. (Macroscelididae); Parageogale, n. gen. (Tenrecidae): Prochrysochlorinae, n. subfam. (Chrysochloridae): Propottininae, n. subfam, (Pteropodidae); Chamtwaria pickfordi, n. gen., n. sp. (Vespertilionidae). Gymnurechnínus songhorensis is synonymised with G. camptolophus. The new material provides additional information on the dentition, especially of Myohyrax oswaldi. Galerix africanus. Amphechínus rusingensis, Protenrec tricuspis and Parageogale aletris. Partial skulls are described of Amphechinus rusingensis, Protenrec tricuspis, Prochrysochloris míocaenicus and Taphozous incognita. The oldest member of the Macroscelidinae (Pronasilio) is described from Fort Ternan. Galerix africanus is closely related to G. exilis from Europe. Amphechinus rusingenesis is compared with Asiatic Oligocene Erinaceinae. The Miocene age of Crocidura is rejected. On the evidence of humeri, the following families of Chiroptera are newly reported: Pteropodidae, Nycterididae, Vespertilionidae, Molossidae. Propotto is regarded as an offshoot from the Pteropodidae, not ancestral to modern forms. Chamtwaria is a primitive vespertilionoid, provisionally placed in the Kerivoulinae. Erinaceidae probably entered Africa at the beginning of the Miocene, before 20 Ma. Faunistic differences between deposits are largely to be ascribed to differences in local environment. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 3 (1984) |
|
|

|
An Australian Miocene Brachipposideros (Mammalia, Chiroptera) related to Miocene representatives from FranceBernard Sigé, Suzanne J. Hand and Michael ArcherKeywords: Australia; bats; Chiroptera; MioceneAbstract A new middle Miocene hipposiderid bat is described from a limestone deposit on Riversleigh Station in north-western Queensland. Hipposideros (Brachipposideros) nooraleebus n. sp. is the first record of this subgenus from anywhere in the world outside of France. The palaeoecological setting of the fossil bats appears to have been a relatively quiet, sunny lime-enriched tropical pool that contained tortoises, crocodiles and fish. It is possible that the bats were washed into the pool from an adjacent cave. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 5 (1982) |
|
|

|
Les Otolithes de téléostéens du Miocène de Montpeyroux (Herault),France).Dirk Nolf and Henri CappettaKeywords: Miocene; Montpeyroux; Otolithes; teleostean fishAbstract Sieving and washing of about 700 kg of sediment from the miocene site at Montpeyroux produced otoliths of 34 teleost species, of which four still occur in the present day fauna or are near to extant species. Among the fossil species, eight are new : Ilisha lerichei, «genus Clupeidarum ›› orbiculatus, Dipulus mediterraneus, Morone cornuta, Chanda nelsoni, Pomadasys steurbauti, «genus Sciaenidarum ›› barthassadensis and Paraplagusia roseni. The fauna found is typical for a tropical or subtropical very littoral, probably even estuarine environment; it was living in a period near the boundary between Lower and Middle Miocene, perhaps somewhat earlier. Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 1 (1980) |
|
|

|
Nouvelle interprétation de l'évolution du genre Megacricetodon au cours du MiocèneJean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Megacricetodon; Micromammals; MioceneAbstract La découverte de nouveaux gisements à micromammifères dans le Miocène du Sud de la France et d'Espagne montre que, s'il n'est plus possible d'accepter dans son intégralité le schéma phylétique de Fahlbusch du genre Megacricetodon, il existe toutefois des segments de lignées à l'intérieur de provinces géographiques différentes (Péninsule Ibérique, France, Europe Centrale), avec lesquels on peut établir une biochronologie locale, segments qu'il est aussi possible de placer les uns par rapport aux autres, en utilisant les corrélations que l'on peut reconnaître entre certains niveaux repères des mammalogistes et l'échelle stratigraphique marine. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Rongeurs du Miocène inférieur et moyen en Languedoc. Leur apport pour les correlations Marin-Continental et la Stratigraphie.Jean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Languedoc; Miocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract The rodents (Cricetidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) found in lacustrine, brackish marine and karstic sediments of Miocene age in Languedoc, assign the position of the different localities in the scale of "niveaux repères" used by mammalogists. Some detailed stratigraphical studies bring several correlations between this continental biochronological scale and the marine scale ; the most important results are the Aquitanian age of the "niveaux repères" of Coderet and Paulhiac, the Burdigalian age of Laugnac, Estrepouy, Vieux-Collonges, La Romieu and Sansan and the Langhian or Lower Serravallian age of La Grive M. The correlations between the Tethys and the Central Paratethys for the Lower Neogene profit also of these results, since the locality of Neudorf Spalte 1, 2 (Czechoslovakia) is shown to be younger than Sansan (France). The paleontological study has also several geological inferences for the Miocene of Languedoc ; with the calibration of this Miocene, we know quite precisely that the Lower Miocene is chiefly a time lacustrine sedimentation, and also that the marine Miocene sedimentation ends early in the Miocene Period, in Langhian or lower Serravallian times. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 6 (1980) |
|
|
|
Rongeurs Miocènes dans le Valles-Penedes 2 : Les rongeurs de Castell de BarberaJean-Pierre Aguilar, Jordi Agusti and J. GibertKeywords: Castell de Barbera; Miocene; Rodents; Valles-PenedesAbstract The rodent-fauna (Cricetidae and Gliridae) recently found at Castell de Barbera (Spain) is similar to those from the other locslities of the Valles - Penedes - Can Ponsic 1 and Can Llobateres - : same composition and similar evolutionary level of the different species. On the other hand this fauna is different from those of Upper Vindobonian and Vallesian localities of the Calatayud - Teruel area. Castell de Barbera has an intermediate chronological position between the localities of Anwil (Switzerland) and Can Ponsic 1. It is still not possible to validate or invalidate the initial attribution based on absence of Hipparion of Castell de Barbera to the Upper Vindobonian. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 1 (1979) |
|
|
|
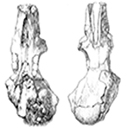
Rongeurs Miocènes dans le valles-Penedes 1 : Les rongeurs de Can Ponsic 1Jean-Louis Hartenberger and Miquel Crusafont i PairóKeywords: Can Ponsic 1; Miocene; Rodents; Valles-PenedesAbstract The rodents from the spanish locality of Can Ponsic 1 bring new data about some rodents species of the beginning of the Upper Miocene in South-West Europe. The criticims made by Mein and Freudenthal about the validity of the species Hispanomys thaleri from Can Llobateres are not justiíied. The study of the anatomy of the skull of Rotundomys from Can Ponsic 1 gives accurate information about the affinity of this genus with Cricetulus, and shows that the hypothesis, according to which Rotundomys is an ancestral form of the Arvicolids, is unlikely. The systematics of Heteroxerus and the phylogeny of the mio-pliocene Muscardinus species are also discussed. The Can Ponsic 1 locality is a little older than Can Llobateres. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 1 (1979) |
|
|

|
Les sélaciens du Miocène de la région de MontpellierHenri CappettaKeywords: Ichtyofauna; Miocene; Montpellierdoi: 10.18563/pv.3.ext.1-139 Abstract The utilization of screen-washing and attack by dilute acetic acid has permitted the collecting, in the Miocene of the department of Hérault (France), of a very rich ichthyofauna. This fauna is presently comprised of about 60 studied species, of which 11 are new, and represents, in the present state of knowledge, the most varied Miocene selachian fauna described in the world. Article infos Published in Vol. 3, Ext (1970) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude de l'anatomie crânienne des rongeurs. 1- Principaux types de cricétodontinésJean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Cricetodon; Cricetodontinae; Miocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.1.2.47-64 Abstract Description, for the first time, of the skull of Ruscinomys Depéret on the basis of a nearly complete specimen, and description of a new facial part of a Megacricetodon Fahlbusch skull (material from upper Miocene, Spain). New description of the skull (facial part) of " Cricetodon" incertum Schlosser on the basis of the specimen from the Oligocene of Quercy phosphorites already published by S. Schaub. Article infos Published in Vol. 01, Fasc. 2 (1967) |
|