Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Introduction à l'oeuvre scientifique de Donald E. Russell, "gentleman paleontologist"Marc Godinot and Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: D.E.Russell; Eocene; Mammals; Paleocene; Paleontology; synthesisAbstract The scientific career of D.E. Russell began with a Pliocene fauna from Oregon, and then turned in the direction of European Paleogene mammals. Field work followed by study of the mammals that were collected, firstly in the Paleocene and later in the early Eocene, greatly rejuvenated learning in this field. Syntheses on the Northwest European Tertiary basin and on European marnmals and stratigraphy came next. Research on the Eocene of Asia was carried out jointly with Gingerich on Pakistan and with Dashzeveg on the faunas of Mongolia. An important synthesis on the entire Paleogene of Asia, joint with Zhai, followed. Field work in Africa with Sigogneau-Russell led to the discovery of Mesozoic mammals there. A synthesis of mammalian paleofaunas of the world was written with Savage, and a similar synthesis of Cenozoic vertebrate faunas is currently being prepared. These achievements reflect the perennial importance of field work, numerous collaborations with both amateurs and professionals, and the human qualities of this author. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Avant-proposMarc Godinot and Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: D.E.RussellAbstract Le présent volume est l'aboutissement d'un projet né il y a presque cinq ans. En décembre 1991, l'un d'entre nous (MG) prenait des contacts en vue de proposer un symposium sur les mammifères fossiles, dédié à D.E. Russell, dans le programme du 4e Congrès de la European Society for Evolutionary Biology. Ce congrès, baptisé "Evolution 93", devait se tenir à Montpellier en août 1993. Son Comité d'Organisation, animé par F. Catzeflis, recherchait des organisateurs de symposiums. L'idée fut acceptée avec enthousiasme par le second d'entre nous (PDG), et le titre de notre Symposium fut précisé: " Palaeobiology and Evolution of Early Cenozoic Mammals - A Symposium in Honor of D.E. Russell". Le projet fut formellement accepté par le Comité d'Organisation en avril 1992. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
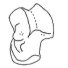
Mode de vie et affinités de Paschatherium (Condylarthra, Hyopsopontidae) d'après ses os du tarseMarc Godinot, Thierry Smith and Richard SmithKeywords: Astragalus; Calcaneum; Condylarthra; Eocene; Functional morphology; Paschatherium; PHYLOGENYAbstract Tarsals that can be confidently attributed to Paschatheríum dolloi from Dormaal (Belgium) are described. The astragalus is short; its broad neck is set at an angle of 30 degrees to the trochlea. The trochlea is pulley-shaped and proximally extended. There is no astragalar foramen. The medial tibial facet extends distally in a cup deeply excavated in the neck and buttressed. The sustentacular facet extends toward the navicular facet but is not fully confluent with it. The calcaneum bears a proximo-distally extended proximal facet for the astragalus. A relatively large peroneal tubercle projects from the body, and is situated distally. Functionally, the trochlea indicates extensive flexion-extension movements of the foot. Calcaneo-astragalar facets indicate sliding and rotation between the two tarsals. The inclination of the navicular facet suggests frequent foot inversion. The peroneal tubercle reflects good muscular capacities for foot rotation. Overall morphology is interpreted as a scansorial adaptation similar to that of sciurids.Comparisons are made with the tarsals of Macrocranion vandebroeki from Dormaal and Hyopsodus paulus from the Bridgerian of Wyoming. Some similarities between the astragali of Paschatherium and Macrocraníon (trochlea) are interpreted as convergences for rapid locomotion. However absence of mobility at the lower ankle and midtarsal joints in M. vandebroekzi suggests that this species was cursorial, as is known for M. tenerum from Messel. Similarities in the calcanea of Paschatherium and Hyopsodus are probably the result of close phylogenetic relations, and confirm the placement of Paschatherium in the hyopsodontids. The differences in the calcanea of Paschatherium and Macrocranion underline that Paschatherium is distinct from erinaceomorph insectivores. The differences in astragalar morphology between Paschatherium and Hyopsodus show that a marked adaptive divergence separates the two genera. We speculate about the common occurrence of a deep tibial cup (“cotylar fossa”) and a pulley-shaped trochlea in Paschatherium and hyracoids, suggesting that an adaptive scenario similar to that having led to Paschatherium (scansoriality) might explain the acquisition of the peculiar hyracoid tarsal characters; such a scenario contradicts the concept of Pantomesaxonia. Other peculiar characters of Hyopsodus suggest that hyopsodontids might be given more consideration in the search for hyracoid (and tethythere) origins. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
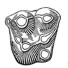
Une faune du niveau d'Egerkinger (MP 14; Bartonien inférieur) dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Sud de la France)Jean Sudre, Bernard Sigé, Jean-Albert Remy, Bernard Marandat, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Marc Godinot and Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Biochronology; Early Bartonian; Eocene; evolution; Mammals; New taxa; QuercyAbstract The Laprade fauna is chronologically situated between those from Egerkingen and Lissieu and consequently, is close to the MP 14 reference-level of the European mammalian biochronological scale (Symposium of Mainz, 1987). Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 1 (1990) |
|
|
|
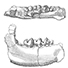
Les mammifères de Rians (Eocène inférieur, Provence)Marc GodinotKeywords: Eocene; Mammals; Provence; RiansAbstract The fossil mammals discovered in the quarry of Rians (Sparnacian, Provence) are described. Among these forms, Hyracotherium is interesting because of the little molarization of the lower premolars and its small size, and Diacodexis by its small size and very primitive astragalus ; they may be the most primitive representatives of their respective orders. Also, Proviverra eisenmanni n. sp. is the smallest and most primitive hyaenodontid yet described. Hyopsodus itinerans is the first species of this genus described France. Among other rare fossils is a new species of bat, a small palaeoryctid, and other forms not yet identified. Marsupials are varied. Several new species are present among the rodents. The fauna is well-balanced and rich in small hyopsodontid condylarths. It is stratigraphically situated at the Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 2 (1981) |
|
|
|
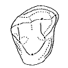
La variabilité morphologique dentaire du Landenodon (Condylarthra) de Dormaal, (Eocène,Belgique)Marc GodinotKeywords: Condylarths; Dormaal; Early Eocene; LandenodonAbstract The study of dental variations in Landenodon from Dormaal (early Eocene, Belgium) shows that only one Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|