Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Acinoptèrygiens du Stéphanien de Montceau-les-Mines (Saône-et-Loire, France).Daniel Heyler and Cécile PoplinKeywords: Aeduelliforms; Biogeography; Palaeonisciforms; paramblypteriforms; StephanienAbstract The study of new specimens from the Stephanian shales of Montceau-les-Mines confirms and enlarges the number of groups already known in this area. Among the Palaeonisciforms, “form A" is now known more completely, although no diagnosis or name can yet be given for it. “Form B" is redescribed and its relationships with “Elonichthys robisoni" are discussed. A palaeoniscid is recorded which resembles those from Bourbon l'Archambault. The paramblypteriforms occur rather frequently, but no genera can be determined. The aeduelliforms comprise some specimens close to Aeduella blainvíllei from Muse (Autun basin), and a new genus. Comparison of the latter with two fossils from Lally allows creation of two new species and a new family. This diversification of the aeduelliforms during this middle Stephanian leads to the hypothesis that the group originated at least as early the lower Stephanian. This material prooves again the characteristic endemism of this fauna, particularly of the aeduelliforms which are known only in the Massif Central where they diversified during the Permo-Carboniferous. Biogeographical consequences are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|

|
Morphotypes dentaires actuels et fossiles des Chiroptères Vespertilioninés. 1e partie: Etude des morphologies dentairesHenri MenuKeywords: bats; Dental morphology; fossils; PHYLOGENY; recent; SystematicsAbstract The classifications of the recent vespertilionine bats were made wihtout taking in account the teeth morphology; this resulted in a reduction of the possibilities of comparison with the available fossils. The generalized use of dental formulae was abusive: this contributed to the admission of artificial genera. These conditions have long delayed the consideration of characters able to frame the phylogeny of the sub-family. In the first part of the study, the teeth morphologies are described and analysed. morphological reference types are established for each upper and lower tooth: they should make an easier elaboration of criteria for the differentiation at generic level. The position of the species in view of these criteria allows one to group them into homogeneous genera, and to appreciate the degree of relationship that the latter have between them. The second part of the study (next publicationà will develop inferences dealing with systematics and phylogeny Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 2 (1985) |
|
|

|
Les rongeurs de l'Eocène d'Afrique Nord-Occidentale [Glib Zegdou ( Algérie) et Chambi (Tunisie)] et l'origine des anomaluridae.Monique Vianey-Liaud, Jean-Jacques Jaeger, Jean-Louis Hartenberger and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Africa; Eocene; New taxa; Paleobiogeography; PHYLOGENY; RodentsAbstract This paper is about the oldest African rodents faunas, from the late Early Eocene, or early Middle Eocene, Glib Zegdou (Algeria) and Chambi (Tunisia) localities. Five species are described and figured, belonging to a new family here created, the Zegdoumyidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Additions to the elasmobranch assemblage from the Bandah Formation (middle Eocene, Bartonian), Jaisalmer District, Rajasthan, India, and the palaeobiogeographic implications of the faunaRajendra S. Rana, Raman Patel, David J. Cicimurri and Jun A. EbersoleKeywords: Chondrichthyes; Elasmobranchii; Indian Ocean; Palaeogene; South Asiadoi: 10.18563/pv.44.2.e1 Abstract Isolated elasmobranch teeth (sharks and rays) from the middle Eocene (Bartonian) Bandah Formation in the Jaisalmer District of Rajasthan, India are described. The remains improve our knowledge of the environment represented by this lithostratigraphic unit and the ecology preserved therein. Seventeen unequivocal taxa were identified, including Nebrius sp., Striatolamia aff. S. macrota, Brachycarcharias atlasi, B. lerichei, cf. Jaekelotodus sp., Carcharhinus mancinae, Rhizoprionodon sp., Physogaleus sp., Galeocerdo clarkensis, G. eaglesomei, Odontorhytis aff. O. pappenheimi, “Rhinobatos” sp., “Dasyatis” sp., Coupatezia sp., “Aetomylaeus” sp., “Rhinoptera” sp., and Ouledia aff. O. lacuna. Of these, “Aetomylaeus” sp., B. atlasi, C. mancinae, G. clarkensis, G. eaglesomei, cf. Jaekelotodus sp., Nebrius sp., Odontorhytis aff. O. pappenheimi, Ouledia aff. O. lacuna, and “Rhinoptera” sp. are reported from the middle Eocene of India for the first time. The Bandah Formation elasmobranch palaeofauna has close affinities to the Palaeocene-Eocene Tethyan/Paratethyan faunas of Africa, Madagascar, Asia, and Europe, and some taxa indicate a western hemisphere influence from North America. The Bandah Formation palaeofauna indicates that deposition occurred in a moderately shallow marine environment. The Bartonian age is primarily based on foraminifera but is corroborated by the presence of elasmobranch taxa that also occur in contemporaneous deposits elsewhere. The marine regression started during the early Palaeogene, and our study indicates that the sea completely withdrew from the Jaisalmer Basin after the deposition of the Bandah Formation. This event may have been synchronous with the middle Eocene uplift of the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau. Article infos Published in 44-2 (2021) |
|
|

|
Revision of the family Cephalomyidae (Rodentia, Caviomorpha) and new cephalomyids from the early Miocene of Patagonia.Alejandro KramarzKeywords: Cephalomyidae; Lower Miocene; Patagonia; Rodentia; Soriamys; SystematicsAbstract A new genus of hystricognath rodent with two new species, Soriamys gaimanensis and Soriamys ganganensis, from the Colhuehuapian Age (Early Miocene), Sarmiento Formation, of Patagonia is described. The first species comes from the south barranca of the valley of Rio Chubut, near Gaiman locality (Chubut Province). It is known through a great number of dental remains in different stages of wear. The teeth are protohypsodont, with cement in the principal valleys. P4 are simpler, more oval inoutline and without a differentiated hypocone-hypoflexus. Upper molars are pentalophodont in early stages of wear and become bilobated in middle and advanced stages; M3 have a temporary third posterior lobe due to the maintenance of the braquiflexus on the posterior wall of the tooth. Lower teeth have a completely asymrnetrical pattern in relation to the uppers. The molars are trilophodont, with only one complex crest in the trigonid composed of the fusion of the anterolophid and mesolophid. The dp4 have a derived pentalophodont pattern due to the loss or fusion of the mesolophid and the development of an accessory transverse crest between the anterolophid and metalophid. The second species is known through a complete skull and jaw and other skull fragments with the dentition, proceeding from Pampa de Gan Gan, Chubut province. Respect to the first species, the teeth are higher crowned, with an earlier occlusal simplification and a third posterior lobe of M3 more developed and persistent. The skull and jaws show many chinchilloid characters, such as jugal bone with an ascending process, concave palate, very prominent dorsal shelf of the masseteric fossa, nasolachrymal duct opened laterally on the maxillary and very developed lateral mandibular fossa. Moreover, Soriamys is closely related to Cephalomys by sharing a similar asymmetric dental pattern and other dental and mandibular characters. These two genera constitute a natural group, the Cephalomyidae, with peculiar dental characters, like the asymmetric pattem of the upper and lower teeth; Cephalomyopsis, and probably Litadontomys, can be considered part of this group. Scotamys and Perimys constitute a distinct lineage (the Neopiblemidae or Perimyidae), more closely related to the chinchillids. Many characters shared by cephalomyids, eocardiids and caviids suggest a closer affinity between the Chinchilloidea and the Cavioiidea as a whole. Abrocoma shows also an asymmetric dental pattern and other chinchilloid features that suggest some degree of relationship with the cephalomyids, still not well determined. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 2 - les carnivoresGérard de BeaumontKeywords: anatomy; Carnivora; France; Montredon; Systematics; Upper MioceneAbstract The locality of Montredon has provided 8 species of camivores, often little documented, that are discribed and depicted. All the remains are fragmentary and generally badly preserved which lowers very much the possible precision of the taxonomic study; this one has however allowed the creation of a new subspecies. The most richlypdocumented forms are an ursid (Indarctos) and a felid (Machairodus). Issuing often from a westem Europe evolution, the carnivores are well inserted between those of the better known faunas of the "Classical Pontian" and of the lower Vallesian and this situation fits also well with their stratigraphic level, that cannot however be more accurately defined with them alone. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Relations phylétiques de Bachitherium filhol, ruminant de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Denis Geraads, Geneviève Bouvrain and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Bachitherium; Cladistic analysis; France; Mammalia; Oligocene; RuminantiaAbstract A detailed comparative study of a complete skeleton of Bachitherium and a cladistic analysis of the sub-order Neoselenodontia lead us to propose a cladogram and a new classification of this group. The Tylopoda are the sister-group of the Ruminantia, which are chiefly defined by the fusion of the cuboid and navicular. Within this infra-order, Amphimeryx is the sister genus of a tetraselenodont group, in which the Hypertragulidae are well-separated group from a monophyletic group defined by the loss of trapezium, fusion of capitatum and trapezoid, and the isolation of the hypoconid on lower molars. The most primitive genera of this group, Lophiomeryx and Iberomeryx still have an open trigonid on the lower molars, but this is lingually closed in Archaeomeryx, sister-genus of the higher Ruminantia which have fused metatarsals and more evolved milk teeth. We divide them into two pan/orders : Tragulina (including the recent and miocene Tragulidae, and the North-American Leptomerycidae), and Pecora, with reduced lateral metacarpals and a new crest (telocristid) on the lower premolars. Within the Pecora, the upper molars of Gelocus are more primitive than those of Bachitherium (a genus with many autapomorphies in the dentition) itself more primitive than the group Prodremotherium + Eupecora, with fused metacarpals. We consider the Eupecora (including several genera without frontal appendages) to be monophyletic. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 2 (1987) |
|
|
|
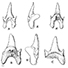
Modification du statut générique de quelques espèces de sélaciens crétacés et tertiairesHenri CappettaKeywords: Cretaceous; Selachians; TertiaryAbstract The re-examination of six fossil selachian species has involved the creation of six new genera: Squatiscyllium, Protolamna, Parotodus, Abdounia, Physogaleus, Hypolophodon and of one new species : Prozolamna sokolovi. The modification of the generic statute of these species allows to clarify their systematic position and to define their relationships at a familial level. Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 1 (1980) |
|
|
|
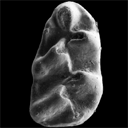
New datation of the Tafna Basin (Algeria): A combination between biochronological and magnetostratigraphical dataSalamet Mahboubi, Mouloud Benammi and Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: correlations; Late Miocene; North Africa; Rodentiadoi: 10.18563/pv.39.1.e1 Abstract The Tafna Basin corresponds to the lowlands, which are located in front of Tessala and Traras ranges, below the Tlemcen mountains, Algeria. This basin displays a complete sedimentary cycle dominated by lagoonal-fluvial and marine deposits. The continental formations located at the base of these deposits are mainly composed of alternating sandstones and clays. An early late Miocene age has been previously attributed to them, based on direct correlations with marine deposits. Search for micromammal fossils led to the discovery of three different rodent species from a single level of the Djebel Guetaf section, located at the bottom of these deposits. The rodent assemblage indicates a late Miocene age. Combined magnetostratigraphical and biostratigraphical investigations were carried out to provide a more accurate age control of these continental deposits. Sixty-four oriented rock samples were collected for a magnetostratigraphic study along a 92 meters thick section including the fossiliferous layer. Rock magnetic investigations indicate the presence of both high and low coercivity minerals. Specimens subjected to progressive thermal demagnetization procedures show that the samples exhibit a high temperature magnetization component and display a normal polarity. Based on biostratigraphic constraints, the Guetaf section is correlated with Chron C4An, indicating an age ranging from Article infos Published in Vol.39-1 (2015) |
|
|
|
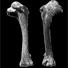
Les gangas (Aves, Columbiformes, Pteroclidae) du Paléocène et du Miocène inférieur de France.Cécile Mourer-ChauviréKeywords: Birds; evolution; Lower Miocene; New taxa; Oligocene; Paleoecology; Paulhiac; Quercy Phosphorites; Saint-Gérand-Ie-Puy; Sandgrouse; Upper EoceneAbstract The two species of Sandgrouse from Quercy, Pterocles validus MILNE-EDWARDS and P. larvatus MILNE-EDWARDS, are ascribed to the genus Archaeoganga MOURER-CI-IAUVIRÉ which includes a third, very large species, A. pinguis. The sandgrouse of Saint-Gérand-le-Puy, Pterocles sepultus MILNE-EDWARDS, is ascribed to a new genus, Lepzoganga. This form appears in the Upper Oligocene of Quercy, in Pech Desse and Pech du Fraysse localities, and is still present in the Lower Miocene of Saint-Gérand-le-Puy and Paulhiac. Recent sandgrouse live in semidesert or desert areas. The indications provided by mammal and bird faunas in the localities where sandgrouse were found, confirm that the paleoenvironment was open and arid. The morphological study of these fossils indicates that, in the Upper Eocene, the Pteroclidae were already completely individualized with respect to Charadriiformes. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|
|
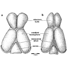
The endocranial cast and encephalization quotient of Ptilodus (Multituberculata, Mammalia)David W. Krause and Zofia Kielan-JaworowskaKeywords: encephaIization quotient; endocranial cast; Montana; Multituberculata; olfactory bulbs; Paleocene; PtilodusAbstract Simpson (1937a) reconstructed the brain of the Paleocene multituberculate Ptilodus as having the olfactory bulbs widest anteriorly, an unusual condition among mammals. Slight preparation and reexamination of the endocast specimens of Ptilodus reveals that the olfactory bulbs in fact taper anteriorly, as in the recently-described endocranial casts of three multituberculate species from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, and as in those of other mammals. The brain of Ptilodus was therefore essentially of the same general pattem as in other multituberculates. Ptilodus differs, however, in having the vermis more deeply inserted between the cerebral hemispheres. Other details concerning the endocast morphology of Ptilodus are clarified. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|

|
Le genre Mesembriacerus (Bovidae, Artiodactyla, Mammalia) : un Oviboviné primitif du Vallésien (Miocène supérieur) de Macédoine (Grèce)Geneviève Bouvrain and Louis de BonisKeywords: Bovidae; Cladistics; Late Miocene; Ovibovinae; VallesianAbstract The bovid Mesembriacerus melentisi, the numerous skulls, teeth and limb bones of which are described from the locality Ravin de la Pluie (Macedonia, Greece), bears some features which allow us to put it in the tribe ovibovini (Ovibovinae) with several other Miocene genera and the Recent one Ovibos. A cladogram gives the phyletic relationships within this tribe. It shows that Mesembriacerus which is one of the oldest genera, is also the most primitive. The limb bones are as elongated as those of Recent cursorial bovids and they show, as does the bulk of the fauna, an open environment for the locality. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 4 (1984) |
|
|
|
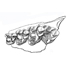
Cryptomerix Schlosser, 1886, Tragulidé de l'oligocène d'Europe ; relations du genre et considérations sur l'origine des ruminants.Jean SudreKeywords: Archaic Ruminants; Paleobiogeography; Quercy Phosphorites; Systematics; TragulidsAbstract The genus Cryptomeryx SCHLOSSER, 1886, inusited during a long period, has been discovered in Lower and Middle Oligocene localities of the Quercy region (South-West France). This new material, as well as specimens from the old collections referred to Cryptomeryx, are described; their study, allows us precising the definition of the genus, and confirming its allocation to the Tragulidae family. The type species of the genus, Crypmmeryx gaudryi (= Lophiomeryx gaudryi FILHOL, 1877), occurs in several localities at the base of the Middle Oligocene (Itardies, La Plante 2, Roqueprune 2, Soulce, Herrlingen 1). The new species C. matsoui n. sp. has been defined in the older locality of Mas de Got (top of Lower Oligocene). It is possible that the species Pseudamphimeryx decedens STEHLIN, 1910 pertains to the same genus. Also to the Tragulids must be referred the monospecific genus Iberomeryx (I. parvus GABOUNIA, 1964) from Upper Oligocene of Benara (Georgie, URSS), with which Cryptomeryx is related. These genera are not direct ancestors of Miocene tragulids; their occurrence in the Western European Oligocene results from a first immigration wawe of the family. These Tragulids are one of the most archaic groups of Ruminants. They are probably derived from a primitive stock which had acquired in Asia the selenodont condition of the dentition. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 1 (1984) |
|
|
|
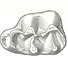
Rongeurs nouveaux de l'Oligocène Moyen d'Espagne.Louis ThalerKeywords: Cricetidae; Oligocene; Pseudocricetodon; Rodents; Theridomysdoi: 10.18563/pv.2.5.191-207 Abstract Description of four new rodents from a recently discovered locality at Montalban. Theridomys crusafonti nov. sp. is considered as the ancestry of T. Iembronicus. Theridomys varian: nov. sp. includes «Theridomys» morphotypes and «Blainvilllimys» morphotypes; it could be ancestral to B. blainvillei. Pseudoltinomys nanus nov. sp. represents a new lineage paralleling in evolution that of P. gaillardi (which is equally found at Montalban). Pseudocricetodon montalbanensis nov. gen., nov. sp. designates a lineage of very small Cricetidae accompanying Eucricetodon. With these well defined new species and six others present in the locality, Montalban appears as the best faunal reference point within the biochronologic zone of La Sauvetat. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 5 (1969) |
|
|
|
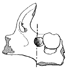
Les Dipodidae (Mammalia, Rodentia) d'Europe occidentale au Paléogène et au Néogène inférieur: origine et évolution.Marguerite Hugueney and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Dipodidae; Late Oligocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The study of three new populations of Plesiosminthuspromyarion from the "phosphorites du Quercy" and of material from "Auvergne" brings new data on european oligocene Dipodidae. They appear in Western Europe at the beginning of late Oligocene. Evolutionary trends of the group are drawn and particularly the emergence of morphotypes announcing P. schaubi, from the Coderet level, is revealed among the most recent populations of P. promyarion. Differences are attempted to be drawn between the three species : P. promyarion, P. myarion and P. schaubi by restudying the type-population of P. myarion from the aquitanian deposits of Chavroches (Allier) in comparison with two other populations from the same age and the same region. Relationships between early european, american and asiatic Dipodidae are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Preliminary report on the fishes (Chondrichthyes & Teleostei) from the lower Oligocene (Rupelian) Red Bluff Clay at site AMo-9, Monroe County, Alabama, USAJun A. Ebersole, David J. Cicimurri, Lindsey M. Stallworth and Andrew D. GentryKeywords: Batomorphii; Elasmobranchii; Galeomorphi; Gulf Coastal Plain; Vicksburg Groupdoi: 10.18563/pv.47.2.e2 Abstract Herein we describe a small but relatively diverse assemblage of fossil fishes derived from the lower Oligocene (Rupelian) Red Bluff Clay at site AMo-9 in Monroe County, Alabama, USA. Identified amongst the remains are 15 unequivocal taxa representing 11 families within five orders, and one additional taxon represents an unknown order and family. Taxa identified include Eostegostoma sp., Otodus (Carcharocles) sp., Mitsukurinidae/Carchariidae indet., Macrorhizodus praecursor, Galeorhinus sp., Negaprion gilmorei, Physogaleus sp., “Sphyrna” sp., Galeocerdo sp., cf. “Aetobatus” sp., Sphyraena sp., Xiphiorhynchus kimblalocki, Xiphiorhynchus sp., Cylindracanthus ornatus, and C. rectus. Several additional fossils could not be identified beyond Lamniformes, Carcharhiniformes, and Teleostei, but they likely belong to one of the identified taxa within this paleofauna. All of the fishes previously reported from the Red Bluff Clay within the entirety of the Gulf Coastal Plain of the USA are otolith-based, and each of the 15 unequivocal taxa reported herein are important new records for this lithostratigraphic unit. In particular, the Eostegostoma sp. and Xiphiorhynchus spp. specimens represent the first occurrences of these taxa in Alabama. The specimens of C. ornatus, Eostegostoma sp., and X. kimblalocki are stratigraphic and temporal range extensions from the middle and late Eocene into the Rupelian Stage of the Oligocene. Other described taxa may represent transitional forms between those described from the late Eocene and late Oligocene within the region. This study provides a tantalizing preliminary view into faunal transitions that occurred amongst marine fishes across the Eocene/Oligocene boundary within the Gulf Coastal Plain of the USA. Article infos in press |
|
|

|
Morphological description and identification of an extraordinary new elephant cranium from the early Pliocene of Ileret, Kenya
|
|
|

|
The evolution of the molar pattern of the Erethizontidae (Rodentia,Hystricognathi) and the validity of Parasteiromys Ameghino, 1904.Adriana M. CandelaKeywords: Argentina; Erethizontidae; Hystricognathi; Miocene; Molar evolution; Porcupines; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract The genus Parasteiromys AMEGHINO, 1904 is revalidated, and P. friantae sp. nov. (Hystricognathi, Erethizontidae) from Colhuehuapian (early Miocene) sediments of the southern cliff of Colhue-Huapi Lake (Province of Chubut, Argentina), is described. The molar morphology of these taxa and of living porcupines adds new elements to understand the dental evolution of the Erethizontidae, and to propose the hypothetical ancestral molar pattern for this family. This pattern does not correspond to any of the morphologies traditionally proposed as ancestral for South American hystricognathous rodents. The proposed pattern is characterized by a metaloph disconnected from the posteroloph and oriented towards the hypocone, and the third loph incompletely developed with the lingual portion homologous to the mesolophule of Baluchimyinae (Chapattimyidae) from the Miocene of Pakistan. The inferred steps of the molar evolution of erethizontids towards the pentalophodont condition, considered derived for the family, are illustrated. This study strengthens the hypothesis placing erethizontids in a basal position among rodents of the suborder Hystricognathi. Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|

|
Preliminary evolution of paleosols and implications for interpreting vertebrate fossil assemblages, Kuldana formation, Northern PakistanAndres Aslan and J. G. M. ThewissenKeywords: Eocene; Kuldana Formation; Pakistan; Paleosols; Pedogenic Carbonate; taphonomy; Time Averaging; Vertebrate FossilsAbstract Paleosols and the taphonomy of vertebrate fossils in the Eocene Kuldana Formation of northern Pakistan provide important information on the preservation and time-averaging of fossil assemblages. Morphologic, mineralogic, and chemical data as well as comparisons with Quaternary soils suggest that Kuldana paleosols formed under generally dry and oxidizing conditions over time intervals of less than 100 000 years and perhaps as short as 1000 years. The distribution of carbonate in Kuldana paleosols further indicates that the upper half of the profiles were acidic whereas the lower halves were alkaline. Vertebrate fossils are rare in Kuldana paleosols and occur primarily in well-cemented sandstones and conglomerates with abundant micritic and iron-stained nodules that were reworked from floodplain soils. The scarcity of vertebrate remains in Kuldana paleosols probably reflects a combination of acidic, dry, and oxidizing conditions in the upper half of the profiles and rapid floodplain sedimentation. Comparisons between the taphonomic characteristics of Kuldana channel fossil assemblages and bone accumulations in modem rivers provide a basis for estimating the length of time represented by Kuldana fossils from several important localities. Vertebrate fossil assemblages from Barbora Banda are characterized by a low-diversity paleofauna, partially articulated skeletons, and bones that are sorted by size and shape. Comparison with bone accumulations in modern rivers suggests that the fossils from Barbora Banda accumulated in 1 to 10 years. Vertebrate fossils from the Lower Kuldana in the Kala Chitta Hills region, typified by locality H-GSP 62, are characterized by a high-diversity paleofauna and generally random and unsorted fossil bone distributions, which suggest that the fossils from these localities represent longer time intervals than the Barbora Banda fossils. Based on the time estimates for Kuldana paleosol development, fossil assemblages in Kuldana channel deposits in the Kala Chitta Hills region probably represent time intervals of about 1000 years. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Origins of avian reproduction: answers and questionsfrom dinosaurs.David J. Varricchio and Frankie D. JacksonKeywords: Avian reproduction; clutch; dinosaurs; egg size; nests; oviducts; parental careAbstract The reproductive biology of living birds differs dramatically from that of other extant vertebrates. Distinctive features common to most birds include a single ovary and oviduct, production of one egg at daily or greater intervals, incubation by brooding and extensive parental care. The prevalence of male parental care is most exceptional among living amniotes. A variety of hypotheses exist to explain the origin of avian reproduction. Central to these models are proposed transitions from a condition of no care to maternal, paternal or biparental care systems. These evolutionary models incorporate a number of features potentially preservable or inferable from the fossil record (integument, skeletal adaptations for flight, egg and clutch size, nest form, hatchling developmental stage, the number and function of oviducts, and the mode of egg incubation). Increasing availability of data on dinosaur reproduction provides a means of assessing these hypotheses with fossil evidence. We compare dinosaur data to a selection of models that emphasize maternal, paternal or biparental care. Despite some congruence with dinosaur features, no single model on the evolution of avian reproduction conforms fully to the fossil record, and the ancestral parental care system of birds remains ambiguous. Further investigation into dinosaur parental care, nest structures, clutch geometry, egg-pairing, eggshell porosity, and embryo identification may eventually resolve these issues. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|