Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 3- Les insectivoresJean-Yves Crochet and Morton GreenKeywords: Hérault; Insectivora; Late Miocene; Micromammals; MontredonAbstract This paper presents a preliminary list of insectivores from the Vallesian beds at Montredon (France). The associated rodent fauna has established a Vallesian age for the fauna. Eleven species belonging to the Soricidae, Talpidae, Erinaceidae, and Dimylidae are identified of which four only are referred with certainty to forms already named. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 1 - Les LagomorphesNieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Lagomorpha; Montredon; Prolagus; Upper MioceneAbstract A sample of 231 isolated teeth of lagomorphs from the upper Miocene of Montredon (southern France), identified as the ochotonid Prolagus crusafonii DOPEZ, 1975, is studied, comparing it with other populations of the same species as well as with its closest species P. oeningensis (KÖNIG, 1825). Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Eggshell microstructure and porosity of the Nicobar scrubfowl (Megapodius Nicobariensis, great Nicobar island, India)Géraldine Garcia, Ashu Khosla, Ashok Sahni and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: conductance porosity; eggshell microstructure; incubation conditions; Megapodesdoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.75-88 Abstract The eggshell of Nicobar scrubfowl (Megapodius nicobariensis) is described for the first time. Its egg porosity is calculated and discussed with data from several taxa (another megapode, some extant and fossil reptiles including a titanosaur group) in order to compare incubation types with eggshell structure. Eggshell microstructure reflects first phylogenetic traits and does not seem to have developed major adaptative features due to the incubation conditions, except for the pore canals. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|
|
Nouvelles espèces de Dendromus (Rongeurs,Muriodea) à Langebaanweg (Pliocène,Afrique du Sud) conséquences stratigraphiques et PaléoecologiquesChristiane DenysKeywords: Dendromurinae; Paleoecology; Pliocene; Rodents; South Africa; StratigraphyAbstract New Dendromus species (Rodentia, Muroídea) from Langebaanweg (Pliocene, South Africa). Stratigraphical and paleoecological consequences. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Nouvelle interprétation de l'évolution du genre Megacricetodon au cours du MiocèneJean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Megacricetodon; Micromammals; MioceneAbstract La découverte de nouveaux gisements à micromammifères dans le Miocène du Sud de la France et d'Espagne montre que, s'il n'est plus possible d'accepter dans son intégralité le schéma phylétique de Fahlbusch du genre Megacricetodon, il existe toutefois des segments de lignées à l'intérieur de provinces géographiques différentes (Péninsule Ibérique, France, Europe Centrale), avec lesquels on peut établir une biochronologie locale, segments qu'il est aussi possible de placer les uns par rapport aux autres, en utilisant les corrélations que l'on peut reconnaître entre certains niveaux repères des mammalogistes et l'échelle stratigraphique marine. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Rythme et modalités de l'évolution chez les rongeurs à la fin de l'Oligocène-leurs relations avec les changements de l'environnement.Bernard ComteKeywords: Environment; evolution; Oligocene; Rodents; SystematicsAbstract The analysis of oxygene isotope variations as well as paleobotanical data suggest that the Oligocene/Miocene boundary corresponds to a transitional period marked by floristical and climatic variations. During this period, the pyreneo-alpine tectonics has contribued to modify the geography and western Europe landscapes. Faunal changes (appearances, extinctions, migrations) are observed in different mammalian groups, notably in the rodents. A study of the evolutionary trends and patterns in paleogene rodents is involved for the period ranging from level MP 28 of the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, including the Oligo-Miocene boundary. Article infos Published in Vol. 29, Fasc. 2-4 (2000) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 9 - Une tentative de magnétostratigraphieSevket SenKeywords: France; magnetostratigraphy; Montredon; Upper MioceneAbstract Afin d'étudier la magnétostratigraphie de la colline de Montredon, j'ai prélevé en Avril 1982, 93 carottes orientées réparties sur 29 sites. J.-P. Aguilar et I. Loridant m'ont aidé durant cette opération. Pour la stratigraphie de la coupe échantillonnée et pour le contenu faunique des deux gisements de mammifères de cette colline, voir J.-P. Aguilar & J.-Y. Crochet (1982). Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Avant propos au "Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II"Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Editorial; Type specimensAbstract Avant propos au "Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II". View editorial Published in Vol. 23, Ext (1994) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude de l'anatomie crânienne des rongeurs. 1- Principaux types de cricétodontinésJean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Cricetodon; Cricetodontinae; Miocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.1.2.47-64 Abstract Description, for the first time, of the skull of Ruscinomys Depéret on the basis of a nearly complete specimen, and description of a new facial part of a Megacricetodon Fahlbusch skull (material from upper Miocene, Spain). New description of the skull (facial part) of " Cricetodon" incertum Schlosser on the basis of the specimen from the Oligocene of Quercy phosphorites already published by S. Schaub. Article infos Published in Vol. 01, Fasc. 2 (1967) |
|
|
|
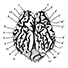
Etude paléoneurologique comparative de Parabos Cordieri (De Christol), un bovidae (Mammalia, Artiodactyla) du Pliocène d'Europe Occidentale.Catherine GromolardKeywords: Bovidae; endocranial cast; Europe; PlioceneAbstract A skull of Parabos cordieri, undamaged by fossilisation, allows us to make an endocranial cast, which is compared to those of Bos taurus, Boselaphus tragocamelus and Hippotragus equinus. These are studied by general form (shape, volume, « rolling-up›› and inclination), and by detailed morphology (gyri and sulci patterns, rete mirabile, importance of rhinencephalon and cerebellum). Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 2 (1982) |
|
|

|
Eléments nouveaux sur l'évolution des genres Eucricetodon et Pseudocricetodon (Eucricetodontinae, Rodentia,Mammalia, de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Bernard ComteKeywords: evolution; Occidental Europe; Oligocene; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract The review of material recently collected in the new localities from the “Phosphorites du Quercy", and different localities from the South of France, bring new informations on the genus Eucricetodon THALER. 1966, and Pseudocricetodon THALER, I969 (Middle and Upper Oligocene. Western Europe). Thanks to Eucricetodon huerzeleri VIANEY-LIAUD, 1972, which were unsufficiently known until now, is proposed. During the middle Oligocene Eucricetodon atavus MISONNE, 1957 seems to give rise to two lineages. One of them led to Eucricetodon huberi,which however exhibits a larger size and a development of progressive characters on the teeth. The other would be Eucricetodon huerzeleri well differentiated at the “Mas de Pauffié" standard level (beginning of the upper Oligocene). The ornementation of lower incisors is described, when possible. Though the fossils are not abundant, it seems that the ancestral lineage, Eucriretodon atavus, remains in the upper Oligocene (Boningen standard level). evolving into Eucricetodon praecursor SCHAUB, 1925 (Rickenbach standard level). The characters of Eucricetodon dubius (SCHAUB. 1925), represented by a numerous population in Pech Desse and Pech du Fraysse (Quercy). confirm that this species and Eucricetodon praecursor belong to two different lineages. As Eucricetodon dubius shows more primitive features, this species could not originale from Eucricetodon atavus -Eucricetodon huberi. The appearance of this species at the level of Mas de Pauffié could be the result of an immigration. A new definition of Pseudocricetodon incertus (SCHLOSSER. 1884) is given. This species has been found in several localities, where it had not been identified until now. lts comparison with Pseudocricetodon moguntiacus (BAHLO. l975), found at several localities from the standard level of Antoingt (end of middle Oligocene). shows a parallel evolution to that of Pseudocetodon incertus, which is of larger size and with a less complicated pattern of teeth. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 1 (1985) |
|
|
|
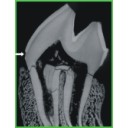
Enamel hypoplasia on rhinocerotoid teeth: Does CT-scan imaging detect the defects better than the naked eye?Manon Hullot and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: fossil teeth; method; micro-CT imaging; Rhinocerotoideadoi: 10.18563/pv.45.1.e2 Abstract Micro-CT imaging is an increasingly popular method in paleontology giving access to internal structures with a high resolution and without destroying precious specimens. However, its potential for the study of hypoplasia defects has only recently been investigated. Here, we propose a preliminary study to test whether hypoplastic defects can be detected with micro-CT (μCT) scan and we assess the costs and benefits of using this method instead of naked eye. To do so, we studied 13 fossil rhinocerotid teeth bearing hypoplasia from Béon 1 (late early Miocene, Southwestern France) as positive control and 11 teeth of the amynodontid Cadurcotherium (Oligocene, Phosphorites du Quercy, Southwestern France), for which enamel was partly or totally obscured by cement. We showed that all macroscopically-spotted defects were retrieved on 3D reconstructions and selected virtual slices. We also detected additional defects using μCT scan compared to naked eye identification. The number of defects detected using μCT was greater in the Cadurcotherium dataset (paired-sample Wilcoxon test, p-value = 0.02724) but not for our control sample (paired-sample Wilcoxon test, p-value = 0.1171). Moreover, it allowed for measuring width and depth of the defects on virtual slices (sometimes linked to stress duration and severity, respectively), which we could not do macroscopically. As μCT imaging is both expensive and time consuming while not drastically improving the results, we recommend a moderate and thoughtful use of this method for hypoplasia investigations, restricted for instance to teeth for which enamel surface is obscured (presence of cement, uncomplete preparation, or unerupted germs). Article infos Published in 45-1 (2022) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
La variabilité morphologique dentaire du Landenodon (Condylarthra) de Dormaal, (Eocène,Belgique)Marc GodinotKeywords: Condylarths; Dormaal; Early Eocene; LandenodonAbstract The study of dental variations in Landenodon from Dormaal (early Eocene, Belgium) shows that only one Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Un nouveau type de coquille d'oeuf présumé Dinosaurien dans la Campanien et le Maestrichtien continental de Provence.Philippe KerourioKeywords: Campanian/Maastrichtian; eggshell microstructure; ProvenceAbstract The discovery of eggshells of ornithoid type is signaled for the first time in the continental Campanian and Maastrichtían of Provence. The taxonomie relationship of these eggshells and their interest in the biostratigraphical study of Upper Cretaceous of Provence are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 4 (1982) |
|
|

|
Origins of avian reproduction: answers and questionsfrom dinosaurs.David J. Varricchio and Frankie D. JacksonKeywords: Avian reproduction; clutch; dinosaurs; egg size; nests; oviducts; parental careAbstract The reproductive biology of living birds differs dramatically from that of other extant vertebrates. Distinctive features common to most birds include a single ovary and oviduct, production of one egg at daily or greater intervals, incubation by brooding and extensive parental care. The prevalence of male parental care is most exceptional among living amniotes. A variety of hypotheses exist to explain the origin of avian reproduction. Central to these models are proposed transitions from a condition of no care to maternal, paternal or biparental care systems. These evolutionary models incorporate a number of features potentially preservable or inferable from the fossil record (integument, skeletal adaptations for flight, egg and clutch size, nest form, hatchling developmental stage, the number and function of oviducts, and the mode of egg incubation). Increasing availability of data on dinosaur reproduction provides a means of assessing these hypotheses with fossil evidence. We compare dinosaur data to a selection of models that emphasize maternal, paternal or biparental care. Despite some congruence with dinosaur features, no single model on the evolution of avian reproduction conforms fully to the fossil record, and the ancestral parental care system of birds remains ambiguous. Further investigation into dinosaur parental care, nest structures, clutch geometry, egg-pairing, eggshell porosity, and embryo identification may eventually resolve these issues. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|

|
Les Gruiformes (Aves) des phosphorites du Quercy (France). 1. sous-ordre cariamae (Cariamidae et Phorusrhacidae), systématique et biostratigraphie.Cécile Mourer-ChauviréKeywords: Aves; Biostratigraphy; Birds; Cariamae; gruiformes; Quercy Phosphorites; SystematicsAbstract The revision of the old collections of fossil birds from the “Phosphorites du Quercy” and the study of new material give the following results (Gruiformes, Cariamae) : The humeri and most of the carpometacarpi described under the name Filholornis belong in Elaphrocnemus. The ulnae ascribed to Fïlholornis belong in Idiornis. Most of the post-cranial elements of the genera Elaphrocnemus and Idiornis are described and show great similarities with recent Cariamidae and Opisthocomidae, and fossil Bathornithinae. A new genus and a new species, Oblitavis insolitus, are created in the sub-family Idiornithinae; two new species are described in the genera Elaphrocnemus (E. brodkorbz) and Idiornis (I. itardiensis), and the species Elaphrocnemus gracilis is transferred to the genus Idiornis. The genus Propelargus Lydekker is transferred from the family Ciconiidae to Cariamidae. A new generic name, Occitaniavis, is created for the species Geranopsis elatus, which belong in Cariamidae, while the type-species of the genus, Geranopsis hastingsiae, is a member of the Gruidae. The affinities between the Quercy avifauna and the Neotropical one is emphasized by the occurrence of Phorusrhacidae, previously known only from the Cenozoic of South America and the Late Pliocene or Early Pleistocene of North America. Thanks to the material collected during the new excavations, the stratigraphical position of most of the species is stated precisely, and evolutionary lineages are outlined. This study shows that the suborder Cariamae, presently restricted to two South American genera, was already extremely diversified during the Eocene, and widespread in Europe and North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 4 (1983) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 4 - Les chiroptèresBernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Hérault; Late Miocene; Micromammals; MontredonAbstract The Montredon local fauna yielded very rare bats, represented by damaged isolated teeth. Only a few documents are available for this period of the European Neogene. ln this poor state of knowledge, the material represents three undetermined species, a supposed molossid and two vespertilionids. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|

|
Arvicolinae (Rodentia) du Pliocène terminal et du quaternaire ancien de France et d'Espagne.Jacques MichauxKeywords: Arvicolinae; France; Pleistocene; Pliocene; Spaindoi: 10.18563/pv.4.5.137-214 Abstract Two steps can be distinguished in the history of the first invasion of western and south western Europe by the arvicolines. The first step corresponds to the installation of these rodents with the immigration of Promimonys inxuliferus Kowalski, then of Mimomys stehlini Kormos and of Mimomys gracilis (Kretzoi). The second is characterized by the establishment of a geographic differentiation in the arvicoline fauna between the south of France and Spain, from where are described new species of Mimomys (Mimamys cappettai, Mimomys septimanus, Mimonys medasensis), and the rest of France, where are found only elements already known from central Europe or England (Mimomys polonicus Kowalski, Mimomys pliocaenicus F. Major, Mimomys reidi Hinton, or forms very close to the latter). This geographic differentiation, which is very certainly the consequence of the division of Europe into distinct climatic provinces, one of them being the southern province comprising at least Spain and southern France, could result from a cladogenetic evolution of Mimomys stehlini and Mimomys gracilis after their immigration. The present work is also a contribution to the search for correlations between the diverse micromammal localities of the latest Pliocene (or early Villafranchian) and of the early Quaternary of Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 5 (1971) |
|
|
|
Perutherium altiplanense, un Notongulé du Cretacé Supérieur du PérouLarry G. Marshall, Christian de Muizon and Bernard SigéKeywords: Dental morphology; Late Cretaceous; Notoungulate; Paleobiogeography; PeruAbstract Perutherium altiplanerise THALER, 1967 from the Late Cretaceous of Peru has long been recognized as South America's oldest known placental mammal. Since its description Perutherium has been generally regarded as having condylarth affinity Based on our identification of a unique notoungulate synapomorphy we recognize Perutherium as the oldest and the most generalized known member of that order. This new determination and the large taxonomic diversity (five families) of notoungulates in rocks of Paleocene age in Argentina and Brazil, favor a South American origin for this group. The occurrence of notoungulates in rocks of Late Paleocene age in Asia and North America is explained by dispersal of a notoungulate stock from South America to North America and from there to Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 4 (1983) |
|
|
|
D'important restes de Diplobune minor FILHOL à Itardies (Quercy)Jean SudreKeywords: Diplobune; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|