Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
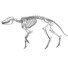
Artiodactyla aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bei Halle (DDR)Jorg Erfurt and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Artiodactyles; Eocene; Europe; Paleoecology; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The present study of Artiodactyla from the Middle Eocene of the Geiseltal lignite beds concems systematics, biostratigraphy, and palaeoecology on the basis of 174 specimens: isolated remains to more complete skeletons. Instead of the formerly known five species of two families are now recognized 14 species of the Diacodexeidae, Dichobunidae, Cebochoeridae, and Haplobunodontidae. New species are Aumelasia maniai, Anthracobunodon neumarkensis, Masillabune franzeni. Four species of the Geiseltalfauna are definitely known from elswere, and five species are closely related to those from other European localities. Evidently the faunal situation of artiodactyls during the Middle Eocene of Europe was largely uniform. The distribution of artiodactyls within the sequence of the Geiseltal strata corroborates the biostratigraphical concept of the land mammal age Geiseltalian (Franzen & Haubold l986b) as well as the mammalian reference levels MP 11-13 (Franzen 1987). Reconstructions of the skulls and skeletons allow conclusions on the functional morphology and palaeoecology of the artiodactyls of the European Middle Eocene Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|
|
Les Amphibiens et les reptiles du Pliocène supérieur de Balaruc II (Herault, France)Salvador BailonKeywords: amphibians; Europe; France; Pliocene; ReptilesAbstract The late Pliocene site (MN 16) of Balaruc II (Hérault, France) has provided remains of the following amphibians and reptiles: Chelotriton pliocenicus nov. sp. and Triturus marmoratus (Salamandridae), cf. Rana (Ranidae), cf. Blanus (Amphisbaenidae), cf. Agama (Agamidae), Gekkonidae indet., Lacerta s.l. (Lacertidae), "Ophisaurus" sp. (Anguidae), Michauxophis occitanus (Aniliidae), Erycinae indet. (Boidae), Elaphe cf. E. longissima and Malpolon sp. (Colubridae), cf. Naja (Elapidae) and Vipera sp. (Viperidae). The salamandrid Chelotriton pliocenicus and the aniliid Michauxophis occitanus constitute, up to now, the only records of these groups in the European Pliocene. The fauna is indicative of a warm, dry Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|
|
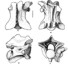
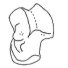
Mode de vie et affinités de Paschatherium (Condylarthra, Hyopsopontidae) d'après ses os du tarseMarc Godinot, Thierry Smith and Richard SmithKeywords: Astragalus; Calcaneum; Condylarthra; Eocene; Functional morphology; Paschatherium; PHYLOGENYAbstract Tarsals that can be confidently attributed to Paschatheríum dolloi from Dormaal (Belgium) are described. The astragalus is short; its broad neck is set at an angle of 30 degrees to the trochlea. The trochlea is pulley-shaped and proximally extended. There is no astragalar foramen. The medial tibial facet extends distally in a cup deeply excavated in the neck and buttressed. The sustentacular facet extends toward the navicular facet but is not fully confluent with it. The calcaneum bears a proximo-distally extended proximal facet for the astragalus. A relatively large peroneal tubercle projects from the body, and is situated distally. Functionally, the trochlea indicates extensive flexion-extension movements of the foot. Calcaneo-astragalar facets indicate sliding and rotation between the two tarsals. The inclination of the navicular facet suggests frequent foot inversion. The peroneal tubercle reflects good muscular capacities for foot rotation. Overall morphology is interpreted as a scansorial adaptation similar to that of sciurids.Comparisons are made with the tarsals of Macrocranion vandebroeki from Dormaal and Hyopsodus paulus from the Bridgerian of Wyoming. Some similarities between the astragali of Paschatherium and Macrocraníon (trochlea) are interpreted as convergences for rapid locomotion. However absence of mobility at the lower ankle and midtarsal joints in M. vandebroekzi suggests that this species was cursorial, as is known for M. tenerum from Messel. Similarities in the calcanea of Paschatherium and Hyopsodus are probably the result of close phylogenetic relations, and confirm the placement of Paschatherium in the hyopsodontids. The differences in the calcanea of Paschatherium and Macrocranion underline that Paschatherium is distinct from erinaceomorph insectivores. The differences in astragalar morphology between Paschatherium and Hyopsodus show that a marked adaptive divergence separates the two genera. We speculate about the common occurrence of a deep tibial cup (“cotylar fossa”) and a pulley-shaped trochlea in Paschatherium and hyracoids, suggesting that an adaptive scenario similar to that having led to Paschatherium (scansoriality) might explain the acquisition of the peculiar hyracoid tarsal characters; such a scenario contradicts the concept of Pantomesaxonia. Other peculiar characters of Hyopsodus suggest that hyopsodontids might be given more consideration in the search for hyracoid (and tethythere) origins. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
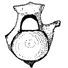
First report of an Eocene reptile fauna from Florida, USAAlan J. HolmanKeywords: Eocene; Fauna; Florida; Reptile; USAAbstract Fossils of the Trionychidae, Bataguridae or Emydidae, Palaeophis and Crocodylia from Chattahoochee, NW Florida, USA, represent the first report of an Eocene reptile fauna from Florida. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|
|
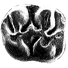
Nouveaux gisements à rongeurs dans les molasses oligo-miocènes de la région toulousaineFrancis DuranthonKeywords: Cricetidae; Eomyidae; GIiridae; Miocene; Oligocene; Rodents; Sciuridae; Southern FranceAbstract The fauna from three new rodent localities (Castelmaurou, Grépiac-carrière et Grépiac-rive gauche) from Oligo-Miocene molasses of the Toulouse area is described. The one from Colomiers is completed. 11 species belonging to 4 families (Cricetidae, Eomyidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) are present. The Miocene localities of Grépiac-carrière and Colomiers are correlated with Balizac, La Brète, Lambert and Lespignan. Grépiac-rive gauche is just a little older than these sites. Castelmaurou is somewhat younger than La Milloque and belongs to Oligocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|

|
Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II (Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc)Bernard MarandatKeywords: Collections; Inventory; Type specimens; University Montpelllier IIAbstract More than 400 paleontological type-specimens housed in the Montpellier University collections have been inventoried in this catalogue which includes charophytes, Paleozoic plants, brachiopodes, molluscs, arthropodes and vertebrates (selachians, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals). The vertebrates have been treated exhaustively in the catalogue and one can consider that it includes most of the type specimens deposited in the Montpelier II collections. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Ext (1994) |
|
|

|
Etude du crâne de Pachynolophus lavocati n. sp. (Perissodactyla, Palaeotheriidae) des Phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Perissodactyla; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.5.2.45-78 Abstract The genus Pachynolophus, one of the poorest known of the Palaeotheriidae, includes the brachyodont forms with reduced and non-molariform premolars and with upper molars lacking a mesostyle. Quantitative characters (divers surface indications and elongation of the teeth), while demonstrating a close relationship to Hyracotherium, permit a better differentiation of the genus, confirm its specific splitting, and permit the distinction of three lineages. The skull from Memerlein is taken as the type of a new species, P. Iavocati, of which the dentition is extremely characterized by its lophiodonty, the strong reduction of the premolars and the reduction of the cingula. This characterization testifies to a late age which extends the existence of the genus quite near to the Eocene-Oligocene limit. Compared with the only two skulls known of related species (Hyracotheríum vulpiceps and Pachynolophus Iivinierensis), that from Memerlein is distinguished by progressive characters affecting diferent regions but most particularly the braincase; it is not possible, however, to isolate within this evolution the part which leads to a systematic differentiation. Modernization is translated by a considerable increase in size of the braincase, principally in the frontal region, a development of the facial region with anterior displacement of the dental series and a greater specialization of the masticatory apparatus. This evolution parallels the history of the Equidae of the North American early Tertiary, but certain particularities, the form of the alisphenoid, the presence of an anterior frontal foramen, and the structure of the paroccipital apophysis, testifies to the independance of the European forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 2 (1972) |
|
|

|
Fossil mammals and the age of the changxindian formation, Northeastern ChinaSpencer G. LucasKeywords: Changxindian Formation; China; Eocene; Fossil mammalsAbstract Re-evaluation of the small collection of mammal fossils from the Changxindian Formation near Beijing, China indicates the following taxa are present: Eutheria, Hypsimilus beifingensis, cf. Miacis sp., Anthracotheriidae and Forstercooperia grandis. The presence of Forstercooperia grandis indicates an Irdinmanhan age and does not support previous assignment of a Sharamurunian age to the Changxindian Formation. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Saturnin Garimond (1914-1987)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: biographyAbstract Biographie et liste des publications de S. Garimond. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 3 (1987) |
|
|
|
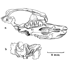
Les rongeurs de l'Oligocène inférieur d'EscampsMonique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Escamps; Quercy Phosphorites; Rodents; TheridomyidaeAbstract La faune de Rongeurs d'Escamps (Lot) bien que relativement pauvre en espèces (dix) s'avère riche d'enseignement pour les Rongeurs de l'Oligocène inférieur d'Europe Occidentale. Cette periode semble caracterisée par une cladogenèse des Théridomyines. A Escamps, un nouveau genre (Patriotheridomys) est décrit ainsi qu'une nouvelle espèce de Theridomys. Avec Oltmamys platyceps, décrit ici plus complètement et désormais bien situé stratigraphiquement, les deux espèces précédentes constituent un ensemble original du Sud de la France. A la même époque, en Angleterre, Allemagne et Espagne, des espèces «régionales» de Théridomyinés se dersifient. A côté de ces formes qui ne semblent pas franchir la «Grande Coupure» sont représentées deux lignées d'Issiodoromyinés (Elfomys sp et Pseudoltmomys cuvieri), une de Théridomyiné (T. (Blainvillimys) rotundidens) ainsi qu'un Gliridé, Gliravus priscus (que l'on différencie nettement de la deuxième lignée des Gliravus oligocènes : G. meridionalis -> G. majori). On retrouve ces formes dans les gisements plus récents du niveau de Hoogbutsel où elles sont à peine plus évoluées. Le fait que les degrés évolutifs de ces lignées soient très proches laisse supposer que le laps de temps séparant les niveaux d'Ecamps et Hoogbutsel fut relativement court. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
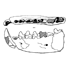
Pantolestidae nouveaux (Mammalia, Insectivora) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller (Alsace).Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Bouxwiller; Insectivora; Mammalia; Middle Eocene; Pantolestidaedoi: 10.18563/pv.3.3.63-82 Abstract The Pantolestidae from the middle eocene of Bouxwiller are the subject of a detailed study. Buxolestes hammeli (n. g., n. sp.) is not closely related to any other European or North American form described until now; it presents, however, some characters in common with Pantolestes, a form of the same age from North America. A parallel evolution from a common ancestral form could explain this ressemblance. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 3 (1970) |
|
|
|
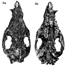
Ein neuer condylarthre und ein tillodontier (Mammalia) aus dem Mitteleozän des Geiseltales.Jens L. Franzen and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Condylarthra; Eocene; Europe; Mammalia; taxonomy; TillodontiaAbstract In the course of a revision of the Equoidea numerous dentitions as well as a partial skeleton of a Phenaeodont were discovered from the Middle Eocene lignite beds of the Geiseltal locality. These fossils are recognized as a new genus and species of Phenacodontidae : HaIlensia matthesi n.g. n.sp.. The species is present in the « untere und obere Unterkohle ›› (uUK, oUK = the lower and upper part of the Lower Coal Seam) as well as in the « obere Mittelkohle ›› (oMK = the upper part of the Middle Coal Seam). Two fragmentary upper jaws described and figured by Matthes (1977) as Propachynolophus gaudryi are also belonging to Hallensia matthesi. Thus the decisive argument for classifying the " Unterkohle " of the Geiseltal section as Lower Eocene has to be dropped. Another relict form of the Geiseltal is Esthonyx tardus n. sp. documented by a fragmentary mandible coming from the « untere Unterkohle ››. This is the latest Tillodont from Europe. Contrasting to E. munieri from the european Lower Eocene the dentition of E. tardus is morphologically more progressive. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
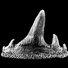
A survey of Cretaceous tribosphenic mammals from middle Asia (Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and Tajikistan), of their geological setting, age and faunal environmentLev A. Nessov, Denise Sigogneau-Russell and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Cretaceous; Environment; Middle Asia; Sharks; Tribosphenic mammalsAbstract This paper is an English concentrate of various Russian publications by the senior author presenting the mammaIian taxa from the Cretaceous (Albian through Santonian) of the region termed Middle Asia by Soviet geographers. The diagnoses are the unmodified, literal translation of the original version, but are followed with short complementary remarks; most of the species are illuslrated anew with SEM photographs, others are by normal photography. The fossiliferous formations are cited and arguments for their dating are given. Finally, the main vertebrate groups accompanying mammaIs are listed and the environment and climate at the time of deposition are suggested. In conclusion, an hypothesis on the origin and high diversity of tribosphenic mammals on the Cretaceous coastal plains of southwest Asia is proposed. In appendix the taxon Khuduklestes bohlini novo gen. novo sp. is formally defined. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Experimental taphonomy inavian eggs and eggshells: effects on early diagenesis.Ana M. Bravo, D. A. Buscalioni, Lauro Merino and B. G. MüllerKeywords: archosaurian eggshells; avian egg; Experimental taphonomy; geochemical analysis; pyritisation; Upper CretaceousAbstract We experimentally explore the early taphonomic stages involving the decay and biodegradation of buried eggs and eggshells. Unfertilised commercial chicken eggs and eggshell fragments were buried in plastic containers and were kept under controlled conditions for eight months. Half of the containers were filled with marl, and the remainder with sand. All were saturated with fresh tap water, acidified water, sulphate water, or seawater. They were kept in the dark at 23.4-26 °C, except one, which was kept in a heating chamber at 37.4°C. We expected that different burial conditions would produce distinct taphonomic outcomes. Instead, the taphonomic alterations of buried eggs parallel that of the alteration of egg proteins (i.e., denaturation and/or putrefaction) with an additional role played by the eggshell. Mummification, encrustation, distortion and fragmentation, and necrokynesis (vertical displacement) depend on organic matter decay. The experiment identifies environmental conditions that may favour or actively promote these taphonomic processes. Of these, early pyritization is one of the most relevant. For comparative purposes, samples of fossil and extinct eggshell representing three distinct environmental burial conditions were examined. These included Megaloolithus, Caiman crocodilus, and Struthio camelus ootypes. The geochemical analysis of these eggshells showed no significant differences among the chemical variables of these fossil and extant ootypes. Eggshells exhibited a stable composition over a range of experimental conditions. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
|
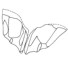
A new species of chimaeroid fish from the upper Paleocene (Thanetian) of Maryland, USAGerard R. CaseKeywords: Chimaeroid nov. sp.; Maryland; U.S.A.; Upper PaleoceneAbstract The recent discovery of several mandibular toothplates of a chimaeroid fish at a dig in the area of the Landover Mall, near Landover, Prince Georges County, Maryland, brings to our attention a new species of the chimaeroid, Ischyodus. Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Fasc. 1-2 (1991) |
|
|
|
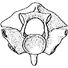
Les serpents des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Claude RageKeywords: Grande Coupure; Quercy Phosphorites; SerpentsAbstract A short review of the genera and species of snakes from the Quercy's phosphorites described by former authors is followed by the study of specimens recently collected. Most of these latter specimens belong to the Aniliidae, Boidae, Colubridae and to the Scolecophidia; the precise systematic position of some of them is not defined yet. The following genera and species are described: Eonilius europae nov. gen. and nov. sp., Platyspondylia lepta nov. gen. and nov. sp., Coluber cadurci nov. sp. and Dunnophis cadurcensis nov. sp.; a species described by de Rochebrune (Palaeopython filholi) is revised. One of the most important conclusions of this study is that the Colubridae appear as early as the Upper Eocene. The stratigraphic repartition of these snakes shows that the rich Upper Eocene fauna is followed by the very reduced fauna of the Lower Oligocene; then the oligocene «Grande Coupure» corresponds to a very important faunistic renewal. The fauna remains poor and little diversified during the beginning of the Middle Oligocene after which there is a new faunistic explosion. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
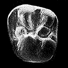
Middle Eocene rodents from the Subathu group, Northwest Himalya.Kishor Kumar, Rahul Srivastava and Ashok SahniKeywords: Chapattimyidae; Eocene; evolution; India; Rodentia; Subathu group; SystematicsAbstract Extensive collecting in previously known and new Middle Eocene rodent localities in the Subathu Group of the Rajauri and Reasi districts, Jammu and Kashmir (northwest Himalaya, India) has yielded over 500 isolated cheek teeth, numerous incisors and cheek tooth fragments, and two mandibular fragments with M/1-M/3. An analysis of this additional material and a restudy of that reported earlier from the Metka (Rajauri) area has revealed the presence of diverse Middle Eocene ctenodactyloid rodents in India. The assemblage comprises six genera and twelve species, viz.., Bírbalomys woodi, B. ibrahimshahi, B. sondaari, Basalomys vandermeuleni, B. ijlsti, B. lavocati, Chapattimys wilsoni, C. debruijni, Gumbatomys asifi, cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 1 and cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 2. Most species of this assemblage are endemic to the Indian subcontinent and are referred to the Family Chapattimyidae. However, at least three taxa, viz.., cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp.indet. 1 and cf. Pezrokoslovia sp. indet. 2 show close affinities with their Central and Eastern Asiatic contemporaries and are attributed to the Family Yuomyidae. The dentitions of most of the Middle Eocene rodents from India are described here in better detail thus providing more precise characterization than was available earlier. The taxonomie status of Basalomys, formerly a subgenus of Birbalomys has been raised to that of a genus. Basalomys vandermeuleni is here designated as the type species of Basalomys in place of B. ijlsti. The rodent assemblage from the Subathu Group is specifically similar to that from the coeval Kuldana Formation of Pakistan. The absence of Birbalomys ibrahimshahi and cf. Advenimus bohlini in Pakistan is related to sampling bias. The identifications of the Early Eocene rodents from Barbara Banda, Pakistan have been reexamined and the familial assignments of some of the Early and Middle Eocene rodents from Central and Eastern Asia have been discussed and reviewed in the light of recent discovery of early rodents in Mongolia. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|
|
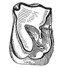
Hyracodontids and rhinocerotids (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Rhinocerotoidea) from the Paleogene of MongoliaDemberelyin DashzevegKeywords: Hyracodontidae; Mongolia; Paléogène; Perissodactyla; RhinocerotidaeAbstract Two families are reviewed (Hyracodontidae and Rhinocerotidae) from the Paleogene of Mongolia. The following taxa are described from the former family: Triplopus? mergenensis sp. nov., Prohyracodon meridionale CHOW, Prohyracodon? parvus sp. nov., Forstercooperia ergiliinensis GABUNIA & DASHZEVEG, Ardynia praecox MATTHEW & GRANGER, A. mongoliensis (BELIAYEVA), Ardynia sp., Urtinotheríum sp. (or Indricotherium) and Armania asiana GABUNIA & DASHZEVEG. All of them are from the Paleogene of the eastem Gobi Desert The hyracodontid Pataecops parvus RADINSKY is described from a new locality, Menkhen-Teg (Middle Eocene), in the Valley of Lakes. Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Fasc. 1-2 (1991) |
|
|
|
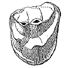
La plus ancienne faune de mammifères du Quercy : Le BretouJean-Louis Hartenberger, Bernard Sigé and Jean SudreKeywords: Le Bretou; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
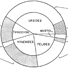
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 8 - Analyse paléoécologique de la faune mammalienneSerge LegendreKeywords: France; Mammalia; Montredon; Paleoecology; Upper MioceneAbstract The species diversity of the mammalian fauna from Montredon (Hérault, France, late Miocene) is examined in terms of richness and abundance. A cenogramic analysis of the fossil mammalian community suggests the prevalence of open habitats, with the presence of marshes and of a poorly developed galery forest, and a climate rather warm and dry. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|