Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Nouvelles données sur les Ichnites de dinosaures d'El Bayadh (Crétacé Inférieur, Algérie)Mostefa Bessedik, Cheikh Mammeri, Lahcene Belkebir, Mahammed Mahboubi, Mohamed Adaci, Hakim Hebib, Mustapha Bensalah, Bouhameur Mansour and Mohammed E. H. MansouriKeywords: Algeria; Brezina; El Bayadh; Ichnites; Lower Cretaceous; Sauropoids; Theropoidsdoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.7-35 Abstract Evidence of 350 Lower Cretaceous Dinosaur footprints is pointed out in El Bayadh area. Their preliminary study allow to distinguish four trackway assemblages which reveal vertebrate bipedal presence forms of tri-and tetradactylous Dinosauroïds (Assemblages 1-3) and quadrupidal Sauropoïd (Assemblage 4). Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
Systematic and evolutionary relationships of the hipparionine horses from Maragheh, Iran (Late Miocene, Turolian age)Raymond L. BernorKeywords: evolution; Hipparionine horses; Iran; Systematics; TurolianAbstract A systematic analysis of an hipparionine horse assemblage from Maragheh, Iran is made. A brief orientation to systematic philosophy and informal superspecific characterizations of some Old World hipparionines is given as a background to this work. A character state analysis of skulls is made, and has revealed five distinct species. A character state and stratigraphic trend analysis of isolated check tooth and postcranial remains, with known provenance, is also made. These two combined analyses reveal that the most resolute discrimination of hipparionine species and their evolutionary relationships occurs when multiple character complexes of associated skulls, maxillary and mandibular dentitions are made. When this is not possible, skulls have provided the best basis for discriminating species and their evolutionary relationships. Traditional characters of isolated cheek teeth and postcranial remains are shown here to offer limited information content for hipparionine phylogenetic systematics. The systematic portion of this study includes a comprehensive description of cranial and postcranial remains, and has further corroborated the distinction of five species which belong to at least three superspecific groups including: «Hipparion» geltyi sp. nov., Group 1; Hipparion prostylum (s. l.), and Hipparion campbelli sp. nov., Group 3; «Hipparíon» aff. moldavicum and «Hipparion» ?matthewi, Group 2. These species stratigraphic ranges and evolutionary relationships are also given here and argued to be important for establishing future hipparionine geochronologic correlations between a number of Eurasian late Miocene provinces. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 4 (1985) |
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
Morphological description and identification of an extraordinary new elephant cranium from the early Pliocene of Ileret, Kenya
|
|
|

|
A partial skeleton of Metaxytherium medium from the middle Miocene of La Morfassière quarry (Indre-et-Loire, France)
|
|
|

|
The paramyid rodent Ailuravus from the middle and late Eocene of Europe, and its relationshipsAlbert E. WoodKeywords: Ailuravinae; RodentiaAbstract The complex taxonomic history of the paramyid rodent genus Ailuravus is reviewed. It has been described as Hyracotherium, as a creodont carnivore and as a lemuroid primate - errors at the ordínal level that are most unusual for a rodent. The genus is a member of the poorly known subfamily Ailuravinae, probably derived from some European Early Eocene species of Paramys. Aíluravus was a large arboreal paramyid with highly rugose cheek teeth, very well developed hypocone, and a remarkably weak lower incisor. It was tropical to subtropical. Three named species are recognized, A. macrurus from the Lutetian of Messel; the genotype, A. picteti, from Egerkingen, Buchsweiler and the Geiseltal, slightly later in the Lutetian; and A. stehlinschaubi, new name, from the Bartonian of Mormont-Eclépens and Robiac. One or more unnamed species are present in the Ypresian of Cuis. The species are close to a phyletic sequence. No later representatives of the genus are known. The late Eocene to earliest Oligocene North American paramyid Mytonomys, whose relationships have been obscure, is tentatively referred to the Ailuravinae. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 1-2 (1976) |
|
|

|
Agriotherium intermedium (Stach 1957) from a Pliocene fissure filling of Xiaoxian County (Anhuei Province, China) and the phylogenetic position of the genus.Zhanxiang Qiu and Norbert Schmidt-KittlerKeywords: Carnivora; China; PHYLOGENY; Pliocene; skull anatomy; UrsidaeAbstract A fragmentary mandible and maxilla of a small sized Agriotherium of a young individual discovered from a Pliocene fissure filling in Xiaoxian county (Anhuei Province, China) are described. Judging from the morphology of the dentition and its dimensions the new material can be identified as Agriotherium inlermedium (STACH l957). Hendey's proposition (1980) that the Agriotherium species are derived from Indarctos is reconsídered on the basis of the new documents. As a result of a more general phylogenetic discussion it can be stated, that: 1. the supposed size increase as well as other trends, leading from Indarctos to Agriotherium are untenable ; 2. there are no positive indications to assume a phylogenetic transition of these two genera. 3. there are no real arguments in favor of an adaptational reversal in the evolution of Agriotherium. Hence, many features of that genus supposed by Hendey to be derived are plesiomorphic ; 4. regardless of the previous points it is methodologícally impossible to establish direct ancestor - descendant relationships between Indarctos and Agriotherium species, as Hendey did. Based on the data available and especially on the characters of the new material from China it is more likely that Agriotherium and Indarctos are two genera which developed independently. While advanced Agriotherium species, e.g. A. africanum, resemble in some respects Indarctos by adaptational analogies, more primitive species, e.g. Agriotherium intermedium, are quite dissimilar to lndarctos. While Indarctos might be derived from an Ursavus like forerunner, Agriotherium has its roots more likely somewhere in between Ursavus and the Hemicyon-group. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|

|
Physogaleus hemmooriensis (Carcharhinidae, Elasmobranchii), a new shark species from the early to middle Miocene of the north sea basin.Thomas Reinecke and Kristiaan HoedemakersKeywords: Carcharhinidae; Early Miocene; Elasmobranchii; Hemmoorian; new species; North Sea Basin; PhysogaleusAbstract A new carcharhinid shark species, Physogaleus hemmooriensis sp. nov., is described from the Lower Hemmoorian (Behrendorfian, late Burdigalian, early Miocene) of Werder, Lower Saxony, Germany. P. hemmooriensis also occurs in the Edegem and Antwerpen Sands Members of the Berchem Formation, Belgium, and in the Miste Bed, Aalten Member of the Breda Formation, The Netherlands, which have an early to middle Miocene age. In the Western Atlantic region, the taxon is present in the early Miocene Calvert Formation of Delaware, U.S.A, which is largely contemporaneous with the Hemmoorian. Article infos Published in Vol. 34, Fasc. 1-2 (2006) |
|
|
|
New murids and gerbillids (Rodentia, Mammalia) from Pliocene Siwalik sediments of India.Rajeev PatnaikKeywords: Dental morphology; evolution; new species of murids and gerbillids; phylogenetic relationships; SystematicsAbstract Murids and gerbillids (Rodentia, Mammalia) recovered from four Upper Siwalik localities; Moginand (around 3.5-4.5 m.y.), Kanthro (around 2.5 m.y.), Ghaggar (around 2 m.y.) and Nadah (around 1.8-2 m.y.) are described herein. A comparison of Mus linnaeusi sp. nov. reveals its close relationship towards the house mouse Mus musculus. In contradiction to earlier proposals that Golunda migrated to the Indian subcontinent from Africa sometime during Late Pliocene, it is suggested here that Golunda (in the form of Golunda tatroticus sp. nov.) evolved from Parapelomys robertsí of Late Miocene deposits of Siwaliks. Golunda tatroticus sp. nov. exhibits a progressive relationship to the extant Indian Bush Rat Golunda ellioti through Golunda kelleri and Golunda sp. Tatera pinjoricus sp. nov. is considered here to be a link between the extinct Abudhabia kabulense and the extant Tatera indica. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|
|
Lower Paleogene crocodilians from Silveirinha, Portugal.Miguel T. AntunesKeywords: ?Upper Paleocene / Lowermost Eocene; Crocodilians; Ecology; PortugalAbstract The presence at Silveirinha of one of the earliest, ? Late Paleocene or Lowermost Eocene, european representatives of the genus Diplocynodon is based mostly on isolated bones and teeth (often from juveniles). This small-sized form is the only crocodilian so far recognized in this site. The longevity of Diplocynodon in Portugal becomes much extended; the genus survived there until the Middle Miocene at least. A discussion on the possible affinities with other eocene Díplocynodon and especially those from Cubillos-Valdegallina (Zamora, Spain) is presented. On the other hand, differences have been detected in comparison with: Díplocynodon tormis, from the middle Eocene of the Douro basin in Spain, which may belong to another phyletic line; and the aff. Diplocynodon from Dormaal (Belgium) and Le Quesnoy (France), nearly contemporaneous of Silveirinha. The Silveirinha Diplocynodon and many other data strongly suggest moist, subtropical, quite limited in space environments related to an alluvial plain crossed by small, meandering channels. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 1 (2003) |
|
|
|
Sur les empreintes de pas des gros mammifères de l'Eocène supérieur de Garrigues-ste-Eulalie (Gard)Paul EllenbergerKeywords: Eocene; Euzet; Footprints; IchnofaunaAbstract Is hereby described an impressive lchnoiauna belonging to the Lower to Middle Ludian of the Gard (S. France). The slab, already cleaned over a length of 18 m, is located near the top of the Potamides aporoschema lacustrine limestone (Lower Ludian, Euzet zone). It is therefore older than the Célas sandstone deposit, and still more than the Melanoides albigensis and M. acutus marly limestone corresponding to the Upper Levels of the Ludian stage. Although biostratigraphically older than the La Débruge and Montmartre zone, the biotope shows already a sampling of very tall Artiodactyles, Perissodactyles and Carnivorous. One of the most « majestic ›› Artiodactyles, Anopolotheriipus lavocati, nov., points out a huge size type. To mention also among the Ichnotypes described, 10, the big Perissodactyle Palaeotheriipus similimedius, nov., and the big Carnivorous Hyaenodontipus praedator, nov. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Systematic revision of Ctenodactylidae (Mammalia, Rodentia) from theMiocene of Pakistan.J.A. BaskinKeywords: Ctenodactylidae; Miocene; Prosayimys; Rodents; Sayimys; SiwalikAbstract Extensive sampling of the Siwalik deposits of the Potwar Plateau of northem Pakistan and from the Zinda Pir dome of central Pakistan has produced a fossil record of Miocene ctenodactylids that can be correlated with the paleomagnetic time scale. The early Miocene Prosayimys flynni (n. gen., n. sp.) is recognized as the first ctenodactylid in the Indian subcontinent. Prosayimys is ancestral to Sayimys. From the late early Miocene to the early late Miocene, there is an anagenetic succession of three species of Sayimys: S. cf. S. intermedius, S. sivalensis, and S. chinjiensis (n. sp.). Sayimys chinjiensis gave rise to the late late Miocene S. perplexus. A second lineage is represented by Sayimys minor, S. sp. A, and S. sp. B. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 1 (1996) |
|
|

|
Experimental taphonomy inavian eggs and eggshells: effects on early diagenesis.Ana M. Bravo, D. A. Buscalioni, Lauro Merino and B. G. MüllerKeywords: archosaurian eggshells; avian egg; Experimental taphonomy; geochemical analysis; pyritisation; Upper CretaceousAbstract We experimentally explore the early taphonomic stages involving the decay and biodegradation of buried eggs and eggshells. Unfertilised commercial chicken eggs and eggshell fragments were buried in plastic containers and were kept under controlled conditions for eight months. Half of the containers were filled with marl, and the remainder with sand. All were saturated with fresh tap water, acidified water, sulphate water, or seawater. They were kept in the dark at 23.4-26 °C, except one, which was kept in a heating chamber at 37.4°C. We expected that different burial conditions would produce distinct taphonomic outcomes. Instead, the taphonomic alterations of buried eggs parallel that of the alteration of egg proteins (i.e., denaturation and/or putrefaction) with an additional role played by the eggshell. Mummification, encrustation, distortion and fragmentation, and necrokynesis (vertical displacement) depend on organic matter decay. The experiment identifies environmental conditions that may favour or actively promote these taphonomic processes. Of these, early pyritization is one of the most relevant. For comparative purposes, samples of fossil and extinct eggshell representing three distinct environmental burial conditions were examined. These included Megaloolithus, Caiman crocodilus, and Struthio camelus ootypes. The geochemical analysis of these eggshells showed no significant differences among the chemical variables of these fossil and extant ootypes. Eggshells exhibited a stable composition over a range of experimental conditions. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
|
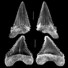
Palaecarcharodon orientalis (Sinzow) (Neoselachii : Cretoxyrhinidae), from the Paleocene of maryland, USA.Gerard R. CaseKeywords: Maryland; Palaeocarcharodon; Paleocene; Selachian; Systematics; U.S.A.Abstract Recent collecting of fossil vertebrate remains from the lowermost member of the Aquia Formation (Paleocene), has enabled me to report here for the very fIrst time, the earliest occurrence for the teeth of Palaeocarcharodon in the fossil record of the New World. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|

|
The fossil rabbit from Valdemino cave (Borgio Verezzi,Savona) in the context of western Europe Oryctolagini of Quaternary.Giulia Nocchi and Benedetto SalaKeywords: Lagomorpha; Mammals; North-western Italy; Oryctolagus; Plio-Pleistocene; SavonaAbstract The present research deals with the remains of a lagomorph found at Valdemino cave and comes to the conclusion that it is a rabbit with peculiar characteristics in comparison with the other known species Oryctolagus laynensis, O. lacosti and 0. cuniculus. We studied other fossil remains of rabbit populations from Villafranchían and middle Pleistocene deposits and compared them with data from the literature and with recent material. The analysis leads us to maintain two phylogenetic hypotheses about the history of Oryctolagini. The ñrst one, already formulated by Lopez Martinez, suggests that 0. cuniculus derives from O. laynensis,while the origin of O. lacostí is unknown; according to the second hypothesis 0. laynensis would be the common ancestor of two phyletic lineages, 0. lacosti and 0. cuniculus. In both cases the lagomorph from Valdemino would be the form derived from 0. lacosti, from which however it differs in peculiar characteristics. Since the rabbit from Valdemino survives until the beginning of Postgalerian, its disappearance may coincide with the retreat of 0. cuniculus from western Europe in Spain and, perhaps, in south-western France, before the last glaciation. O. cuniculus survived in Spain, from where it spread once again over western Europe as a result of man. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
The late Miocene percrocutas (Carnivora,Mammalia) of Madedonia, Greece.George D. KoufosKeywords: Biochronology; Carnivora; Comparisons; Dinocrocuta; Greece; Late Miocene; MammaliaAbstract Some new material of percrocutas from the late Miocene of Axios valley (Macedonia, Greece) is studied. They have been found in the locality of "Pentalophos 1" (PNT). The material has been described and compared with the known late Miocene percrocutas of Eurasia. This comparison indicates that it can be identified as Dinocrocuta gigantea (SCHLOSSER, 1903). A maxilla of a percrocuta, named ”Hyaena" salonicae, was found in the same area (Andrews, 1918). "Hyaena" salonicae is smaller than the PNT material. It is also compared with other material from Eurasia while its taxonomic and age problems are discussed. It belongs to Dinocrocuta and shows close relationships with D. robusta and D. senyureki; its age can be considered as late Vallesian-early Turolian. The age of the locality PNT is also discussed and a possible Vallesian age is proposed for it. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
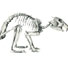
Osteology of Prolagus sardus, a Quaternary Ochotonid (Mammalia, Lagomorpha).Mary R. DawsonKeywords: Lagomorpha; Ochotonidae; Prolagusdoi: 10.18563/pv.2.4.157-190 Abstract Prolagus sardus is the last representative of the diverse lineages of European endemic ochotonids. It is also the most abundant in the collections. The previous studies made of this species have established rather well its dental morphology, its phylogenetic position, its geographic and temporal distribution, and its intraspecific individual variation. On the other hand, no osteologic study has fully utilized the superb material from Corsica and Sardinia collected by Forsyth Major. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 4 (1969) |
|
|

|
Les gisements de Robiac (Eocène supérieur) et leurs faunes de Mammifères.Jean SudreKeywords: Fauna; Late Eocene; Mammalia; Robiacdoi: 10.18563/pv.2.3.95-156 Abstract Designated the type-locality of a late Eocene paleomammal zone, Robiac has recently been the object of important excavations. The first results of the new collecting, as well as a revision of the material in old collections, are given in this work. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 3 (1969) |
|
|

|
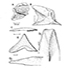
Multituberculate endocranial castsZofia Kielan-JaworowskaKeywords: Allotheria; Cretaceous; endocranial cast; Mongolia; multituberculatesAbstract A reconstruction of a multituberculate endocranial cast is made on the basis of a complete natural cast prepared from the skull of Chulsanbaatar vulgaris, and other less complete endocasts, all from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. The multituberculate endocast is of mammalian pattern but it has retained a therapsid-like lateral profile with a deep rhombencephalon and a shallow telencephalon. It is characterized by: a heart-shaped cross-section of the telencephalon; an extensive lissencephalic neocortex; a very prominent pons placed far anteriorly; a lack of cerebellar hemispheres, and very large paraflocculi. Its structure, very different from the brains of other mammals, suggests thats the Multituberculata branched very early from the main mammalian stock. This supports Simpson's (1945) idea that the Multituberculata should be placed in a subclass of their own: Allotheria MARSH. The endocast and braincase structure show that the Multituberculata had strongly developed senses of smell and hearing. The encephalization quotient of approx. 0.55 evaluated for Ch. vulgaris is relatively high for a Mesozoic mammal. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 1-2 (1983) |
|
|
|
A new vertebrate locality in the eifelian of the khush-yeilagh formation, Eastern Alborz, IranAlain Blieck, Farrokh Golshani, Daniel Goujet, Amir Hamdi, Philippe Janvier, Elga Mark-Kurik and Michel MartinKeywords: Devonian; Iran; khush-yeilagh formation; VertebrateAbstract A new Devonian vertebrste locality has been discovered in 1976 in the basal part of the Khush-Yeilagh Formation in the eastern Alborz Mountains of Iran. The fossils occur in a band one centimeter thick which is identifiable at other outcrops in the area. A preliminary study of the remains has yielded the following faunal list : Placodermata (Phlyctaeniida indet.. Groenlandaspididae indet.. Coccosteidae indet., Holonema sp., Ptyctodontida indet., Antiarcha indet., Bothriolepis cf. kwangtungensis), Elasmobranchii (Ctenacanthidae indet.), Acanthodii (Gyracanthus sp., « Onchus » overathensis, Ischnacanthiforme indet.), Dipnoi (? Dipteridae indet.), « Crossopterygii ›› (Onychodus cf. sigmoides, Holoptychiidae indet., Osteolepididae indet.). This fauna is older than the Middle Givetian and probably of Middle or Lower Eifelian age. Owing to its diversity, it may prove possible to use it in the future as a reference fauna for the study of the Devonian vertebrates in Central Asia and the Middle East. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 5 (1980) |
|