Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Observations sur des remaniements structuraux post-mortem dans des dents de mammifères fossiles provenant des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Quercy Phosphorites; rearrangements; TeethAbstract Deux types de remaniements post mortem me paraissent caractéristiques de l'état de conservation des dents de mammifères fossiles dans les Phosphorites du Quercy : Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
Evolution et extinction des reptiles marins au cours du Mésozoïque.Nathalie BardetKeywords: Crocodiles; evolution; Extinctions; faunal assemblages; Helveticosaurs; Hupehsuchians; Ichthyoaurs; lizards; Marine Reptiles; Mesozoic; Nothosaurs; Pachypleurosaurs; Placodonts; Plesiosaurs; Snakes; Thalattosaurs; Turnovers; TurtlesAbstract An interpretation of the marine reptile fossil record, based on the existing litterature and complemented by the review of ancient collections and the study of new material, permits a better understanding of Mesozoic marine ecosystems. An inventory of the marine reptiles known from the Lower Triassic to the Paleocene is presented: 46 families, about 200 genera and 400 species have been recorded. This data base includes commentaries about systematics, stratigraphical ranges and geographical distribution of taxa. Marine reptiles include a mosaic of not necessarily closely related groups: ichthyosaurs, thalattosaurs, hupehsuchians, pachypleurosaurs, placodonts, nothosaurs, plesiosaurs, pliosaurs but also crocodiles, lizards, snakes, turtles. The diversity studies reveal that the fossil record of marine reptiles has been punctuated by two mass extinctions, during the Middle-Upper Triassic transition and at the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. The Jurassic-Cretaceous and Cenomanian-Turonian boundaries (the latter marked by the disappearance of ichthyosaurs) are potential crisis periods, but current data are not sufficient to reach conclusions. The Ladinian-Carnian transition is characterized by the disappearance of 64 % of families and affects essentially coastal forms. This extinction coincides with an important regressive phase. During the Upper Triassic, a faunal reorganisation within marine reptiles leads to the progressive disappearance of near-shore forms and to the development of pelagic groups. During the Maastrichtian-Danian crisis, 36% of families died out. Large-sized pelagic forms such as mosasaurs and elasmosaurs were the most affected and their extinction seems to have been rather sudden. On the other hand, pliosaurs and protostegid turtles became extinct, but were already declining. The survivors were near-shore forms such as crocodiles, snakes and some turtles and they may have taken refuge in freshwater environments. A break in the food chain based on phytoplankton is proposed as an extinction scenario for pelagic forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 3-4 (1995) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 8 - Analyse paléoécologique de la faune mammalienneSerge LegendreKeywords: France; Mammalia; Montredon; Paleoecology; Upper MioceneAbstract The species diversity of the mammalian fauna from Montredon (Hérault, France, late Miocene) is examined in terms of richness and abundance. A cenogramic analysis of the fossil mammalian community suggests the prevalence of open habitats, with the presence of marshes and of a poorly developed galery forest, and a climate rather warm and dry. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Les mammifères Montiens de Hainin (Paléocène moyen de Belgique) Part III : MarsupiauxJean-Yves Crochet and Bernard SigéKeywords: Belgium; Marsupials; Paleobiogeography; PaleoceneAbstract The oldest european marsupials are described from some specimens (isolated upper molars) recently found from the Hainin sediment (Middle Paleocene of Belgium). These fossils document a new species of the Peradectes genus. They give evidence of a much older occurrence of the marsupials in Europe than it was assumed. They allow us to postulate a didelphid dispersal from South America towards the western-holarctic area operating in two phases : the first one of the Peradectes genus at the end of the Cretaceous; the second one of the Didelphíni tribe at the end of the Paleocene. A central american crossing is likely for the first one, whereas a transafrican way is tentatively argued for the second one. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
Une nouvelle espèce de Steneosaurus (Thalattosuchia, Teleosauridae) dans le Callovien du Poitou (France) et la systématique des Steneosaurus longirostres du Jurassique moyen d'Europe Occidentale.Patrick VignaudKeywords: middle Jurassic; nov. sp.; phylogenetic relationships; skulls; Steneosaurus pictaviensis; Systematics; thalattosuchian crocodileAbstract The study of all the available skulls allows us to review the systematic relationships of the longirostrine Steneosaurus from the Middle Jurassic of western Europe. Up to now, Aalenian and Bajocian deposits have not yielded any significant Steneosaurus remain. In the Bathonian, the only valid longirostrine species, S. megistorhynchus, is known in the Britain-Normandy Basin, the Poitou and the Lorraine. In the Callovian, most of the longirostrine Steneosaurus remains can be attributed to the species S. leedsi. Nevertheless, some remains from the Middle Callovian of Poitou (France) show important differences with S. leedsi. A new Steneosaurus species, only known in Poitou, is created and named S. pictaviensis. The specific characters are carried by the skull (preorbital pit well marked, orbit and ptetygoid fossae shapes), by the mandible (symphysis shape) and by the teeth (ornamentation). S. megistorhynchus is probably situated near the stem of the Callovian species but remains from the Bathonian and Lower Callovian are very scarce and it is very difficult to precise the phylogenetic relationships between the longirostrine species of the Middle Jurassic. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 1-2 (1998) |
|
|

|
La palichnofaune de vertébrés tétrapodes du permien supérieur du Bassin de Lodève (Languedoc-France).Georges Gand, Jacques Garric, Georges Demathieu and Paul EllenbergerKeywords: Footprints; France; Languedoc; Lodève basin; new ichnotypus; Saxonian; Upper PermianAbstract Near "la Lieude", in the Lodève basin, more than a thousand of footprints are distributed in a twenty of trackways which amounts to 220 m length. They have been found on calcareous siltstone level in the B site named also "Réserve Naturelle Volontaire". This last is located in the Saxonian summit dated Upper Permian. "La Lieude" tracks are described by using statistical methods then they are compared with others from the world Permian. What allows to distinguish 4 following ichnotaxa: Lunaepes ollierorum nov.ichnosp., Merifontichnus thalerius nov. ichnogen. and nov. ichnosp., Planipes brachydactylus nov.ichnosp. and Brontopus circagiganteus nov. ichnosp. All these traces are attributed with possibility or probability to Therapsida or to Therosauria, except Brontopus circagiganteus nov. ichnosp. that could be due to Caseamorpha. All these animals whose sizes have been estimated between l and 5 m lived probably in a playa environment.The biological and sedimentological data from "la Lieude" footprints levels compared with informations provided by the tracks orientations, suggest the following scenario. Animals coming from the North have crossed a sandy channel bank with plants zones by directing to the South for the majority. Maybe, they were going to the lacustrine part of the playa, close to "la Lieude" footprints that they have just trampled on. Article infos Published in Vol. 29, Fasc. 1 (2000) |
|
|
|
Muridae (Rodentia) du Pliocène supérieur d'Espagne et du midi de la France.Jacques MichauxKeywords: Anthracomys meini; Castillomys crusafonti; Pliocene; Rodents; Valerymys ellenbergeridoi: 10.18563/pv.3.1.1-25 Abstract The murid fauna of the terminal Pliocene of southwest Europe is rich in at least eight genera and ten species. With the species belonging to the genera Apodemus, Rhagapodemus, and Stephanomys not being studied here, the study of the other murids resulted for one thing in the description of three new genera and three new species: Castillomys crusafonti n. g., n. sp., Occitanomys brailloni n. g., n. sp., Anthracomys meini n. sp., Valerymys ellenbergerí (THALER) n. g., and for another thing in the recognition of a form hitherto unknown in this region, Micromys praeminutus KRETZOI. Systematic study has shown that certain species of the terminal Pliocene fauna had their ancestors in the Turolian fauna presently known in Spain. The evolutionary lineages thereby recognized have been studied more in detail and a list of the evolutionary tendencies of the dendal characters has been given. A chart of the probable phyletic relationships between the different murids of the Pliocene faunas of southwest Europe (With the genus Rhagapodemus and Apodemus dominans being excluded) is given in conclusion of this work. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 1 (1969) |
|
|
|
Les serpents des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Claude RageKeywords: Grande Coupure; Quercy Phosphorites; SerpentsAbstract A short review of the genera and species of snakes from the Quercy's phosphorites described by former authors is followed by the study of specimens recently collected. Most of these latter specimens belong to the Aniliidae, Boidae, Colubridae and to the Scolecophidia; the precise systematic position of some of them is not defined yet. The following genera and species are described: Eonilius europae nov. gen. and nov. sp., Platyspondylia lepta nov. gen. and nov. sp., Coluber cadurci nov. sp. and Dunnophis cadurcensis nov. sp.; a species described by de Rochebrune (Palaeopython filholi) is revised. One of the most important conclusions of this study is that the Colubridae appear as early as the Upper Eocene. The stratigraphic repartition of these snakes shows that the rich Upper Eocene fauna is followed by the very reduced fauna of the Lower Oligocene; then the oligocene «Grande Coupure» corresponds to a very important faunistic renewal. The fauna remains poor and little diversified during the beginning of the Middle Oligocene after which there is a new faunistic explosion. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
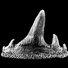
Designating a lectotype for Mesacanthus pusillus (Gnathostomata: Acanthodii)Matthew Baron and Kevin SeymourKeywords: acanthodians; Chordata; Devonian; Midland Valley; Orcadian Basindoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e2 Abstract The early gnathostome genus Mesacanthus is well represented in both Lower Old Red Sandstone and Middle Old Red Sandstone assemblages of northern and central Scotland. This ‘acanthodian’ taxon is currently thought to comprise two valid species: M. mitchelli and M. pusillus. Although the whereabouts of the holotype of M. mitchelli (NHMUK PV P560) is known, the syntype material for M. pusillus has long been thought lost. Here we identify at least one specimen that formed part of the original syntype material for M. pusillus, albeit in a slightly different condition than when it was originally figured. This specimen is ROM 25872, which is here designated as the lectotype. A second specimen – ELGNM 1978.191.1 – could represent another of the syntype specimens, but poor preservation quality makes it impossible to be certain. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
S.I. Data |

|
The new Algerian locality of Bir el Ater 3: validity of Libycosaurus algeriensis (Mammalia, Hippopotamoidea) and the age of the Nementcha FormationFabrice Lihoreau, Lionel Hautier and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Dispersal event; Miocene; North Africa; Tetralophodondoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e1 Abstract The description of original material of anthracothere and proboscidean in the new locality of Bir el Ater 3 from East Algeria, and a thorough review of early Libycosaurus remains of Bir el Ater 2 allows us validating L. algeriensis as the smallest and earliest species of Libycosaurus and probably the earliest migrant of the genus from Asia. The presence of a Tetralophodon in the Neogene Nementcha formation might represent the earliest occurrence of the genus in Africa. These original fossil remains allow us to discuss the age of the Neogene part of the Nementcha formation close to the Serravalian/Tortonian boundary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|

|
Avant-proposMarc Godinot and Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: D.E.RussellAbstract Le présent volume est l'aboutissement d'un projet né il y a presque cinq ans. En décembre 1991, l'un d'entre nous (MG) prenait des contacts en vue de proposer un symposium sur les mammifères fossiles, dédié à D.E. Russell, dans le programme du 4e Congrès de la European Society for Evolutionary Biology. Ce congrès, baptisé "Evolution 93", devait se tenir à Montpellier en août 1993. Son Comité d'Organisation, animé par F. Catzeflis, recherchait des organisateurs de symposiums. L'idée fut acceptée avec enthousiasme par le second d'entre nous (PDG), et le titre de notre Symposium fut précisé: " Palaeobiology and Evolution of Early Cenozoic Mammals - A Symposium in Honor of D.E. Russell". Le projet fut formellement accepté par le Comité d'Organisation en avril 1992. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Un nouveau genre de ?Palaeotheriidae (Perissodactyla, Mammalia) décelé dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Eocène supérieur ou Oligocène) d'après un arrière crâne sans dents.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: endocranial cast; Epitympanic sinus; Palaeotheriidae; Paléogène; Quercy Phosphorites; skull anatomyAbstract A rear skull from the Quercy Phosphorites is described. It documents a new perissodactyl genus, likely assignable to the family Palaeotheriidae and probably paleogene of age. Owing to the lack of any tooth, this family assignment remains however somewhat hypothetical. The specimen is firstly characterised by the presence of a wide epitympanic sinus swelling and hollowing the squamosal shell and the post-glenoid process. This cavity might make up a peculiar pattern of improvement for the hearing apparatus by carrying out a kind of drum near the middle ear, whereas the bony tympanic remains barely bulged and forms but a few developed auditory bulla. This pattern appears an outcome of a trend observed with many palaeotheriids, such as Plagiolophus. Furthermore, the endocranial cast shows a rather high degree of gyrencephaly for a paleogene mammal. The prominent lambdoidal crest points out a powerful nape musculature and a lowered head bearing. Consequently, it is assumed that such an animal was probably living in somewhat open places, at the expense of rather tough vegetables. It might have been accordingly provided with a semi-hypsodont, cement covered, "plagiolophoid" dentition. Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|
|
Mammals and stratigraphy : the Paleocene of EuropeDonald E. Russell, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Charles Pomerol, Sevket Sen, Norbert Schmidt-Kittler and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Europe; Mammalia; Mammalian biochronology; Paléogène; StratigraphyAbstract The mammalian faunas of the Paleogene of Europe and their localities are reviewed with comments on problems of European stratigraphy (epoch, stage and substage limits) and on the possibilities of faunal migrations. Radiometric dating is discussed. A stratigraphic scale for the Paleogene is presented, as well as a refined system of sequential faunal levels. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Ext (1982) |
|
|

|
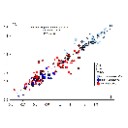
A new species of Propalaeotherium (Palaeotheriidae, Perissodactyla, Mammalia) from the Middle Eocene locality of Aumelas (Hérault, France).Jean-Albert Remy, Gabriel Krasovec and Bernard MarandatKeywords: Eocene; new species; Palaeotheriidae; Propalaeotheriumdoi: 10.18563/pv.40.2.e1 Abstract A new Propalaeotherium species, clearly distinct from the genus Eurohippus, is described. It is characterized by having a similar size as P. voigti from the German Geiseltal localities (MP 11 to MP 13 reference-level), but differs in several features suggesting a slighty more derived morphology. It presents indeed less brachyodont crowns with less prominent and less elevated cingula, slightly larger relative surface of premolars, and a more marked metaconid splitting on cheek teeth. This new species is unknown from other European localities except the nearby Saint-Martin de Londres locality which has been considered older than the MP 13 level. Article infos Published in Vol.40-2 (2016) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
Critical comments on the genus Propachynolophus Lemoine, 1891 (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Equoidea)
|
|
S.I. Data |
|
A survey of Cretaceous tribosphenic mammals from middle Asia (Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and Tajikistan), of their geological setting, age and faunal environmentLev A. Nessov, Denise Sigogneau-Russell and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Cretaceous; Environment; Middle Asia; Sharks; Tribosphenic mammalsAbstract This paper is an English concentrate of various Russian publications by the senior author presenting the mammaIian taxa from the Cretaceous (Albian through Santonian) of the region termed Middle Asia by Soviet geographers. The diagnoses are the unmodified, literal translation of the original version, but are followed with short complementary remarks; most of the species are illuslrated anew with SEM photographs, others are by normal photography. The fossiliferous formations are cited and arguments for their dating are given. Finally, the main vertebrate groups accompanying mammaIs are listed and the environment and climate at the time of deposition are suggested. In conclusion, an hypothesis on the origin and high diversity of tribosphenic mammals on the Cretaceous coastal plains of southwest Asia is proposed. In appendix the taxon Khuduklestes bohlini novo gen. novo sp. is formally defined. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
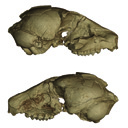
The digital endocast of Necrolemur antiquusArianna Harrington, Gabriel Yapuncich and Doug BoyerKeywords: brain evolution; Eocene; Omomyiforms; Primatesdoi: 10.18563/pv.43.2.e1 Abstract The study of endocasts, or casts of the endocranial space, have played an important role in shaping understanding of mammalian, and particularly primate, brain evolution. Recently, the reconstructions of three-dimensional virtual endocasts from high-resolution computed tomography images have allowed for the visualization and quantification of endocasts in several Paleocene and Eocene primate species. Here we present the virtual endocast of MaPhQ 289 (informally known as the Montauban 9 skull), a specimen of Necrolemur antiquus Filhol 1873, a middle to late Eocene European primate of the family Microchoeridae. The virtual endocast of MaPhQ 289 reveals a lissencephalic surface morphology with expanded temporal poles and minimal overlap of the cerebellum or olfactory bulb by the cerebrum, which closely resembles the morphology of the endocast of its contemporary relative, Microchoerus erinaceus (Primates, Microchoeridae). MaPhQ 289 yields an endocranial volume (ECV) of 2.36 cm3, about 60% smaller than the volume of the most commonly cited ECV of N. antiquus. Thus, the size of the brain of N. antiquus relative to its body size is likely to be smaller than has been reported in previous literature, highlighting the importance of corroborating older ECV estimates with new evidence using 3-D imaging techniques. Related dataset Article infos Published in 43-2 (2020) |
|
|
|
Mammifères nouveaux de l'Ilerdien des Corbières et du Minervois (Bas-Languedoc, France)Bernard MarandatKeywords: Bas-Languedoc; Early Eocene; France; Ilerdian; Mammals; New taxaAbstract Four new taxa (two genera, one subgenus, and four species) conceming the orders Condylarthra, Rodentia, Pantolesta, and an undetermined order from middle and middle/upper Ilerdian localities (lower Ypresian) of the Corbières and Minervois regions (Bas-Languedoc, Southem France) are presented in this short paper Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|

|
Les traces de pas d'amphibiens, de dinosaures et autres reptiles du Mesozoïque Français : inventaire et interprétations.Georges Gand, Georges Demathieu and Christian MontenatKeywords: Footprints; France; Inventory; Mesozoic; palaeontology; palaeovenvironments; Stratigraphydoi: 10.18563/pv.35.1-4.1-149 Abstract Since the 19th century, thousands of footprints were observed in the geological series of the French Mesozoic. All are located in the Triassic and Jurassic. After a promising beginning, in France, it is only a few papers which will be published in the first half 20th century, unlike the USA and of others countries of Western Europe. One ought to wait about 1950 for a revival and now they are nearly 200 papers which were devoted to the ichnofossils. The literature abundance and the renewed interest of the naturalists for the palichnologic studies decided to us to write a synthesis work. This one begins with a stratigraphic inventory in which, localisation, age and paleontological contents of about 180 fossiliferous sites are specified. After having pointed out the followed methods, the footprints paleontological interpretation is then approached in detail and the results obtained are replaced in stratigraphy to deduce the fauna evolution during the Mesozoic. So, it appears that Ichnologic data, more varied and rich in the Triassic and Liassic than those relating to the bones, very rare for the considered periods, are very informative. The middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian), thus reveals Cotylosauria, Lepidosauria, Crurotarsi with Rauisuchia, Ornithosuchidae, Crocodylia and Dinosauromorpha more the "Prodinosauria": Dinosamiforme whose skeletons are known in Argentina but only in Ladinian. The rather fast domination of Dinosaurs during Norian is also as well shown. The almost exclusive presence of their footprints, up to fifty cm long, in the Lower Hettangian indicates their supremacy in the environments. Footprints characterise not very deep life places located between inter-supratidal limits and often out of water. Sedimentologic and Palaeontologic studies showed that they were great coastal spaces during Middle Triassic, flood-plain with sebkhas while Upper Triassic, and a large !!coastal marsh!! in Grands-Causses during Liassic in which, mainly, fine stromatolithic layers were deposited. During the same periad, bay beaches spread in Vendée. During the Middle Jurassic, they are also brackish to lacustrine environments and recifallagoons in- the Upper Jurassic. Numerous measurements of the footprints and trackways directions showed that the animaIs moved there in weil defined directions, for long periods. They seem due to the palaeotopography of the life environments relatively stable. Also, the discovery of vegetal radicular networks and small footprints far away from the continental borderlands has suggested that the animals continuously lived in these palaeoenvironnements, belonging to large ecosystems, where the sedimentation rate was weak. This explains that thebadies could not fossilize there but only their footprints through the cyanobacterian action in main cases. From the vertical distribution of different ichnospecies, defined with adapted statistical methods, explained in this work, a palichnostratigraphy was established for the Middle Triassic. Although the footprints are also abundant in Hettango-Sinemurian of "Grands-Causses" and the Vendée, it was not possible, up to now, to establish any zonation in this series; Probably because the palichnofauna is too little diversified there, currently reduced to a majority of Theropods II-IV tridactyl traces. Article infos Published in Vol. 35, Fasc. 1-4 (2007) |
|