Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
A classic in the making : VERTEBRATE PALAEONTOLOGY (4th edition). By Michael J. Benton.Eric BuffetautKeywords: Book review; Vertebrate Palaeontologydoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e1 Abstract When the first edition of Mike Benton’s Vertebrate Palaeontology came out in 1990, sauropods still dragged their tails on the ground, the closest relatives of whales were mesonychids, and Mesozoic birds consisted essentially of Archaeopteryx, Ichthyornis and Hesperornis. Twenty-five years later, the book, now in its fourth edition, is a third longer, in a larger format and sports fine colour plates – in addition to a companion website. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
|

|
A new species of bat (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from the early Oligocene global cooling period, Brule Formation, North Dakota, USANicholas Czaplewski, Jeff Person, Clint Boyd and Robert EmryKeywords: Eocene-Oligocene global cooling; Mammalia; Oligocene; Plecotini; Quinetiadoi: 10.18563/pv.42.2.e2 Abstract We report the first confirmed fossil bats from North Dakota, including a new species referable to the Vespertilionidae represented by a maxilla with P4-M3 from the Brule Formation, Fitterer Ranch local fauna, early Oligocene, Whitneyan North American Land Mammal Age. Unassociated postcranial fragments of the humerus and femur also represent a vespertilionoid, but appear to reflect a different, unidentified species. The new taxon, Quinetia frigidaria sp. nov., is referred to the genus Quinetia, previously known only from approximately contemporaneous deposits in Europe. The new species is larger than Quinetia misonnei from the early Oligocene of Belgium. It is similar in some morphological characters to Chadronycteris rabenae (Chiroptera incertae sedis) of the late Eocene (Chadronian) of northwestern Nebraska and to Stehlinia species (?Palaeochiropterygidae) from the Eocene and Oligocene of Europe, but differs from each in morphological details of the dentition and maxilla. An unassociated talonid of a lower molar from Fitterer Ranch shows myotodont morphology, unlike the nyctalodont lower molars in Q. misonnei, and thus represents a second chiropteran taxon in the fauna. Quinetia frigidaria is a member of a Paleogene radiation of bats near the low point of the Eocene-early Oligocene decline in global temperatures, increased seasonal aridity, and loss of tropical floras from mid-latitude North America. Article infos Published in Vol 42-2 (2019) |
|
|
|
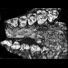
Un Haplobunodontidae nouveau Hallebune krumbegeli nov.gen. nov.sp. (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) dans l'Eocène moyen du Geiseltal près Halle (Sachsen-Anhalt, Allemagne)Jorg Erfurt and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Geiseltal; Germany; Mammal; Middle Eocene; new gen.; new sp.Abstract A new genus and species of haplobunodontid artiodactyl, Hallebune krumbiegeli nov. gen. nov. sp., is described from the middle Eocene Geiseltal Fauna (Saxon-Anhalt, Germany). Its stratigraphic range is restricted to the MP 13 ("obere Mittelkohle") of the Geiseltalian. The material consists of seven fragments, representing both upper and lower jaws. It is indicated, that H. krumbiegeli was a small bunodont herbivore. The size and primitive character of the teeth suggest that the genus possibly is directly derived from Diacodexeidae.The new material forms the basis for reinterpreting the haplobunodontid phylogeny. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
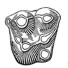
Une faune du niveau d'Egerkinger (MP 14; Bartonien inférieur) dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Sud de la France)Jean Sudre, Bernard Sigé, Jean-Albert Remy, Bernard Marandat, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Marc Godinot and Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Biochronology; Early Bartonian; Eocene; evolution; Mammals; New taxa; QuercyAbstract The Laprade fauna is chronologically situated between those from Egerkingen and Lissieu and consequently, is close to the MP 14 reference-level of the European mammalian biochronological scale (Symposium of Mainz, 1987). Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 1 (1990) |
|
|
|
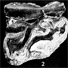
Prospection paléontologique de la région de Torralba de Ribota (Burdigalien du bassin de Calatayud, prov. de Zaragoza, Espagne)Edouard Boné, Maria T. Alberdi, Manuel Hoyos and Nieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Faunal assemblage; Macromammals; Spain; Zaragoza prov.Abstract The study of another faunal assemblage (mostly macromammals) from Torralba de Ribota (Calatayud, Zara- Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
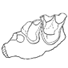
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 10 - Paléothérides (Perissodactyles).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract La poche à phosphorite de Sainte-Néboule (Lot) a livré au cours des récentes campagnes de fouilles effectuées dans le cadre de la Rep 311 une douzaine de dents ou fragments de dents de paléothéridés à rapporter à 3 taxons. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
Un nouveau chiroptère vespertilionide de l'Oligocène d'EuropeBernard Sigé and Henri MenuKeywords: bats; Europe; nov. sp.; Oligocene; VespertilionidAbstract A fossil species of the extant genus Leuconoe, L. lavocati n. sp. from Le Garouillas Oligocene locality, Quercy phosphorites, SW-France, is established in nomenclatural standards. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|
|
|
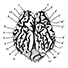
Etude paléoneurologique comparative de Parabos Cordieri (De Christol), un bovidae (Mammalia, Artiodactyla) du Pliocène d'Europe Occidentale.Catherine GromolardKeywords: Bovidae; endocranial cast; Europe; PlioceneAbstract A skull of Parabos cordieri, undamaged by fossilisation, allows us to make an endocranial cast, which is compared to those of Bos taurus, Boselaphus tragocamelus and Hippotragus equinus. These are studied by general form (shape, volume, « rolling-up›› and inclination), and by detailed morphology (gyri and sulci patterns, rete mirabile, importance of rhinencephalon and cerebellum). Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 2 (1982) |
|
|
|
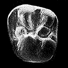
Middle Eocene rodents from the Subathu group, Northwest Himalya.Kishor Kumar, Rahul Srivastava and Ashok SahniKeywords: Chapattimyidae; Eocene; evolution; India; Rodentia; Subathu group; SystematicsAbstract Extensive collecting in previously known and new Middle Eocene rodent localities in the Subathu Group of the Rajauri and Reasi districts, Jammu and Kashmir (northwest Himalaya, India) has yielded over 500 isolated cheek teeth, numerous incisors and cheek tooth fragments, and two mandibular fragments with M/1-M/3. An analysis of this additional material and a restudy of that reported earlier from the Metka (Rajauri) area has revealed the presence of diverse Middle Eocene ctenodactyloid rodents in India. The assemblage comprises six genera and twelve species, viz.., Bírbalomys woodi, B. ibrahimshahi, B. sondaari, Basalomys vandermeuleni, B. ijlsti, B. lavocati, Chapattimys wilsoni, C. debruijni, Gumbatomys asifi, cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 1 and cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 2. Most species of this assemblage are endemic to the Indian subcontinent and are referred to the Family Chapattimyidae. However, at least three taxa, viz.., cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp.indet. 1 and cf. Pezrokoslovia sp. indet. 2 show close affinities with their Central and Eastern Asiatic contemporaries and are attributed to the Family Yuomyidae. The dentitions of most of the Middle Eocene rodents from India are described here in better detail thus providing more precise characterization than was available earlier. The taxonomie status of Basalomys, formerly a subgenus of Birbalomys has been raised to that of a genus. Basalomys vandermeuleni is here designated as the type species of Basalomys in place of B. ijlsti. The rodent assemblage from the Subathu Group is specifically similar to that from the coeval Kuldana Formation of Pakistan. The absence of Birbalomys ibrahimshahi and cf. Advenimus bohlini in Pakistan is related to sampling bias. The identifications of the Early Eocene rodents from Barbara Banda, Pakistan have been reexamined and the familial assignments of some of the Early and Middle Eocene rodents from Central and Eastern Asia have been discussed and reviewed in the light of recent discovery of early rodents in Mongolia. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
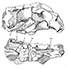
New material of “Eurysternidae” (Thalassochelydia, Pan-Cryptodira) from the Kimmeridgian of the Swiss Jura MountainsChristian Püntener, Jérémy Anquetin and Jean-Paul Billon-BruyatKeywords: Eurysternidae; Late Jurassic; morphology; Switzerland; Testudines; Thalassochelydiadoi: 10.18563/pv.43.1.e2 Abstract The region of Porrentruy (Swiss Jura Mountains) is known for its rich and diverse assemblage of Late Jurassic coastal marine turtles (Thalassochelydia). Dominated by the “Plesiochelyidae”, this assemblage also includes representatives of the two other thalassochelydian groups, the “Thalassemydidae” and “Eurysternidae.” In this study, we present new shell-based material from Porrentruy referable to eurysternids. One specimen represents a juvenile individual or a relatively small taxon, and is notably characterized by a well fenestrated plastron exhibiting a wider than long central plastral fontanelle. Two other specimens are much larger and possibly represent the largest eurysternids known to date. The fourth specimen is characterized by a unique plastral morphology otherwise only known in very small juveniles. This is the first time this unique plastral morphology is known to persist in an adult or subadult. The new material described herein represents at least three distinct taxa, all of them probably new. However, we refrain from naming new species based on this incomplete material in order to avoid adding confusion to an already complex taxonomical situation. This study provides new insights into the great diversity of eurysternids during the Late Jurassic. Article infos Published in Vol 43-1 (2020) |
|
|
|
Les rongeurs du site Pliocène à Hominidés de Hadar (Ethiope)Maurice SabatierKeywords: Ethiopia; hominids; Muridae; PlioceneAbstract The intensive exploration of the Pliocene Hadar Formation, rich in hominid remains, led us to the discovery of several micromammals levels. ln some of them, rodents are very abundant. The stratigraphic repartition of these levels do not cover the whole fossiliferous series of the formation but takes place only in the sedimentary members from Sidi Hakoma and Denen-Dora (rancing from 3.1 - 3.2 MY to 2.8 - 2.9 MY, according to the recent geochronological data). During this gap of time, the species do not show morphological changes, what allowed us to gather, in the same taxa, forms of slighty different ages. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 1 (1982) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. Avant propos.Bernard SigéKeywords: Editorial; Mammalia; Montredon; Upper MioceneAbstract Le Mémoire Extraordinaire 1988 de PALAEOVERTEBRATA regroupe dix articles consacrés au gisement à mammifères du Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault), connu et classique depuis la fin du siècle dernier, et auquel est lié le nom du savant paléontologue lyonnais Charles Depéret. View editorial Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
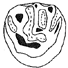
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 2 - les carnivoresGérard de BeaumontKeywords: anatomy; Carnivora; France; Montredon; Systematics; Upper MioceneAbstract The locality of Montredon has provided 8 species of camivores, often little documented, that are discribed and depicted. All the remains are fragmentary and generally badly preserved which lowers very much the possible precision of the taxonomic study; this one has however allowed the creation of a new subspecies. The most richlypdocumented forms are an ursid (Indarctos) and a felid (Machairodus). Issuing often from a westem Europe evolution, the carnivores are well inserted between those of the better known faunas of the "Classical Pontian" and of the lower Vallesian and this situation fits also well with their stratigraphic level, that cannot however be more accurately defined with them alone. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Nouvelles faunes de rongeurs de la fin Miocène inférieur en Provence. Implications géologiques et Paléogéographiques.Dominique LalaïKeywords: Biogeographic province; Biozonation; Correlation; Miocene; Palaeogeography; RodentiaAbstract Rodents from the new localities of Châteauredon (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence) and La Denise (Bouches-du-Rhône) show more similarities with the rodents known from the Czecho-Slovak locality of Franzenbad than with the species found in contemporaneous Lower Miocene faunas located westward of the present Rhône Valley. This is another data wich support the existance of several biogeographical provinces in Southern France during Lower Miocene. The correlations which have been settled down allow new datations of several formations in Provence and give new information on the Aquitanian and Burdigalian paleogeographies of this region. More precise stratigraphical allocations are given to some other localities of Central Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 2 (1986) |
|
|
|
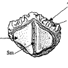
Révision des Rhombodontidae (Neoselachii Batomorphii) des bassins à phosphate du MarocAbdelmajid Noubhani and Henri CappettaKeywords: Batomorphii; Maastrichtian; Morocco; New taxa; Phosphate; RbombodontidaeAbstract The revision of the Rhombodontidae from the Maastrichtian of Morocco led us to the description of a new species: Rhombodus andriesi. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
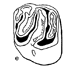
Pairomys et Ectropomys : la fin d'une ambiguïté ; mise au point sur les Oltinomyinae et Remyinae (Rodenia, Theridomyidae).Monique Vianey-Liaud, Norbert Schmidt-Kittler and Pablo Pelaez-CampomanesKeywords: PHYLOGENY; taxonomy; Theridomyidae; Upper EoceneAbstract The description of new material of the Upper Eoœne of France, Southem Germany and Spain together with the restudy of the material described by Thaler (1966b) as Pairomys allows to confirm the validity of the genus Ectropomys up to know controversally discussed. As a consequence the subfamily Remyinae and Oltinomyinae can be defined precisely. The study of the dental characters shows that the Remyinae in fact belong to the Theridomyidae and represent a derived evolutionary unit within this family. The Oltinomyinae together with the Theridomyinae and Issiodoromyinae very probably form a monophyletic unit. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
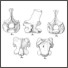
An unusual cranial fossil of the giant lower Pliocene shrew (Paranourosorex gigas Rzebik-Kowalska, 1975) from Podlesice, PolandDavid L. Harrison and Barbara Rzebik-KowalskaKeywords: Mammalia; Paranousorex gigas; Pliocene; Poland; Ruscinian; SoricidaeAbstract A well-preserved anterior cranium of Paranourosorex gigas RZEBIK-KOWALSKA, 1975 from Podlesice, Poland, provides additional knowledge of this rare shrew, including almost complete maxillary dentition. The systematic status of this species as a relative of recent Anourosorex MILNE- Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Fasc. 1-2 (1991) |
|
|
|
La poche à Phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien supérieur. 5-SquamatesJean-Claude RageKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The Squamates from Sainte-Néboule are charateristic of the Upper Eocene from the Phosphorites du Quercy. Most genera known from this locality do not survive the « Grande Coupure ». Cadurcoboa insolita gen. nov., sp. nov. is a small Boidae very characteristic of the Upper Eocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
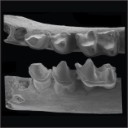
An evening bat (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from the late Early Eocene of France, with comments on the antiquity of modern batsSuzanne J. Hand, Bernard Sigé, Michael Archer and Karen H. BlackKeywords: evolution; palaeobiogeography; Prémontré; Western Europe; Ypresiandoi: 10.18563/pv.40.2.e2 Abstract Bats are among the most numerous and widespread mammals today, but their fossil record is comparatively meagre and their early evolution poorly understood. Here we describe a new fossil bat from dental remains recovered from late Early Eocene sediments at Prémontré, northern France. This 50 million-year-old bat exhibits a mosaic of plesiomorphic and apomorphic dental features, including the presence of three lower premolars, a single-rooted p3, short p4 with metaconid, myotodont lower molars and a tall coronoid process of the dentary. This combination of features suggests it is an early member of Vespertilionidae, today’s most speciose and geographically widespread bat family. The Prémontré bat has bearing on hypotheses about the origins of vesper or evening bats (Family Vespertilionidae), as well as crown-group chiropterans. Article infos Published in Vol.40-2 (2016) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères Montiens de Hainin (Paléocène moyen de Belgique) Part II : Les CondylarthresJean Sudre and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Belgium; Condylarths; Louisininae; Oxyclaeninae; PaleoceneAbstract The Condylarths from Hainin (Hainault, Belgium) show no affinity at the generic level to those known in other Paleocene localities of Europe and North America ; they are described as new forms : Monshyus praevius n. gen., n. sp. and Prolatidens waudruae n. gen., n. sp. Monshyus praevius, discovered in only one of the levels in the excavation at Hainin, is similar to the genera Microhyus TEILHARD and Louisina RUSSELL ; with them it is included in the subfamily Louisininae (Hyopsodontidae). With respect to Microhyus and Louisina, Monshyus is distinguished by the precociously modern aspect of its upper molars, the only teeth that are referable. Prolatidens waudruae, known only by lower molars, was found in several levels in the pit at Hainin. It is an arctocyonid presenting possible relationships to the North American form Oxyprimus galadrielae ; it therefore has been provisionally attributed to the subfamily Oxyclaeninae. If this attribution is confirmed, this species will constitute the first and only representative of the group in Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 6 (1982) |
|