Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
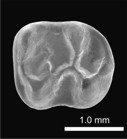
The beginning of the adaptive radiation of Theridomorpha (Rodentia) in Western Europe: morphological and phylogenetic analyses of early and middle Eocene taxa; implications for systematics
|
|
S.I. Data |
|
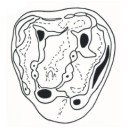
A new and primitive species of Protophiomys (Rodentia, Hystricognathi) from the late middle Eocene of Djebel el Kébar, Central TunisiaLaurent Marivaux, El M. Essid, Wissem Marzougui, Hayet Khayati Ammar, Sylvain Adnet, Bernard Marandat, Gilles Merzeraud, Rodolphe Tabuce and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Adaptive radiation; Bartonian; Dental morphology; North Africa; Paleobiogeographydoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e2 Abstract Based on fossil discoveries and phylogenetic studies, an Eocene Asian origin for hystricognathous rodents and anthropoid primates has gained strong support in recent years. The two groups then invaded both Africa and South America, which promoted their evolutionary success. However, the fossil record has so far failed to constrain the nature and precise timing of these pivotal dispersal events. In Africa, given the apparent absence of hystricognaths and anthropoids in early to early middle Eocene localities, it is suggested that these mammal groups dispersed from Asia to Africa sometime during the middle Eocene. In this paper, we report the discovery of several isolated teeth of a rodent from a new vertebrate locality situated in central Tunisia (Djebel el Kébar, KEB-1), dating from the late middle Eocene (Bartonian, ~39.5 Myr). These fossils document a diminutive new species of Protophiomys (P. tunisiensis nov. sp.), a basal genus of hystricognathous rodents which is well known from several North African mammalian-bearing localities of the end of the Eocene. The teeth of P. tunisiensis display a suite of anatomical details comparable with those observed in the other species of the genus, but with a lesser degree of development. Such an apparent primitive evolutionary stage is corroborated by the greater antiquity of this Tunisian species. P. tunisiensis nov. sp. is so far the most ancient representative of hystricognaths in Africa. However, it can be expected that hystricognaths were already present on that landmass given the new data on early caviomorphs recently reported from South America (at ~41 Myr). The arrival of hystricognaths in Africa from South Asia certainly predates the depositional period of the Kébar sediments, but perhaps not by much time. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|
|

|
La morphologie dentaire des Thalattosuchia (Crocodylia, Mesosuchia).Patrick VignaudKeywords: Dental morphology; Dental types; feeding habits.; Jurassic; Metriorhynchidae; Systematics; Teleosauridae; ThalattosuchiaAbstract The tooth morphology of the Thalattosuchia (marine crocodilians from the Jurassic and the Early Cretaceous) is analysed. The Callovian from Poitou and the Kimmeridgian from Quercy have yielded many remains of Metriorhynchus, Steneosaurus and Machimosaurus. These remains allow us to study the variations of tooth morphology during ontogenic growth, tooth replacement and the location of the teeth. We have defined different tooth types for these genera. In Metriorhynchus, the two tooth types defined do not coincide with the two groups recognized in the Callovian (broad-skulled and narrow-skulled metriorhynchids) but reflect the prey preferences of these forms. In Steneosaurus and Machimosaurus the five tooth types deñned are in agreement with the main taxa known from the Bathonian to the Early Cretaceous. This study allows to precise the function and the prey preference of the Thalattosuchia during the Jurassic and the Early Cretaceous. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|
|
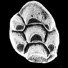
New murids and gerbillids (Rodentia, Mammalia) from Pliocene Siwalik sediments of India.Rajeev PatnaikKeywords: Dental morphology; evolution; new species of murids and gerbillids; phylogenetic relationships; SystematicsAbstract Murids and gerbillids (Rodentia, Mammalia) recovered from four Upper Siwalik localities; Moginand (around 3.5-4.5 m.y.), Kanthro (around 2.5 m.y.), Ghaggar (around 2 m.y.) and Nadah (around 1.8-2 m.y.) are described herein. A comparison of Mus linnaeusi sp. nov. reveals its close relationship towards the house mouse Mus musculus. In contradiction to earlier proposals that Golunda migrated to the Indian subcontinent from Africa sometime during Late Pliocene, it is suggested here that Golunda (in the form of Golunda tatroticus sp. nov.) evolved from Parapelomys robertsí of Late Miocene deposits of Siwaliks. Golunda tatroticus sp. nov. exhibits a progressive relationship to the extant Indian Bush Rat Golunda ellioti through Golunda kelleri and Golunda sp. Tatera pinjoricus sp. nov. is considered here to be a link between the extinct Abudhabia kabulense and the extant Tatera indica. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
Nouvelle quantification de l'Hypsodontie chez les Theridomyidae : l'exemple de Theridomys ludensis nov. sp.Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Dental morphology; evolution; Hypsodonty; Oligocene; TheridomyidaeAbstract A new example of parallelism in the dental pattern ofthe Theridomyidae is illustrated by the description ofa new species: Theridomys Iudensis from the standard level of Antoingt (middle Oligocene). Considering the occurence ofthis parallelism phenomenon. the use of numerous qualitative and quantitative criteria is essential to characterize the different stages ofthe different evolutive lineages. Thus, a new simple parameter is proposed (CHY = H+l/0,5 L) to estimate hypsodonty of the medium hypsodont Rodentia. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 3 (1985) |
|
|

|
Morphotypes dentaires actuels et fossiles des Chiroptères Vespertilioninés. 1e partie: Etude des morphologies dentairesHenri MenuKeywords: bats; Dental morphology; fossils; PHYLOGENY; recent; SystematicsAbstract The classifications of the recent vespertilionine bats were made wihtout taking in account the teeth morphology; this resulted in a reduction of the possibilities of comparison with the available fossils. The generalized use of dental formulae was abusive: this contributed to the admission of artificial genera. These conditions have long delayed the consideration of characters able to frame the phylogeny of the sub-family. In the first part of the study, the teeth morphologies are described and analysed. morphological reference types are established for each upper and lower tooth: they should make an easier elaboration of criteria for the differentiation at generic level. The position of the species in view of these criteria allows one to group them into homogeneous genera, and to appreciate the degree of relationship that the latter have between them. The second part of the study (next publicationà will develop inferences dealing with systematics and phylogeny Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 2 (1985) |
|
|
|
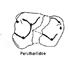
Perutherium altiplanense, un Notongulé du Cretacé Supérieur du PérouLarry G. Marshall, Christian de Muizon and Bernard SigéKeywords: Dental morphology; Late Cretaceous; Notoungulate; Paleobiogeography; PeruAbstract Perutherium altiplanerise THALER, 1967 from the Late Cretaceous of Peru has long been recognized as South America's oldest known placental mammal. Since its description Perutherium has been generally regarded as having condylarth affinity Based on our identification of a unique notoungulate synapomorphy we recognize Perutherium as the oldest and the most generalized known member of that order. This new determination and the large taxonomic diversity (five families) of notoungulates in rocks of Paleocene age in Argentina and Brazil, favor a South American origin for this group. The occurrence of notoungulates in rocks of Late Paleocene age in Asia and North America is explained by dispersal of a notoungulate stock from South America to North America and from there to Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 4 (1983) |
|
|

|
Essai de filiation des campagnols et des lemmings (Arvicolidae, Rodentia) en zone holartique d'après la morphologie dentaire.Jean ChalineKeywords: Arvicolidae; Dental morphology; Paleogeography; phyletic relationshipsAbstract The Arvicolid evolution results in an increase of the dental structure complexity. The M3/ differenciation seems to characterise the tribe subdivisions, that of M/1 being variable from one to another lineage. The phyletic relationships of fossil lineages are discussed from a paleogeographic point of view. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|