Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Eggshell microstructure and porosity of the Nicobar scrubfowl (Megapodius Nicobariensis, great Nicobar island, India)Géraldine Garcia, Ashu Khosla, Ashok Sahni and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: conductance porosity; eggshell microstructure; incubation conditions; Megapodesdoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.75-88 Abstract The eggshell of Nicobar scrubfowl (Megapodius nicobariensis) is described for the first time. Its egg porosity is calculated and discussed with data from several taxa (another megapode, some extant and fossil reptiles including a titanosaur group) in order to compare incubation types with eggshell structure. Eggshell microstructure reflects first phylogenetic traits and does not seem to have developed major adaptative features due to the incubation conditions, except for the pore canals. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 3- Les insectivoresJean-Yves Crochet and Morton GreenKeywords: Hérault; Insectivora; Late Miocene; Micromammals; MontredonAbstract This paper presents a preliminary list of insectivores from the Vallesian beds at Montredon (France). The associated rodent fauna has established a Vallesian age for the fauna. Eleven species belonging to the Soricidae, Talpidae, Erinaceidae, and Dimylidae are identified of which four only are referred with certainty to forms already named. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|
|
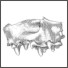
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 8- Insectivores et Chiroptères.Bernard SigéKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The small insectivorous placental mammals from Ste-Néboule are poorly varied. Two orders of insectivores are documented : the Proteutheria by Pseudorhyncocyon cayluxi (leptictids), the Lipotyphla by Saturninia gracilis and S. beata (nyctitheriids). The bats are only rhinolophoids and mostly hipposiderids. Sufficient populations allow us to restrict the original definitions of three previous species (Hipposideros schlosseri, Palaeophyllophora quercyi, P. oltina). From now, these species can be regarded as monophyletíc. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
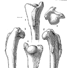
Données nouvelles sur le genre Stehlinia (Vespertilionoidea, Chiroptera) du Paléocène d'EuropeBernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Palaeocene; VespertilionoideaAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
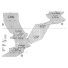
The microfauna of the Djebel Qafze CaveG. HaasKeywords: Micromammals; RodentsAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|
|
Rates of evolution in divergent species lineages as a test of character displacement in the fossil record : tooth size in Paleocene Plesiadapis (Mammalia, Proprimates)Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: character displacement; character divergence; fractal time series; Plesiadapis; Rates of evolutionAbstract Two species lineages of North American late Paleocene Plesiadapis exhibit a pattern of size divergence from a common ancestral lineage. Time series of fossils in each of these lineages are analyzed to test the idea that size divergence represents competitive character displacement. The critical factor in a test of character divergence is showing that divergent lineages evolved directionally rather than randomly (multifactorially). Analysis of evolutionary rates and their temporal scaling in Plesiadapis shows that both divergent species lineages have the scaling slope expected for lineages evolving randomly rather than directionally, and size divergence in Plesíadapis does not represent character displacement. Rates of evolution commonly observed on a per-generation time scale are high enough to produce character displacement within a few generations. Thus character displacement is not likely to be visible on scales of time that can be studied in the fossil record. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
EditorialHenri CappettaKeywords: EditorialAbstract Editorial for celebrating the publication of the volume 20. View editorial Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 4 (1991) |
|
|
|
D'important restes de Diplobune minor FILHOL à Itardies (Quercy)Jean SudreKeywords: Diplobune; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
Essai de filiation des campagnols et des lemmings (Arvicolidae, Rodentia) en zone holartique d'après la morphologie dentaire.Jean ChalineKeywords: Arvicolidae; Dental morphology; Paleogeography; phyletic relationshipsAbstract The Arvicolid evolution results in an increase of the dental structure complexity. The M3/ differenciation seems to characterise the tribe subdivisions, that of M/1 being variable from one to another lineage. The phyletic relationships of fossil lineages are discussed from a paleogeographic point of view. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Sainte-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébrés du Ludien supérieur. 13-RongeursJean-Louis Hartenberger and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Sainte-Néboule has yielded only 4 species of Rodents. But the Theridomyids (Blainvillimys rotundidens and Patriotheridomys altus) are very significative of the age of the locality: Ste-Néboule is lower than the marker level of Escamps Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Sur le statut taxonomique de Myotis KAUP 1829 (Mammalia, Chiroptera).Henri MenuKeywords: Myotis; taxonomyAbstract Suite à la récente publication d'une révision systématique des Chiroptera Vespertilioninae, conduite sur la base des morphologies dentaires comparées (Menu 1987), une remarque bienveillante du Dr. V. Aellen (Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Genève) a attiré l'attention de l'auteur sur un point précis du Code International de Nomenclature Zoologique. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 4 (1988) |
|
|
|
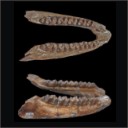
A mandible of the hyracoid mammal Titanohyrax andrewsi in the collections of the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris (France) with a reassessment of the speciesRodolphe TabuceKeywords: Afro-Arabia; Fayum; Oligocene; Titanohyracidaedoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e4 Abstract An unpublished mandible of the large hyracoid Titanohyrax andrewsi from the early Oligocene Jebel Qatrani Formation, Fayum Depression, Egypt is described. This specimen has a twofold importance. Firstly, it opens an unexpected window on early paleontological research in the Fayum because it was discovered as early as 1904 by the French paleontologist René Fourtau during an expedition to the Fayum organized by the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris (MNHN). This expedition has remarkably never been mentioned in the literature. Secondly, the mandible documents the best-preserved specimen of T. andrewsi, permitting a revision of one of the very rare Paleogene hyracoids. Interestingly, the new mandible was discovered two years before the first report of the species by Charles W. Andrews. The hypodigm of T. andrewsi is reviewed and the dentition as a whole is compared in detail, notably with other Titanohyrax species from the Fayum. The validity of the large Titanohyrax “schlosseri” species is discussed, but a pronounced sexual size dimorphism for T. andrewsi is favoured. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
|

|
Handbuch der Paläeoherpetologie Teil 11: SerpentesJacques MichauxKeywords: Book reviewAbstract Le volume 11 du «Handbuch der Paläeoherpetologie», consacré aux «Serpellles» et redigé par Jean-Claude Rage, apporte une remarquable information sur ce groupe particulier de reptiles dont on ne pouvait guere se faire une idée très précise à partir, par exemple, des seuls chapitres des traités classiques de Paléontologie et de Zoologie. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 3 (1984) |
|
|

|
Arvicolinae (Rodentia) du Pliocène terminal et du quaternaire ancien de France et d'Espagne.Jacques MichauxKeywords: Arvicolinae; France; Pleistocene; Pliocene; Spaindoi: 10.18563/pv.4.5.137-214 Abstract Two steps can be distinguished in the history of the first invasion of western and south western Europe by the arvicolines. The first step corresponds to the installation of these rodents with the immigration of Promimonys inxuliferus Kowalski, then of Mimomys stehlini Kormos and of Mimomys gracilis (Kretzoi). The second is characterized by the establishment of a geographic differentiation in the arvicoline fauna between the south of France and Spain, from where are described new species of Mimomys (Mimamys cappettai, Mimomys septimanus, Mimonys medasensis), and the rest of France, where are found only elements already known from central Europe or England (Mimomys polonicus Kowalski, Mimomys pliocaenicus F. Major, Mimomys reidi Hinton, or forms very close to the latter). This geographic differentiation, which is very certainly the consequence of the division of Europe into distinct climatic provinces, one of them being the southern province comprising at least Spain and southern France, could result from a cladogenetic evolution of Mimomys stehlini and Mimomys gracilis after their immigration. The present work is also a contribution to the search for correlations between the diverse micromammal localities of the latest Pliocene (or early Villafranchian) and of the early Quaternary of Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 5 (1971) |
|
|

|
Table ronde sur les phosphorites du Quercy Montauban 15-16 Décembre 1972Louis Thaler and Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Voici une centaine d'années débutait sur les Causses du Quercy l'exploitation des phosphorites qui devait permettre d'amasser des collections de Vertébrés fossiles uniques au monde. Ces fossiles firent l'objet de nombreuses publications et les noms de Filhol, Gaudry, Schlosser, Stehlin, Teilhard de Chardin sont attachés à ces premières études. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|
|
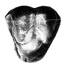
Carolocoutoia ferigoloi nov. and sp. (Protodidelphidae), a new Paleocene "opossum-like" marsupial from Brazil.Francisco J. Goin, Edison V. Oliveira and Adriana M. CandelaKeywords: Brazil; Didelphimorphia; Itaborai; Marsupialia; New taxa; Paleocene; Protodidelphidae; South AmericaAbstract Carolocoutoia ferigoloi gen. et sp. nov. is the largest of protodidelphid marsupials, known from Middle Paleocene levels at Itaboraí Formation, southeastern Brazil. It differs from other members of this family in having molars with low cusps which are basally inflated, rounded crests without cutting edges, and a thick enamel layer which is wrinkled, specially at the labial half. A comparative analysis among representatives of this family led us to recognize only three genera undoubtely assignable to it: Protodidelphis PAULA COUTO, 1952, Robertbutleria MARSHALL, 1987, and Carolocoutoia gen. nov. Protodidelphids lack the basic derived features diagnostic of Polydolopimorphian marsupials, while most of its derived features agree with its belonging to the Didelphimorphia. Protodidelphids comprise a specialized clade of opossum-like marsupials adapted to frugivorous or frugivore-omnivorous feeding habits. They differ from other didelphimorphians in having very large, spire-like entoconids, reduced and antero-posteriorly compressed paraconids, absence of stylar cusp C and of para- and metaconules, large stylar cusps B and D which are proximate to each other, short postmetacristae, eccentric protocones, and molars that increase rapidly in size from M/ml to M/m3. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 3-4 (1998) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 1 - Les LagomorphesNieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Lagomorpha; Montredon; Prolagus; Upper MioceneAbstract A sample of 231 isolated teeth of lagomorphs from the upper Miocene of Montredon (southern France), identified as the ochotonid Prolagus crusafonii DOPEZ, 1975, is studied, comparing it with other populations of the same species as well as with its closest species P. oeningensis (KÖNIG, 1825). Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. 2- Amphibiens. Etude PreliminaireJean-Claude Rage and Colette Vergnaud-GrazziniKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The Caudata are known by two Salamandridae ; one of them is attributed to the genus Megalotriton. The Pelobatidae form the major part of the Anura ; a few bones indicate also the presence of Neobatrachia. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Les Gruiformes (Aves) des phosphorites du Quercy (France). 1. sous-ordre cariamae (Cariamidae et Phorusrhacidae), systématique et biostratigraphie.Cécile Mourer-ChauviréKeywords: Aves; Biostratigraphy; Birds; Cariamae; gruiformes; Quercy Phosphorites; SystematicsAbstract The revision of the old collections of fossil birds from the “Phosphorites du Quercy” and the study of new material give the following results (Gruiformes, Cariamae) : The humeri and most of the carpometacarpi described under the name Filholornis belong in Elaphrocnemus. The ulnae ascribed to Fïlholornis belong in Idiornis. Most of the post-cranial elements of the genera Elaphrocnemus and Idiornis are described and show great similarities with recent Cariamidae and Opisthocomidae, and fossil Bathornithinae. A new genus and a new species, Oblitavis insolitus, are created in the sub-family Idiornithinae; two new species are described in the genera Elaphrocnemus (E. brodkorbz) and Idiornis (I. itardiensis), and the species Elaphrocnemus gracilis is transferred to the genus Idiornis. The genus Propelargus Lydekker is transferred from the family Ciconiidae to Cariamidae. A new generic name, Occitaniavis, is created for the species Geranopsis elatus, which belong in Cariamidae, while the type-species of the genus, Geranopsis hastingsiae, is a member of the Gruidae. The affinities between the Quercy avifauna and the Neotropical one is emphasized by the occurrence of Phorusrhacidae, previously known only from the Cenozoic of South America and the Late Pliocene or Early Pleistocene of North America. Thanks to the material collected during the new excavations, the stratigraphical position of most of the species is stated precisely, and evolutionary lineages are outlined. This study shows that the suborder Cariamae, presently restricted to two South American genera, was already extremely diversified during the Eocene, and widespread in Europe and North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 4 (1983) |
|
|
|
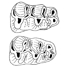
Rongeurs du Miocène supérieur de Chorora (Ethiopie): Cricetidae, Rhizomyidae,Phiomyidae, Thryonomyidae,Sciuridae.Denis GeraadsKeywords: cricetids; Ethiopia; phiomyids; rhizomyids; Rodentia; sciurids; thryonomyids; Upper MioceneAbstract Besides Dendromurids and Murids, the Chorora Rodents include 7 taxa, two of which are new. Afaromys nov. gen. is a Cricetodontine with very complicated lower molars, certainly isolated for a long time from Eurasian species. A Paraphiomys, with tetralophodont upper molars, is also quite different from other East African species, and its roots should probably he searched in the middle Miocene. Other taxa are less original, and more similar to the South Asiatic ones. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 3-4 (1998) |
|