Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
A new vertebrate locality in the eifelian of the khush-yeilagh formation, Eastern Alborz, IranAlain Blieck, Farrokh Golshani, Daniel Goujet, Amir Hamdi, Philippe Janvier, Elga Mark-Kurik and Michel MartinKeywords: Devonian; Iran; khush-yeilagh formation; VertebrateAbstract A new Devonian vertebrste locality has been discovered in 1976 in the basal part of the Khush-Yeilagh Formation in the eastern Alborz Mountains of Iran. The fossils occur in a band one centimeter thick which is identifiable at other outcrops in the area. A preliminary study of the remains has yielded the following faunal list : Placodermata (Phlyctaeniida indet.. Groenlandaspididae indet.. Coccosteidae indet., Holonema sp., Ptyctodontida indet., Antiarcha indet., Bothriolepis cf. kwangtungensis), Elasmobranchii (Ctenacanthidae indet.), Acanthodii (Gyracanthus sp., « Onchus » overathensis, Ischnacanthiforme indet.), Dipnoi (? Dipteridae indet.), « Crossopterygii ›› (Onychodus cf. sigmoides, Holoptychiidae indet., Osteolepididae indet.). This fauna is older than the Middle Givetian and probably of Middle or Lower Eifelian age. Owing to its diversity, it may prove possible to use it in the future as a reference fauna for the study of the Devonian vertebrates in Central Asia and the Middle East. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 5 (1980) |
|
|

|
Preliminary report on the fishes (Chondrichthyes & Teleostei) from the lower Oligocene (Rupelian) Red Bluff Clay at site AMo-9, Monroe County, Alabama, USAJun A. Ebersole, David J. Cicimurri, Lindsey M. Stallworth and Andrew D. GentryKeywords: Batomorphii; Elasmobranchii; Galeomorphi; Gulf Coastal Plain; Vicksburg Groupdoi: 10.18563/pv.47.2.e2 Abstract Herein we describe a small but relatively diverse assemblage of fossil fishes derived from the lower Oligocene (Rupelian) Red Bluff Clay at site AMo-9 in Monroe County, Alabama, USA. Identified amongst the remains are 15 unequivocal taxa representing 11 families within five orders, and one additional taxon represents an unknown order and family. Taxa identified include Eostegostoma sp., Otodus (Carcharocles) sp., Mitsukurinidae/Carchariidae indet., Macrorhizodus praecursor, Galeorhinus sp., Negaprion gilmorei, Physogaleus sp., “Sphyrna” sp., Galeocerdo sp., cf. “Aetobatus” sp., Sphyraena sp., Xiphiorhynchus kimblalocki, Xiphiorhynchus sp., Cylindracanthus ornatus, and C. rectus. Several additional fossils could not be identified beyond Lamniformes, Carcharhiniformes, and Teleostei, but they likely belong to one of the identified taxa within this paleofauna. All of the fishes previously reported from the Red Bluff Clay within the entirety of the Gulf Coastal Plain of the USA are otolith-based, and each of the 15 unequivocal taxa reported herein are important new records for this lithostratigraphic unit. In particular, the Eostegostoma sp. and Xiphiorhynchus spp. specimens represent the first occurrences of these taxa in Alabama. The specimens of C. ornatus, Eostegostoma sp., and X. kimblalocki are stratigraphic and temporal range extensions from the middle and late Eocene into the Rupelian Stage of the Oligocene. Other described taxa may represent transitional forms between those described from the late Eocene and late Oligocene within the region. This study provides a tantalizing preliminary view into faunal transitions that occurred amongst marine fishes across the Eocene/Oligocene boundary within the Gulf Coastal Plain of the USA. Article infos in press |
|
|
|
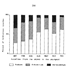
Analysis of mammalian communities from the late Eocene and Oligocene of southern FranceSerge LegendreKeywords: Late Eocene; Mammalian communities; Oligocene; Quercy; Southern FranceAbstract Valverde's cenogram method is used to analyse mammalian communities from the late Eocene to late Oligocene of southern France, mainly from the "Phosphorites du Quercy". Cenogram analysis involves plotting the size of each component species in a fauna on a semilog diagram in rank order, permitting fossil faunas to be compared with Recent ones. The configurations of Recent communities serve as models for establishing the general environmental characteristics of fossil mammalian faunas. This method of analysis applied to faunal sequence can reveal major and sudden ecological perturbations. The paleobiogeographical event (i.e. the mammalian immigration wave) at the Eocene-Oligocene Boundary in western Europe, known as the «Grande Coupure", is here shown to represent a drastic and sudden ecological change: late Eocene tropical environments in Europe deteriorated rapidly turning to subdesert or desert environments al the beginning of the Oligoccne. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 4 (1986) |
|
|
|
New remains of the very small cuckoo, Chambicuculus pusillus (Aves, Cuculiformes, Cuculidae) from the late Early/early Middle Eocene of Djebel Chambi, TunisiaCécile Mourer-Chauviré, El M. Essid, Hayet Khayati Ammar, Laurent Marivaux, Wissem Marzougui, Rim Temani, Monique Vianey-Liaud and Rodolphe TabuceKeywords: Cuckoos; Eocene; Fossil birddoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e2 Abstract Abstract: A very tiny cuckoo, Chambicuculus pusillus, was recently described after a few fragments of tarsometatarsi from the late Early/early Middle Eocene of Djebel Chambi, Tunisia. New remains, notably a coracoid, confirm the attribution of this genus to the recent family Cuculidae. This coracoid shows a very elongate and strap-like processus procoracoideus. This morphological feature is otherwise only known in the family Cuculidae. The characteristics of the coracoid and tarsometatarsi show that Chambicuculus is morphologically more advanced over the other stem cuculids described in Europe and North America. Chambicuculus is the oldest Cuculidae known so far. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
|
|
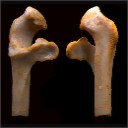
A primitive Emballonurid bat (Chiroptera, Mammalia) from the Earliest Eocene of EnglandJerry J. HookerKeywords: bats; Early Eocene; Emballonuridae; Origins; PHYLOGENYAbstract A new genus, Eppsillycteris, is erected for Adapisorex? allglicus COOPER, 1932, from the earliest Eocene Blackheath Beds of Abbey Wood, London, England. Various derived character states indicate that it belongs to the order Chiroptera (bats) rather than to the extinct "insectivore" family Adapisoricidae. Other derived character states are shared with fossil and modern members of the family Emballonuridae. Placement of the new genus in this family extends the record of the Emballonuridae back in time by about 10 million years. It is the earliest record of a modern bat family and one of the earliest bats. This implies that the differentiation of at least some modern bat families took place in the Palaeocene, where no authenticated records of bats yet exist. The primitive characters of the earliest bats make the family Nyctitheriidae an unlikely stem group for the order Chiroptera. A tentative plausible alternative exists in some unnamed upper molars from the Palaeocene of Walbeck, Germany. Wyollycteris chalix, described as a bat from the Late Palaeocene of Wyoming, U,S.A., fits better in the family Nyctitheriidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Second international symposium on Dinosaur, Eggs and Babies (Montpellier-Aix-en-Provence, 25-29 Août 2003).Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: amniotic eggshells; dinosaursAbstract Le premier Symposium International sur les ceufs de dinosaures et leurs petits a connu un francs succès, à Isona, en Catalogne (Espagne) en 1999. I1 faisait suite à la publication en 1994 d'un premier ouvrage "Dinosaurs eggs and babies" édité par K. Carpenter, K. Hirsch et J. Homer. Entre 1994 et 1999, les nouvelles découvertes ont augmenté significativement, notamment celles d'ceufs embryonnés, et le nombre de chercheurs impliqués dans ce domaine a accompagné cet accroissement. Jusque là, l'étude de ces objets, les coquilles d'ceufs, est restée longtemps marginale, faute d'une méthodologie scientifique appropriée. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|

|
The lower Miocene artiodactyls of Tagai bay, Olhon island, lake Baikal (Russia)Inesa VislobokovaKeywords: Artiodactyls; Mammals; Miocene; SiberiaAbstract The mammalian fauna of the Tagai locality of Olhon Island in Lake Baikal contains six artiodactyls: Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
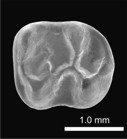
A new and primitive species of Protophiomys (Rodentia, Hystricognathi) from the late middle Eocene of Djebel el Kébar, Central TunisiaLaurent Marivaux, El M. Essid, Wissem Marzougui, Hayet Khayati Ammar, Sylvain Adnet, Bernard Marandat, Gilles Merzeraud, Rodolphe Tabuce and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Adaptive radiation; Bartonian; Dental morphology; North Africa; Paleobiogeographydoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e2 Abstract Based on fossil discoveries and phylogenetic studies, an Eocene Asian origin for hystricognathous rodents and anthropoid primates has gained strong support in recent years. The two groups then invaded both Africa and South America, which promoted their evolutionary success. However, the fossil record has so far failed to constrain the nature and precise timing of these pivotal dispersal events. In Africa, given the apparent absence of hystricognaths and anthropoids in early to early middle Eocene localities, it is suggested that these mammal groups dispersed from Asia to Africa sometime during the middle Eocene. In this paper, we report the discovery of several isolated teeth of a rodent from a new vertebrate locality situated in central Tunisia (Djebel el Kébar, KEB-1), dating from the late middle Eocene (Bartonian, ~39.5 Myr). These fossils document a diminutive new species of Protophiomys (P. tunisiensis nov. sp.), a basal genus of hystricognathous rodents which is well known from several North African mammalian-bearing localities of the end of the Eocene. The teeth of P. tunisiensis display a suite of anatomical details comparable with those observed in the other species of the genus, but with a lesser degree of development. Such an apparent primitive evolutionary stage is corroborated by the greater antiquity of this Tunisian species. P. tunisiensis nov. sp. is so far the most ancient representative of hystricognaths in Africa. However, it can be expected that hystricognaths were already present on that landmass given the new data on early caviomorphs recently reported from South America (at ~41 Myr). The arrival of hystricognaths in Africa from South Asia certainly predates the depositional period of the Kébar sediments, but perhaps not by much time. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|
|
|
Types dentaires adaptatifs chez les sélaciens actuels et post-paléozoïques.Henri CappettaKeywords: Dental types; evolution; Fossil selachians; Recent selachians; Trophic adaptationsAbstract The dentition of selachians is characterized by an often very pronounced heterodonty involving a great morphological diversity. Despite this fact, the dentitions of selachians can be grouped in a rather reduced number of dental types corresponding to trophic adaptations: grasping, tearing, cutting, crushing, grinding and grasping-grinding type. The numerous exemples of convergence and parallelism that can be observed in fossil selachians and between Recent and fossil ones is the result of this reduced number of dental types. These dental specialisations allow to try a reconstruction of the way of life of fossil forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 2 (1986) |
|
|

|
Revision des faunes de vertébrés du site de Provenchères-sur-Meuse (Trias terminal, Nord-Est de la France)Gilles CunyKeywords: amphibians; Fishes; Reptiles; Rhetian; TriassicAbstract Revision of ancient collections and study of new material from Provenchères-sur-Meuse (Rhaetian) lead to signíficant changes in the faunal list of this site. This bring to us important information about the effect of the rhaetian transgression on the evolution of the faunas at this period of time. However, study of Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|

|
Fossil mammals and the age of the changxindian formation, Northeastern ChinaSpencer G. LucasKeywords: Changxindian Formation; China; Eocene; Fossil mammalsAbstract Re-evaluation of the small collection of mammal fossils from the Changxindian Formation near Beijing, China indicates the following taxa are present: Eutheria, Hypsimilus beifingensis, cf. Miacis sp., Anthracotheriidae and Forstercooperia grandis. The presence of Forstercooperia grandis indicates an Irdinmanhan age and does not support previous assignment of a Sharamurunian age to the Changxindian Formation. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
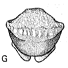
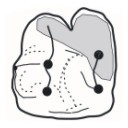
A late Eocene palaeoamasiine embrithopod (Mammalia, Afrotheria) from the Adriatic realm (Island of Rab, Croatia)Fabrice Lihoreau, Ljerka Marjanac, Tihomir Marjanac, Ozan Erdal and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: Balkanatolia; Grande Coupure; Great Adria; Paleobiogeography; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.47.1.e1 Abstract A cheek tooth recently unearthed in the Lopar Sandstone unit, of late Eocene age, in the northern part of Rab Island, Croatia, is one of the very few Eocene mammalian remains found in the Adriatic area. Thorough comparison of this tooth with those of Old-World Palaeogene mammalian orders suggests that it is a M3 belonging to an embrithopod afrothere. The specimen is referred to as Palaeoamasia sp. This genus was formerly known only in Eocene deposits of Anatolia but with close relatives in Romania among Palaeoamasiinae. The geographical distribution of this subfamily perfectly matches the recently-named Balkanatolian landmass, which experienced in-situ evolution of endemic mammals prior to the Grande Coupure event that occurred around the Eocene–Oligocene transition. This last event is characterised by massive Asian immigration in Western Europe and the supposed extinction of many endemic Central and Western European mammals, including Palaeoamasiinae. Article infos Published in 47-1 (2024) |
|
|

|
Batoids (Rajiformes, Torpediniformes, Myliobatiformes) from the Sülstorf Beds (Chattian, Late Oligocene) of Mecklenburg, northeastern Germany: a revision and description of three new speciesThomas ReineckeKeywords: Batoids; Chattian; Elasmobranchii; North Sea Basin; Oligocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e2 Abstract Bulk-sampling of fossil-rich tempestites from the Chattian Sülstorf Beds of Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|

|
Introduction à l'oeuvre scientifique de Donald E. Russell, "gentleman paleontologist"Marc Godinot and Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: D.E.Russell; Eocene; Mammals; Paleocene; Paleontology; synthesisAbstract The scientific career of D.E. Russell began with a Pliocene fauna from Oregon, and then turned in the direction of European Paleogene mammals. Field work followed by study of the mammals that were collected, firstly in the Paleocene and later in the early Eocene, greatly rejuvenated learning in this field. Syntheses on the Northwest European Tertiary basin and on European marnmals and stratigraphy came next. Research on the Eocene of Asia was carried out jointly with Gingerich on Pakistan and with Dashzeveg on the faunas of Mongolia. An important synthesis on the entire Paleogene of Asia, joint with Zhai, followed. Field work in Africa with Sigogneau-Russell led to the discovery of Mesozoic mammals there. A synthesis of mammalian paleofaunas of the world was written with Savage, and a similar synthesis of Cenozoic vertebrate faunas is currently being prepared. These achievements reflect the perennial importance of field work, numerous collaborations with both amateurs and professionals, and the human qualities of this author. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Mammals of the Eocene locality Toru Ajgyr (Kyrgyzstan)Jorg Erfurt and Alexander AverianovKeywords: Eocene; Kyrgyzstan; Mammalia; Olsenia; Palaeoecology; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract Morphological descriptions are given of Eocene mammals from the locality Toru Ajgyr (NEKyrgyzstan) that were excavated in 1997 and 1998 in a cooperation between the Martin-Luther-University Halle (Germany), the Zoological Institute in St. Petersburg (Russia) and the Seismological Institute in Bishkek (Kyrgyzstan). The species found belong mostly to perissodactyls, as Lophialetes sp., Teleolophus sp. and brontotheres. The primitive ungulate family Olseniidae is represented by a complete foot skeleton of cf. Olsenia sp. In addition, postcranial materials of Gobiatherium mirificum (Dinocerata) and of artiodactyls have been collected and are described herein. Based on mammals, the locality is part of the Asian Land Mammal Age Arshantan and is stratigraphically equivalent with the Bridgerian Land Mammal Age in North America and with the lower and middle Geiseltalian of the European Middle Eocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 34, Fasc. 3-4 (2006) |
|
|

|
Study of the Turolian hipparions of the lower Axios valley (Macedonia, Greece). 4. Localities of Dytiko.George D. KoufosKeywords: Equidae; Greece; Hipparion; Lower Axios Valley; Macedonia; Mammalia; TurolianAbstract The hipparions from the Dytiko localities of the lower Axios valley (Macedonia, Greece) are studied. The material comes from three localities Dytiko-l, 2, 3 (DTK, DIT, DKO), which are situated near the village of Dytiko, about 60 km northwest to Thessaloniki. Three species have been determined, the medium-sized H. mediterraneum, the small-sized H. matthewi and the very small-sized H. periafricanum. The determined Hipparion species, their morphological characters and their comparison with the other Axios valley material indicate a Late Turolian age for the Dytiko localities. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 4 (1988) |
|
|

|
Hexanchiforme nouveau (Neoselachii) du Crétacé inférieur du Sud de la FranceHenri CappettaKeywords: Hexanchiformes; New genera; Southern France; Systematics; ValanginianAbstract The dentition of Welcommia bodeuri nov. gen. nov. sp. from the Valanginian of Southem France is described and reconstructed. Species and genera of Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous Hexanchiformes are reviewed and discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 1 (1990) |
|
|

|
Preliminary evolution of paleosols and implications for interpreting vertebrate fossil assemblages, Kuldana formation, Northern PakistanAndres Aslan and J. G. M. ThewissenKeywords: Eocene; Kuldana Formation; Pakistan; Paleosols; Pedogenic Carbonate; taphonomy; Time Averaging; Vertebrate FossilsAbstract Paleosols and the taphonomy of vertebrate fossils in the Eocene Kuldana Formation of northern Pakistan provide important information on the preservation and time-averaging of fossil assemblages. Morphologic, mineralogic, and chemical data as well as comparisons with Quaternary soils suggest that Kuldana paleosols formed under generally dry and oxidizing conditions over time intervals of less than 100 000 years and perhaps as short as 1000 years. The distribution of carbonate in Kuldana paleosols further indicates that the upper half of the profiles were acidic whereas the lower halves were alkaline. Vertebrate fossils are rare in Kuldana paleosols and occur primarily in well-cemented sandstones and conglomerates with abundant micritic and iron-stained nodules that were reworked from floodplain soils. The scarcity of vertebrate remains in Kuldana paleosols probably reflects a combination of acidic, dry, and oxidizing conditions in the upper half of the profiles and rapid floodplain sedimentation. Comparisons between the taphonomic characteristics of Kuldana channel fossil assemblages and bone accumulations in modem rivers provide a basis for estimating the length of time represented by Kuldana fossils from several important localities. Vertebrate fossil assemblages from Barbora Banda are characterized by a low-diversity paleofauna, partially articulated skeletons, and bones that are sorted by size and shape. Comparison with bone accumulations in modern rivers suggests that the fossils from Barbora Banda accumulated in 1 to 10 years. Vertebrate fossils from the Lower Kuldana in the Kala Chitta Hills region, typified by locality H-GSP 62, are characterized by a high-diversity paleofauna and generally random and unsorted fossil bone distributions, which suggest that the fossils from these localities represent longer time intervals than the Barbora Banda fossils. Based on the time estimates for Kuldana paleosol development, fossil assemblages in Kuldana channel deposits in the Kala Chitta Hills region probably represent time intervals of about 1000 years. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Paleobiology of Messel ErinaceomorphsGerhard StorchKeywords: Erinaceomorpha; Germany; Grube Messel; Lipotyphla; Middle Eocene; PaleobiologyAbstract Three erinaceomorph species are known from the early Middle Eocene of Grube Messel near Darmstadt, Germany, which are referred to the family Amphilemuridae. Pholidocercus hassiacus, Macrocranion tupaiodon, and Macrocranion tenerum showed extraordinary adaptations to their different life strategies, and several of their specializations are unknown among living insectivores. Pholídocercus was a well-defended robust animal with an opportunistic feeding strategy. Macrocraníon zupaiodon was a slender forest floor-dweller with saltatorial specializations to escape from predators; fishes were the preferred component of its omnivorous diet. Macrocranion tenerum exhibited a combination of both survival strategies, extremely elongated hind limbs for rapid and even ricochetal flight and a spiny exterior as an effective protective device; it was probably specialized for feeding on ants. Thus, closely related, omnivorous-insectivorous forest floor-dwellers could exploit the Messel ecosystem. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Les Chiroptères du Miocène inférieur de Bouzigues. 1- Etude systématique.Bernard SigéKeywords: batsdoi: 10.18563/pv.1.3.65-133 Abstract In recent years, the techniques of chemical preparing have permitted a rich paleontologic material to be obtained from the phosporitic sediment of Bouzigues (Hérault, France). The fauna of this locality is comprised of quite varied microvertebrates, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals. Twenty five species of the latter, belonging to seven orders, are today known from the site. Among them, the numerous rodents have allowed L. Thaler to chronologically situate this fauna in the Zone of Laugnac (<< late Aquitanian ›> of some authors). Article infos Published in Vol. 01, Fasc. 3 (1968) |
|