Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
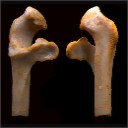
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
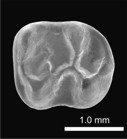
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
New remains of the very small cuckoo, Chambicuculus pusillus (Aves, Cuculiformes, Cuculidae) from the late Early/early Middle Eocene of Djebel Chambi, TunisiaCécile Mourer-Chauviré, El M. Essid, Hayet Khayati Ammar, Laurent Marivaux, Wissem Marzougui, Rim Temani, Monique Vianey-Liaud and Rodolphe TabuceKeywords: Cuckoos; Eocene; Fossil birddoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e2 Abstract Abstract: A very tiny cuckoo, Chambicuculus pusillus, was recently described after a few fragments of tarsometatarsi from the late Early/early Middle Eocene of Djebel Chambi, Tunisia. New remains, notably a coracoid, confirm the attribution of this genus to the recent family Cuculidae. This coracoid shows a very elongate and strap-like processus procoracoideus. This morphological feature is otherwise only known in the family Cuculidae. The characteristics of the coracoid and tarsometatarsi show that Chambicuculus is morphologically more advanced over the other stem cuculids described in Europe and North America. Chambicuculus is the oldest Cuculidae known so far. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
|
|
A new and primitive species of Protophiomys (Rodentia, Hystricognathi) from the late middle Eocene of Djebel el Kébar, Central TunisiaLaurent Marivaux, El M. Essid, Wissem Marzougui, Hayet Khayati Ammar, Sylvain Adnet, Bernard Marandat, Gilles Merzeraud, Rodolphe Tabuce and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Adaptive radiation; Bartonian; Dental morphology; North Africa; Paleobiogeographydoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e2 Abstract Based on fossil discoveries and phylogenetic studies, an Eocene Asian origin for hystricognathous rodents and anthropoid primates has gained strong support in recent years. The two groups then invaded both Africa and South America, which promoted their evolutionary success. However, the fossil record has so far failed to constrain the nature and precise timing of these pivotal dispersal events. In Africa, given the apparent absence of hystricognaths and anthropoids in early to early middle Eocene localities, it is suggested that these mammal groups dispersed from Asia to Africa sometime during the middle Eocene. In this paper, we report the discovery of several isolated teeth of a rodent from a new vertebrate locality situated in central Tunisia (Djebel el Kébar, KEB-1), dating from the late middle Eocene (Bartonian, ~39.5 Myr). These fossils document a diminutive new species of Protophiomys (P. tunisiensis nov. sp.), a basal genus of hystricognathous rodents which is well known from several North African mammalian-bearing localities of the end of the Eocene. The teeth of P. tunisiensis display a suite of anatomical details comparable with those observed in the other species of the genus, but with a lesser degree of development. Such an apparent primitive evolutionary stage is corroborated by the greater antiquity of this Tunisian species. P. tunisiensis nov. sp. is so far the most ancient representative of hystricognaths in Africa. However, it can be expected that hystricognaths were already present on that landmass given the new data on early caviomorphs recently reported from South America (at ~41 Myr). The arrival of hystricognaths in Africa from South Asia certainly predates the depositional period of the Kébar sediments, but perhaps not by much time. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|