Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Henri Menu, 1925-2007Bernard SigéKeywords: bats; biographydoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.1-5 Abstract Record of life and works of Henri Menu, French zoologist, contributor to the knowledge of living and fossil bats. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 2- Les rongeursJean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Hérault; Late Miocene; Micromammals; Montredon; RodentsAbstract The recent excavation of the Upper Miocene locality of Montredon (Hérault) provides a rich material of Mammals. The present study deals with rodents. The new quarry is 10 meters above the classical Depéret's Quarry. No differences have been noticed between the rodent populations coming grom these two sites. The description of two new species : Hispanomys mediterraneus and Muscardinus heintzi is given and the dormouse Eliomys is recorded there for the first time. The new zonation of the Miocene given by Aguilar (1982) and the previously established correlations between marine and continental chronological scales give Tortonien age (estimated between 9 and 10 M.Y. old) to the site of Montredon, which belongs to the Mammal zone D 2. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères Montiens de Hainin (Paléocène moyen de Belgique) Part II : Les CondylarthresJean Sudre and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Belgium; Condylarths; Louisininae; Oxyclaeninae; PaleoceneAbstract The Condylarths from Hainin (Hainault, Belgium) show no affinity at the generic level to those known in other Paleocene localities of Europe and North America ; they are described as new forms : Monshyus praevius n. gen., n. sp. and Prolatidens waudruae n. gen., n. sp. Monshyus praevius, discovered in only one of the levels in the excavation at Hainin, is similar to the genera Microhyus TEILHARD and Louisina RUSSELL ; with them it is included in the subfamily Louisininae (Hyopsodontidae). With respect to Microhyus and Louisina, Monshyus is distinguished by the precociously modern aspect of its upper molars, the only teeth that are referable. Prolatidens waudruae, known only by lower molars, was found in several levels in the pit at Hainin. It is an arctocyonid presenting possible relationships to the North American form Oxyprimus galadrielae ; it therefore has been provisionally attributed to the subfamily Oxyclaeninae. If this attribution is confirmed, this species will constitute the first and only representative of the group in Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 6 (1982) |
|
|
|
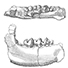
Les mammifères de Rians (Eocène inférieur, Provence)Marc GodinotKeywords: Eocene; Mammals; Provence; RiansAbstract The fossil mammals discovered in the quarry of Rians (Sparnacian, Provence) are described. Among these forms, Hyracotherium is interesting because of the little molarization of the lower premolars and its small size, and Diacodexis by its small size and very primitive astragalus ; they may be the most primitive representatives of their respective orders. Also, Proviverra eisenmanni n. sp. is the smallest and most primitive hyaenodontid yet described. Hyopsodus itinerans is the first species of this genus described France. Among other rare fossils is a new species of bat, a small palaeoryctid, and other forms not yet identified. Marsupials are varied. Several new species are present among the rodents. The fauna is well-balanced and rich in small hyopsodontid condylarths. It is stratigraphically situated at the Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 2 (1981) |
|
|

|
Une nouvelle espèce d'Hipparion du Miocène terminal d'Espagne.Miquel Crusafont i Pairó and P. SondaarKeywords: Hipparion; Late Miocene; Spain; Villafranchiandoi: 10.18563/pv.4.2.59-66 Abstract The recently discovered, very rich, Pliocene locality of Layna (Soria, Spain), has already yielded 30 species of mammals. Hipparion fissurae, described here is more dolichopodic than other Hipparion. It is related to Hipparion crusafonti from Villaroya (Villafranchian), but more slender between other characters. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 2 (1971) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 4 - Les artiodactyles Suidae.Léonard GinsburgKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Mammalia; Montredon; Upper MioceneAbstract There is only one suid known in the Upper Miocene of Montredon (Hérault): Microstonyx (Limnostonyx nov. subgen.) antiquus (KAUP). It is differenciated from Microstonyx major by the presence of upper and lower canines which are considerably longer and biger. Its presence at Montredon corroborates the palustrine habitat for the species. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude de l'anatomie crânienne des rongeurs. 1- Principaux types de cricétodontinésJean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Cricetodon; Cricetodontinae; Miocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.1.2.47-64 Abstract Description, for the first time, of the skull of Ruscinomys Depéret on the basis of a nearly complete specimen, and description of a new facial part of a Megacricetodon Fahlbusch skull (material from upper Miocene, Spain). New description of the skull (facial part) of " Cricetodon" incertum Schlosser on the basis of the specimen from the Oligocene of Quercy phosphorites already published by S. Schaub. Article infos Published in Vol. 01, Fasc. 2 (1967) |
|
|

|
Les Bovidae (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) du Miocène moyen de la formation Hofuf (Province du Hasa, Arabie Saoudite).Herbert ThomasKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Bovidae; Middle Miocene; Palaeogeography; Saudi ArabiaAbstract The study of the bovids from Al Jadidah (Hofuf Formation, Saudi Arabia) confirms that the fauna comes from a pre-Hipparion level. The Al Jadidah age is close to that of Fort Ternan (14 m.y.) and Beni Mellal, but cannot be older than that of Fort Ternan. The age of the Hofuf Formation is close to but slightly older than the oldest deposits of the Ngorora Formation (Kenya). 7 to 9 species have been recorded, of which 2 to 4 remain indeterminate. If the great specific diversity of te bovids from this locality gives evidence of immigrations from anterior Asia (Turkey) (e.g. Pachytragus Iigabuei sp. nov.), the bovid assemblage of Al Jadidah results in fact from a double influence: from the anterior Asia and mainly from Africa (e.g. the Caprotragoides lineage and the Neotragini? Homoiodorcas). The Al Jadidah bovids reflect, on the whole, the predominant character of open to very open environment, which supports the conclusions drawn from our two preliminary studies. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 5 (1983) |
|
|

|
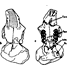
Eléments nouveaux sur l'évolution des genres Eucricetodon et Pseudocricetodon (Eucricetodontinae, Rodentia,Mammalia, de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Bernard ComteKeywords: evolution; Occidental Europe; Oligocene; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract The review of material recently collected in the new localities from the “Phosphorites du Quercy", and different localities from the South of France, bring new informations on the genus Eucricetodon THALER. 1966, and Pseudocricetodon THALER, I969 (Middle and Upper Oligocene. Western Europe). Thanks to Eucricetodon huerzeleri VIANEY-LIAUD, 1972, which were unsufficiently known until now, is proposed. During the middle Oligocene Eucricetodon atavus MISONNE, 1957 seems to give rise to two lineages. One of them led to Eucricetodon huberi,which however exhibits a larger size and a development of progressive characters on the teeth. The other would be Eucricetodon huerzeleri well differentiated at the “Mas de Pauffié" standard level (beginning of the upper Oligocene). The ornementation of lower incisors is described, when possible. Though the fossils are not abundant, it seems that the ancestral lineage, Eucriretodon atavus, remains in the upper Oligocene (Boningen standard level). evolving into Eucricetodon praecursor SCHAUB, 1925 (Rickenbach standard level). The characters of Eucricetodon dubius (SCHAUB. 1925), represented by a numerous population in Pech Desse and Pech du Fraysse (Quercy). confirm that this species and Eucricetodon praecursor belong to two different lineages. As Eucricetodon dubius shows more primitive features, this species could not originale from Eucricetodon atavus -Eucricetodon huberi. The appearance of this species at the level of Mas de Pauffié could be the result of an immigration. A new definition of Pseudocricetodon incertus (SCHLOSSER. 1884) is given. This species has been found in several localities, where it had not been identified until now. lts comparison with Pseudocricetodon moguntiacus (BAHLO. l975), found at several localities from the standard level of Antoingt (end of middle Oligocene). shows a parallel evolution to that of Pseudocetodon incertus, which is of larger size and with a less complicated pattern of teeth. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 1 (1985) |
|
|
|
Les Pseudosciuridae (Mammalia, Rodentia) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller, Egerkingen et Lissieu.Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Bouxwiller; cranium; Egerkingen; Middle Eocene; Rodentsdoi: 10.18563/pv.3.2.27-64 Abstract The description of new material from three classic middle Eocene localities of western Europe permits the addition of details to the systematics of primitive Pseudosciurids. The cranial anatomy of Protadelomys cartieri (STEHLIN and SCHAUB) from Egerkingen is described here and compared to that of the Adelomyines from the late Eocene, until now the only ones known. The morphologic and biometric study of the dentition of P. cartieri compared to that of P. alsaticus n. sp. from Bouxwiller and P. Iugdunensis n. sp. from Lissieu, forms respectively older and younger than P. cartieri, permits the evolutionary tendencies of the group to be demonstrated and shows that notable differences in age exist between these localities. This ensemble of forms can constitute a valuable guide lineage in the establishment of a fine stratigraphy of the period. Other less well known lineages are present at Egerkingen along with P. cartieri. They can be related to genera that have been noted int he late Eocene. In conclusion, a criticism of recent zonation proposals, made by divers authors, completes this article. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 2 (1969) |
|
|
|
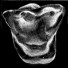
Decouverte d'un nouveau Diacodexis (Artiocactyla, Mammalia) dans l'Eocène inférieur de Silveirinha, Portugal.Carmen Estravis and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Artiodactyla; Eocene; Migration; Portugal; SilveirinhaAbstract A new artiodactyl, Diacodexis antunesi n.sp., is described from the early Eocene of Silveirinha, Portugal. Comparisons are made with Diacodexis gazini GODINOT, 1978, D. varleti SUDRE et al., 1983, D. cf. varleti from Paris Basin sites, D. sp. from Dormaal and from localities in Spain and England, D. secans from North America and D. pakistanensis from Asia; affinities and evolutive tendencies are discussed. The presence of Diacodexis in the locality of Silveirinha confirms the very early Eocene age of the latter. As Diacodexis antunesi appears ta be more primitive than D. gazini from Rians (early Eocene of France), it lends corroboration to the interpretation (essentially based previously on condylarths) of the Silveirinha assemblage as the oldest Eocene fauna known in Europe and supports the hypothesis that early artiodactyls migrated from Europe to North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|

|
THE ANIMALS Systematische ZoologieLeigh M. Van ValenKeywords: Book review; SystematicsAbstract Systematische Zoologie by A. REMANE, V. STORCH, and U. WELSCH. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
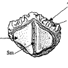
Révision des Rhombodontidae (Neoselachii Batomorphii) des bassins à phosphate du MarocAbdelmajid Noubhani and Henri CappettaKeywords: Batomorphii; Maastrichtian; Morocco; New taxa; Phosphate; RbombodontidaeAbstract The revision of the Rhombodontidae from the Maastrichtian of Morocco led us to the description of a new species: Rhombodus andriesi. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
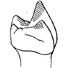
Les rongeurs de l'Eocène d'Afrique Nord-Occidentale [Glib Zegdou ( Algérie) et Chambi (Tunisie)] et l'origine des anomaluridae.Monique Vianey-Liaud, Jean-Jacques Jaeger, Jean-Louis Hartenberger and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Africa; Eocene; New taxa; Paleobiogeography; PHYLOGENY; RodentsAbstract This paper is about the oldest African rodents faunas, from the late Early Eocene, or early Middle Eocene, Glib Zegdou (Algeria) and Chambi (Tunisia) localities. Five species are described and figured, belonging to a new family here created, the Zegdoumyidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
L'occlusion dentaire chez Peradectes, Amphiperatherium et Peratherium, Marsupiaux du tertiaire d'Europe.Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Didelphidae; Eocene; Mastication; Oligocene; Wear facetsAbstract The general principles guiding the study of wear facets which develop during mastication in mammals possessing tribosphenic molars are named. The application of this method of study to the molars of European Tertiary Didelphidae shows that the lineage of this family as represented by the species Peratherium cuvieri (Upper Eocene), P. elegans (Lower-middle Oligocene) and P. antiquum (Upper Oligocene) has propessively evolved toward a more carnivorous diet. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
La Poche à phosphate de Ste-Neboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. 3- ChéloniensFrance de BroinKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The few remains recently collected at Ste Néboule (upper Eocene) belong to three genera: the Testudinid Ergilemys, of which it is the oldest occurence in Western Europa, probably Palaeochelys and an unpublished genus, which is peculiar to the Phosphorites du Quercy. Some statements are made on the chelonian fauna as a whole in that région. After the study of some characters proper to the genus Ergilemys, some remarks are made concerning its antecedents and descendants. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
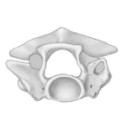
Latest Early-early Middle Eocene deposits of Algeria (Glib Zegdou, HGL50), yield the richest and most diverse fauna of amphibians and squamate reptiles from the Palaeogene of AfricaJean-Claude Rage, Mohamed Adaci, Mustapha Bensalah, Mahammed Mahboubi, Laurent Marivaux, Fateh Mebrouk and Rodolphe TabuceKeywords: Africa; Algeria; amphibians; Eocene; squamatesdoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e1 Abstract HGL50 is a latest Early-early Middle Eocene vertebrate-bearing locality located in Western Algeria. It has produced the richest and most diverse fauna of amphibians and squamate reptiles reported from the Palaeogene of Africa. Moreover, it is one of the rare faunas including amphibians and squamates known from the period of isolation of Africa. The assemblage comprises 17 to 20 taxa (one gymnophionan, one probable caudate, three to six anurans, seven ‘lizards’, and five snakes). Two new taxa were recovered: the anuran Rocekophryne ornata gen. et sp. nov. and the snake Afrotortrix draaensis gen. et sp. nov. The locality has also yielded the first confirmed anilioid snake, the first Palaeogene gymnophionan, and probably the first caudate from the Palaeogene (and possibly from the Tertiary) of Africa. The presence of a caudate at that time in Africa would be of particular interest; unfortunately, the available material does not permit a definitive identification. The fauna comprises Gondwanan and more specifically West Gondwanan vicariants, probably autochthonous groups and a Eurasian immigrant (assuming that the identification of the caudate is accurate). The fauna from HGL50 is clearly distinguished from the few other Eocene assemblages of Africa. However, if this results largely from differences in geological ages, geographic positions of the localities and mainly differences in environments took a part in the composition of the faunas. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
|

|
Pseudorhyncocyon cayluxi Filhol, 1892 insectivore géant des phosphorites du QuercyBernard SigéKeywords: Insectivores; Leptictidae; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Une hémimandibule et une molaire supérieure recueillies dans le gisement oligocène inférieur d'Escamps (phosphorites du Quercy) fournissent de nouvelles informations sur le genre Pseudorhyncocyon FllHOL, grand insectivore longirostre du Paléogène d'Europe, fossile très mal connu jusqu'ici. Des comparaisons avec les macroscélididés africains, géolabididés nord-américains, et leptictidés euraméricains permettent de rattacher cet amimal aux leptictidés, et de le rapprocher du genre Lepticidium TOBIEN, au sein de la sous-famille européenne nouvelle des pseudorhyncocyoninés. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|
|
Le genre Leptolophus (Perissodactyla, Mammalia): morphologie et histologie dentaires, anatomie cranienne, implications fonctionnelles.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: dental histology; Eocene; functional anatomy; Palaeotheriidae; skull anatomy; Southern France; SystematicsAbstract A strong lophodonty, an extreme heterodonty, some hypsodonty and regular overlayings of coronal cement are prominent features of the genus Leptolophus (Palaeotheriinae = Palaeotheriidae s.s.). The histological pattern of the teeth unusually joins type II enamel prisms, characteristic of advanced ungulates, together with archaic features, such as an almost complete lack of Hunter-Schreger zonation and a weak expanse of peritubular dentine. The skull is narrow and slender, with an elongated ante-orbital facial region, a moderately notched nasal aperture, a rather elongated post-canine diastem, parallel zygornatic arches and a fairly dorsally located squamoso-mandibular joint.The functional analysis brings to light "ectolophodont" masticatory cycles with two phases, in which maximum power was applied, contrary to equíds, on hindmost teeth; likewise, skull accomodations to increasing height of the teeth are quite different. This study leads to the assumption that Leptolophus may have been light mammals, living in rather open surroundings, browsing on herbaceous plants or leaves cropped close to the ground. Moreover, it appears that it could have been some inadequacy of dental structures to the dietary, which leaded to quick wear of the teeth and to many enamel notches, but had been somewhat balanced by the early increase of hypsodonty, not induced in such a case by a biotop deterioration (as it will happen at the end of the Eocene). This ínadaptation might account for the short duration of the genus Leptolophus, whose the 3 species, L. stehlini, L. nouletí and L. magnus n. sp. are indeed confined in the level MP 16. Its geographical spreading (as far as known, South of western Europe) and the morphological pattern of its dentition suggest that this genus would have been related to early upper Eocene endemic spanish forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 1-2 (1998) |
|
|

|
Owls, caves and fossils. Predation, preservation and accumulation of small mammal bones in caves, with an analysis of the Pleistocene cave faunas from Westbury-Sub-Mendip, Somerset, UK, par Peter Andrews, 1990. The University of Chicago Press, 232 p.Christiane DenysKeywords: caves; owls; preservation; taphonomyAbstract La taphonomie (science de l'enfouissement et de la fossilisation) des micromammifères a trop souvent été négligée par rapport à celle des grands mammifères. Or, pour expliquer les concentrations parfois très importantes de microfossiles dans les grottes et les sites préhistoriques il faut connaître les mécanismes qui concourrent actuellement à favoriser les accumulations de ces derniers. C'est le but de l'ouvrage de Peter Andrews qui se décompose en deux parties. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|