Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
|
|
|

|
Late Campanian theropod trackways from Porvenir de Jalpa, Coahuila, MexicoHector E. Rivera-Sylva, Eberhard Frey, Christian Meyer, Anne S. Schulp, Wolfgang . Stinnesbeck and Valentin VanheckeKeywords: Dinosaur tracks; Late Cretaceous; Mexico.; Tetanura; Theropoddoi: 10.18563/pv.41.2.e1 Abstract Confident attribution of bipedal tridactyl dinosaur tracks to theropods or ornithopods can be challenging. Here we describe trackways produced by tetanuran dinosaurs, previously attributed to hadrosaurs, from Coahuila State, northeastern Mexico. Multiple trackways headed in the same direction suggest gregarious behaviour in these late Campanian theropods. Article infos Published in Vol 41-2 (2018) |
|
|
|
New remains of the giant bird Gargantuavis philoinos from the Late Cretaceous of Provence (south-eastern France)Eric Buffetaut, Delphine Angst, Patrick Mechin and Annie Mechin-SalessyKeywords: Aves; Gargantuavis; Late Cretaceous; Pelvis; South-eastern Francedoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e3 Abstract
Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|

|
Dating dinosaur oodiversity: chronostratigraphic control of LateCretaceous oospecies succession.Nieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Chronology; dinosaur eggshells; Late CretaceousAbstract An increasing fossil record of dinosaur eggs and eggshells allows putting ootaxa within a chronostratigraphic framework, in order to study their distribution pattern leading eventually to their use as biochronological markers. For these purposes, high-quality data exists in four major regions; North America, South America, Europe and Asia (Central Asia and India). Most of the highly diverse dinosaur egg record has been dated as Latest Cretaceous in age (Campanian-Maastrichtian), reaching the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary closer than the dinosaur bone record. However, dating continental sections is problematic and need to be carefully verified, as it appears when comparing the European dinosaur eggshell record from two well-studied areas. Ootaxa distribution in both sides of the Pyrenees (Tremp and Aix basins) shows comparable oospecies successions, but different chronology. This disagreement probably indicates that one or both successions have a wrong chronostratigraphic calibration. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|

|
The Late Cretaceous nesting site of Auca Mahuevo (Patagonia, Argentina): eggs, nests, and embryos of titanosaurian sauropods.Luis M. Chiappe, Rodolpho. . Coria, Frankie D. Jackson and Lowell DingusKeywords: Argentina; Eggs; embryos; Late Cretaceous; nests; Patagonia; titanosaurian sauropodsAbstract The late Cretaceous Auca Mahuevo nesting site (Neuquén Province, Argentina) has produced a large number of sauropod eggs, many of them containing the remains of embryos. Research at this site has generated important information about the development of the embryos, the morphology and eggshell microstructure of the eggs, and the reproductive behavior of sauropod dinosaurs. Cranial features present in the embryos have allowed their identification as those of titanosaurian sauropods. Differences in the texture of the sediments that contain some of the egg-clutches have illuminated their nest architecture. Microstructural studies of eggshells have expanded our knowledge of their variability and the incidence of pathologies within a reproductive titanosaurian population. Maps showing the spatial distribution of eggs and clutches. the stratigraphic distribution of the egg-beds, and the sedimentological context in which they are contained, have provided the basis for several inferences about the nesting behavior of these dinosaurs. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
|
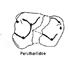
Perutherium altiplanense, un Notongulé du Cretacé Supérieur du PérouLarry G. Marshall, Christian de Muizon and Bernard SigéKeywords: Dental morphology; Late Cretaceous; Notoungulate; Paleobiogeography; PeruAbstract Perutherium altiplanerise THALER, 1967 from the Late Cretaceous of Peru has long been recognized as South America's oldest known placental mammal. Since its description Perutherium has been generally regarded as having condylarth affinity Based on our identification of a unique notoungulate synapomorphy we recognize Perutherium as the oldest and the most generalized known member of that order. This new determination and the large taxonomic diversity (five families) of notoungulates in rocks of Paleocene age in Argentina and Brazil, favor a South American origin for this group. The occurrence of notoungulates in rocks of Late Paleocene age in Asia and North America is explained by dispersal of a notoungulate stock from South America to North America and from there to Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 4 (1983) |
|