Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Henri Menu, 1925-2007Bernard SigéKeywords: bats; biographydoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.1-5 Abstract Record of life and works of Henri Menu, French zoologist, contributor to the knowledge of living and fossil bats. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
Eggshell microstructure and porosity of the Nicobar scrubfowl (Megapodius Nicobariensis, great Nicobar island, India)Géraldine Garcia, Ashu Khosla, Ashok Sahni and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: conductance porosity; eggshell microstructure; incubation conditions; Megapodesdoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.75-88 Abstract The eggshell of Nicobar scrubfowl (Megapodius nicobariensis) is described for the first time. Its egg porosity is calculated and discussed with data from several taxa (another megapode, some extant and fossil reptiles including a titanosaur group) in order to compare incubation types with eggshell structure. Eggshell microstructure reflects first phylogenetic traits and does not seem to have developed major adaptative features due to the incubation conditions, except for the pore canals. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 4 - Les chiroptèresBernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Hérault; Late Miocene; Micromammals; MontredonAbstract The Montredon local fauna yielded very rare bats, represented by damaged isolated teeth. Only a few documents are available for this period of the European Neogene. ln this poor state of knowledge, the material represents three undetermined species, a supposed molossid and two vespertilionids. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|
|
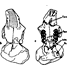
Les Pseudosciuridae (Mammalia, Rodentia) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller, Egerkingen et Lissieu.Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Bouxwiller; cranium; Egerkingen; Middle Eocene; Rodentsdoi: 10.18563/pv.3.2.27-64 Abstract The description of new material from three classic middle Eocene localities of western Europe permits the addition of details to the systematics of primitive Pseudosciurids. The cranial anatomy of Protadelomys cartieri (STEHLIN and SCHAUB) from Egerkingen is described here and compared to that of the Adelomyines from the late Eocene, until now the only ones known. The morphologic and biometric study of the dentition of P. cartieri compared to that of P. alsaticus n. sp. from Bouxwiller and P. Iugdunensis n. sp. from Lissieu, forms respectively older and younger than P. cartieri, permits the evolutionary tendencies of the group to be demonstrated and shows that notable differences in age exist between these localities. This ensemble of forms can constitute a valuable guide lineage in the establishment of a fine stratigraphy of the period. Other less well known lineages are present at Egerkingen along with P. cartieri. They can be related to genera that have been noted int he late Eocene. In conclusion, a criticism of recent zonation proposals, made by divers authors, completes this article. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 2 (1969) |
|
|
|
Rates of evolution in divergent species lineages as a test of character displacement in the fossil record : tooth size in Paleocene Plesiadapis (Mammalia, Proprimates)Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: character displacement; character divergence; fractal time series; Plesiadapis; Rates of evolutionAbstract Two species lineages of North American late Paleocene Plesiadapis exhibit a pattern of size divergence from a common ancestral lineage. Time series of fossils in each of these lineages are analyzed to test the idea that size divergence represents competitive character displacement. The critical factor in a test of character divergence is showing that divergent lineages evolved directionally rather than randomly (multifactorially). Analysis of evolutionary rates and their temporal scaling in Plesiadapis shows that both divergent species lineages have the scaling slope expected for lineages evolving randomly rather than directionally, and size divergence in Plesíadapis does not represent character displacement. Rates of evolution commonly observed on a per-generation time scale are high enough to produce character displacement within a few generations. Thus character displacement is not likely to be visible on scales of time that can be studied in the fossil record. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
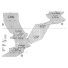
Middle Eocene rodents from the Subathu group, Northwest Himalya.Kishor Kumar, Rahul Srivastava and Ashok SahniKeywords: Chapattimyidae; Eocene; evolution; India; Rodentia; Subathu group; SystematicsAbstract Extensive collecting in previously known and new Middle Eocene rodent localities in the Subathu Group of the Rajauri and Reasi districts, Jammu and Kashmir (northwest Himalaya, India) has yielded over 500 isolated cheek teeth, numerous incisors and cheek tooth fragments, and two mandibular fragments with M/1-M/3. An analysis of this additional material and a restudy of that reported earlier from the Metka (Rajauri) area has revealed the presence of diverse Middle Eocene ctenodactyloid rodents in India. The assemblage comprises six genera and twelve species, viz.., Bírbalomys woodi, B. ibrahimshahi, B. sondaari, Basalomys vandermeuleni, B. ijlsti, B. lavocati, Chapattimys wilsoni, C. debruijni, Gumbatomys asifi, cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 1 and cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 2. Most species of this assemblage are endemic to the Indian subcontinent and are referred to the Family Chapattimyidae. However, at least three taxa, viz.., cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp.indet. 1 and cf. Pezrokoslovia sp. indet. 2 show close affinities with their Central and Eastern Asiatic contemporaries and are attributed to the Family Yuomyidae. The dentitions of most of the Middle Eocene rodents from India are described here in better detail thus providing more precise characterization than was available earlier. The taxonomie status of Basalomys, formerly a subgenus of Birbalomys has been raised to that of a genus. Basalomys vandermeuleni is here designated as the type species of Basalomys in place of B. ijlsti. The rodent assemblage from the Subathu Group is specifically similar to that from the coeval Kuldana Formation of Pakistan. The absence of Birbalomys ibrahimshahi and cf. Advenimus bohlini in Pakistan is related to sampling bias. The identifications of the Early Eocene rodents from Barbara Banda, Pakistan have been reexamined and the familial assignments of some of the Early and Middle Eocene rodents from Central and Eastern Asia have been discussed and reviewed in the light of recent discovery of early rodents in Mongolia. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères post-glaciaires de Corse. Etude Archéozoologique.Jacques MichauxKeywords: Book reviewAbstract Les mammifères post-glaciaires de Corse. Etude Archéozoologique, par Jean-Denis Vigne, 1988. XXVle suppléments à "Gallia Préhistoire". Editions du C.N.R.S., Paris, 337 p. FRF 300. ISSN 0072-0100, ISBN 2-222-04130-9. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|
|
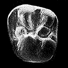
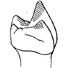
L'occlusion dentaire chez Peradectes, Amphiperatherium et Peratherium, Marsupiaux du tertiaire d'Europe.Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Didelphidae; Eocene; Mastication; Oligocene; Wear facetsAbstract The general principles guiding the study of wear facets which develop during mastication in mammals possessing tribosphenic molars are named. The application of this method of study to the molars of European Tertiary Didelphidae shows that the lineage of this family as represented by the species Peratherium cuvieri (Upper Eocene), P. elegans (Lower-middle Oligocene) and P. antiquum (Upper Oligocene) has propessively evolved toward a more carnivorous diet. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
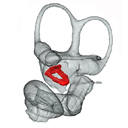
Fallen in a dead ear: intralabyrinthine preservation of stapes in fossil artiodactylsMaeva J. Orliac and Guillaume BilletKeywords: allometry; bony labyrinth; inner ear; middle ear ossiclesdoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e3 Abstract The stapes is the last of the middle ear ossicle chain and the smallest bone of the mammalian skeleton. Because it rests on the membrane of the fenestra vestibuli during life, the stapes may often fall within the bony labyrinth cavity when soft structures decay after death. In this work, we highlight the unexpected role that the bony labyrinth plays in the preservation of the stapes. Systematic investigation of the bony labyrinth of 50 petrosal bones of extinct and extant artiodactyls led to the discovery of eight cases of “intralabyrinthine” stapes. Three dimensional reconstructions of these stapes allow documenting stapes morphology of four extinct artiodactyl taxa: Microstonyx erymanthius (Suidae), Elomeryx borbonicus (Hippopotamoidea), ?Helohyus plicodon (Helohyidae), and an undetermined Cainotheriidae; and four extant ones Choeropsis and Hippopotamus (Hippopotamidae), and Tayassu and Phacochoerus (Suoidea). ?Helohyus plicodon from the Middle Eocene documents the oldest stapes known for the order Artiodactyla. Morphological study and metric analyses of our sample of artiodactylan stapes show that stapes are likely to carry relevant phylogenetic characters/signal within artiodactyls, and a potential Euungulata signature. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
S.I. Data |

|
Owls, caves and fossils. Predation, preservation and accumulation of small mammal bones in caves, with an analysis of the Pleistocene cave faunas from Westbury-Sub-Mendip, Somerset, UK, par Peter Andrews, 1990. The University of Chicago Press, 232 p.Christiane DenysKeywords: caves; owls; preservation; taphonomyAbstract La taphonomie (science de l'enfouissement et de la fossilisation) des micromammifères a trop souvent été négligée par rapport à celle des grands mammifères. Or, pour expliquer les concentrations parfois très importantes de microfossiles dans les grottes et les sites préhistoriques il faut connaître les mécanismes qui concourrent actuellement à favoriser les accumulations de ces derniers. C'est le but de l'ouvrage de Peter Andrews qui se décompose en deux parties. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|
|
|
Etude de la Variabilité chez Lophiodon lautricense NouletJean SudreKeywords: Cheek teeth; Eocene; Lophiodon; variabilitydoi: 10.18563/pv.4.3.67-95 Abstract The biometric and morphologie variability of the cheek teeth in the end-of-the-phylum species Lophiodon lautricense Noulet studied in this note, reposes on the observation of about 800 teeth. These were revealed to be little variable in absolute dimensions. The considerable morphologie variability in the upper premolars permitted the problem of the molarization process to be taken up. An hypothesis concerning the order of eruption of the cheek teeth is formulated based on an examination of a large number of milk dentitions. In conclusion, it is suggested that reservations be held on the value of dental characters classically used in systematics for the group under consideration. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 3 (1971) |
|
|
|
Le genre Leptolophus (Perissodactyla, Mammalia): morphologie et histologie dentaires, anatomie cranienne, implications fonctionnelles.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: dental histology; Eocene; functional anatomy; Palaeotheriidae; skull anatomy; Southern France; SystematicsAbstract A strong lophodonty, an extreme heterodonty, some hypsodonty and regular overlayings of coronal cement are prominent features of the genus Leptolophus (Palaeotheriinae = Palaeotheriidae s.s.). The histological pattern of the teeth unusually joins type II enamel prisms, characteristic of advanced ungulates, together with archaic features, such as an almost complete lack of Hunter-Schreger zonation and a weak expanse of peritubular dentine. The skull is narrow and slender, with an elongated ante-orbital facial region, a moderately notched nasal aperture, a rather elongated post-canine diastem, parallel zygornatic arches and a fairly dorsally located squamoso-mandibular joint.The functional analysis brings to light "ectolophodont" masticatory cycles with two phases, in which maximum power was applied, contrary to equíds, on hindmost teeth; likewise, skull accomodations to increasing height of the teeth are quite different. This study leads to the assumption that Leptolophus may have been light mammals, living in rather open surroundings, browsing on herbaceous plants or leaves cropped close to the ground. Moreover, it appears that it could have been some inadequacy of dental structures to the dietary, which leaded to quick wear of the teeth and to many enamel notches, but had been somewhat balanced by the early increase of hypsodonty, not induced in such a case by a biotop deterioration (as it will happen at the end of the Eocene). This ínadaptation might account for the short duration of the genus Leptolophus, whose the 3 species, L. stehlini, L. nouletí and L. magnus n. sp. are indeed confined in the level MP 16. Its geographical spreading (as far as known, South of western Europe) and the morphological pattern of its dentition suggest that this genus would have been related to early upper Eocene endemic spanish forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 1-2 (1998) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 4 - Les artiodactyles Suidae.Léonard GinsburgKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Mammalia; Montredon; Upper MioceneAbstract There is only one suid known in the Upper Miocene of Montredon (Hérault): Microstonyx (Limnostonyx nov. subgen.) antiquus (KAUP). It is differenciated from Microstonyx major by the presence of upper and lower canines which are considerably longer and biger. Its presence at Montredon corroborates the palustrine habitat for the species. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Avant propos au "Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II"Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Editorial; Type specimensAbstract Avant propos au "Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II". View editorial Published in Vol. 23, Ext (1994) |
|
|

|
Rongeurs caviomorphes de l'Oligocène de Bolivie. 1 Introduction au deseadien de BolivieRobert HoffstetterKeywords: Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract The Tertiary of the Salla-Luribay basin consists of red beds affected by the second period of the andine compression, of Miocene ending age. The Tertiary layers are exposed at an approximate elevation of 3.500 to 4.000 meters. Two stratigraphic units can be distinguished in them: the Luribay conglomerates, in which vertical clifts result from erosion, and the Salla layers consisting mostly of consolidated clays. These clays are very fossiliferous and have furnished a rich vertebrate fauna which gave to R. Hoffstetter the possibility to establish the Oligocene age of these beds. Sediments of same age has been reported to be present in several other places of Bolivia, particularly near Lacayani, where have been collected highly hypsodont Rodents, different from those found in Salla-Luribay basin. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 3 (1976) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien superieur. 14 - Conclusions généralesJean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Le matériel provenant de nouvelles fouilles dans les phosphorites du Quercy, soumis aux divers spécialistes, a conduit à la soutenance de plusieurs thèses d'état: sur les rongeurs (Hartenberger, Vianey-Liaud), les Chiroptères et Insectivores (Sigé), les Artiodactyles (Sudre), les Squamates (Rage) et, en partie, les Chéloniens (De Broin). Chacun dans son domaine, à côté des conclusions d'ordre évolutif, paléogéographique ou paléoécologique, a pu établir des successions stratigraphiques des gisements du Quercy qui se sont révélées largement concordantes. Ainsi la succession des faunes du Quercy est actuellement l'une des mieux établies. Dans ce contexte, les différents spécialistes ont décidé de conjuguer leurs efforts dans l'étude monographique de plusieurs gisements repérés le long de cette échelle, afin de rassembler l'information paléontologique sur des faunes bien précises et de tenter d'obtenir des indications d'ordre taphonomique. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
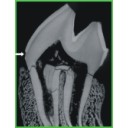
|
Enamel hypoplasia on rhinocerotoid teeth: Does CT-scan imaging detect the defects better than the naked eye?Manon Hullot and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: fossil teeth; method; micro-CT imaging; Rhinocerotoideadoi: 10.18563/pv.45.1.e2 Abstract Micro-CT imaging is an increasingly popular method in paleontology giving access to internal structures with a high resolution and without destroying precious specimens. However, its potential for the study of hypoplasia defects has only recently been investigated. Here, we propose a preliminary study to test whether hypoplastic defects can be detected with micro-CT (μCT) scan and we assess the costs and benefits of using this method instead of naked eye. To do so, we studied 13 fossil rhinocerotid teeth bearing hypoplasia from Béon 1 (late early Miocene, Southwestern France) as positive control and 11 teeth of the amynodontid Cadurcotherium (Oligocene, Phosphorites du Quercy, Southwestern France), for which enamel was partly or totally obscured by cement. We showed that all macroscopically-spotted defects were retrieved on 3D reconstructions and selected virtual slices. We also detected additional defects using μCT scan compared to naked eye identification. The number of defects detected using μCT was greater in the Cadurcotherium dataset (paired-sample Wilcoxon test, p-value = 0.02724) but not for our control sample (paired-sample Wilcoxon test, p-value = 0.1171). Moreover, it allowed for measuring width and depth of the defects on virtual slices (sometimes linked to stress duration and severity, respectively), which we could not do macroscopically. As μCT imaging is both expensive and time consuming while not drastically improving the results, we recommend a moderate and thoughtful use of this method for hypoplasia investigations, restricted for instance to teeth for which enamel surface is obscured (presence of cement, uncomplete preparation, or unerupted germs). Article infos Published in 45-1 (2022) |
|
S.I. Data |
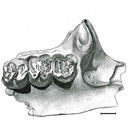
|
Les rongeurs de Chéry-Chartreuve et Rocourt-Saint-Martin (est du bassin de Paris; Aisne, France). Leur place parmi les faunes de l'Eocène Moyen d'EuropeBernard Comte, Maurice Sabatier and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Biochronology; evolution; Middle Eocene; Paris basin; Rodents; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.37.4-5.167-271 Abstract This paper is mainly devoted to the systematics of rodents from two middle Eocene (Bartonian) localities: Chéry-Chartreuve and Rocourt-Saint-Martin (Aisne, Eastern Paris Basin). These two localities are stratigraphically located slightly above the Auversian sands. The two faunas, which comprise 11 and 8 taxa, respectively, are very different in their composition. That of Rocourt-Saint-Martin shows strong similarities with that of the geographically very close locality of Grisolles, referred to the MP16 mammalian Reference level. The very distinct fauna of Chéry-Chartreuve includes a new species of Ailuravinae, Ailuravus nov.sp, and some teeth of the theridomyid Protadelomys, which represent archaic elements in the fauna. The most abundant species of the locality represents a new genus of primitive Theridomyidae. The presence of some teeth belonging to a new species of large Remyinae, Remys nov. sp., of Elfomys engesseri HOOKER & WEIDMANN, and a population of small dimensions referred to the genus Estellomys allow a correlation with Les Alleveys (Switzerland), with however some differences that would indicate an older age for Chéry-Chartreuve. Situated at the base of the "Marinesian" from the Bassin de Paris, this fauna is unquestionably different from those referred to the MP16 reference level and could represent an older level for which the macrofauna remains very poorly known. Conversely, the comparison of rodents from La Livinière II with those present in MP16 faunas, especially those of Robiac (Gard), shows a great similarity between both localities. This casts doubts on whether to keep this La Livinière II faunule to define the current MP15 reference level, while the biostratigraphical position of Pontils 26 (Spain), previously referred to this level, is reconsidered. Chery Chartreuse could be a good candidate for a new definition of the MP15 reference level. Article infos Published in Vol. 37, Fasc. 4-5 (2012) |
|
|

|
Morphotypes dentaires actuels et fossiles des Chiroptères Vespertilioninés. 1e partie: Etude des morphologies dentairesHenri MenuKeywords: bats; Dental morphology; fossils; PHYLOGENY; recent; SystematicsAbstract The classifications of the recent vespertilionine bats were made wihtout taking in account the teeth morphology; this resulted in a reduction of the possibilities of comparison with the available fossils. The generalized use of dental formulae was abusive: this contributed to the admission of artificial genera. These conditions have long delayed the consideration of characters able to frame the phylogeny of the sub-family. In the first part of the study, the teeth morphologies are described and analysed. morphological reference types are established for each upper and lower tooth: they should make an easier elaboration of criteria for the differentiation at generic level. The position of the species in view of these criteria allows one to group them into homogeneous genera, and to appreciate the degree of relationship that the latter have between them. The second part of the study (next publicationà will develop inferences dealing with systematics and phylogeny Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 2 (1985) |
|
|

|
The skull of Arsinoitherium (Mammalia, Embrithopoda) and the higher order interrelationships of ungulatesNicholas CourtKeywords: Arsinoitherium; PHYLOGENY; Skull; UngulateAbstract Detailed anatomical description of arsinoithere cranial remains from the Lower Oligocene, Fayum Depression, Egypt, provides the basic data for a systematic investigation. All cranial and some postcranial features are assessed from a phylogenetic standpoint. Several soft tissue characters are then added to a cladistic analysis based on 54 derived ungulate morphological characters. The resulting phylogenetic hypothesis implies that perissodactyls, sirenians, proboscideans and arsinoitheres constitute a monophyletic unit (5 synapomorphies). However, increasing the tree length by 3 steps reveals a closer association between hyraxes and perissodactyls. Nevertheless, 13 synapomorphies link proboscideans, sirenians and arsinoitheres to the exclusion of all other ungulates. Form of the sphenopalatine and ethmoid foramina, recurved posttympanic process, absence of a fenestra rotundum in the petrosal, vestigial paroccipital process of the exoccipital and the highly unusual absence of a hypoglossal foramen in the skull, imply a robust sister-group relationship between arsinoitheres and proboscideans. In this analysis artiodactyls share only one derived character with all other ungulates studied. Monophyly of Ungulata, including Artiodactyla, is therefore only weakly supported. It is argued that pedal anatomy of hyraxes is non-homologous with that of Tethytheria. Arsinoitherium should now be classified within Tethytheria, sharing a sister-group relationship with Proboscidea. Hyraxes are excluded, thus refuting the concept of Paenungulata. However, monophyly of the wider concept, Pantomesaxonia, containing hyraxes, perissodactyls, sirenians, proboscideans and now, arsinoitheres, is supported by this study. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|