Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
Palaeovertebrata Vol 41-1:June 2018
|
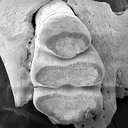
A new Desmodillus (Gerbillinae, Rodentia) species from the early Pliocene site of Langebaanweg (South-western Cape, South Africa)
|
|
S.I. Data |
|
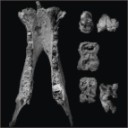
A new species of hippopotamine (Cetartiodactyla, Hippopotamidae) from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation, Abu Dhabi, United Arab EmiratesJean-Renaud Boisserie, Mathieu Schuster, Mark J. Beech, Andrew Hill and Faysal BibiKeywords: Arab Peninsula; Hippopotamidae; Hippopotamine event; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.41.1.e2 Abstract The discovery of new hippopotamid material from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation (Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates) has prompted the revision of the existing material of this as yet unnamed fossil taxon. The Baynunah hippopotamid appears to be distinct from all other contemporary and later species in having a relatively more elongate symphysis, a feature similar to the earlier (and more primitive) Kenyapotamus. Yet, the Baynunah hippopotamid presents a dentition typical of the Hippopotaminae. It is therefore a distinct species attributed to the later subfamily, described and named in this contribution. This species provides further evidence for a ca. 8 Ma evolutionary event (termed “Hippopotamine Event”) that initiated the spread and ecological significance of the Hippopotaminae into wet habitats across Africa and Eurasia. The morphological affinities of the new species from Abu Dhabi suggest that the Arabian Peninsula was not a dispersal route from Africa toward southern Asia for the Hippopotamidae at ca. 7.5 Ma to 6.5 Ma. Article infos |
|
S.I. Data |
|
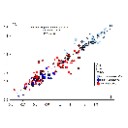
Critical comments on the genus Propachynolophus Lemoine, 1891 (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Equoidea)
|
|
S.I. Data |