Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Eocene otoliths (Clinchfield Formation), Georgia
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Dating dinosaur oodiversity: chronostratigraphic control of Late Cretaceous oospecies succession.
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
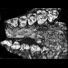
Un Haplobunodontidae nouveau Hallebune krumbegeli nov.gen. nov.sp. (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) dans l'Eocène moyen du Geiseltal près Halle (Sachsen-Anhalt, Allemagne)Jorg Erfurt and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Geiseltal; Germany; Mammal; Middle Eocene; new gen.; new sp.Abstract A new genus and species of haplobunodontid artiodactyl, Hallebune krumbiegeli nov. gen. nov. sp., is described from the middle Eocene Geiseltal Fauna (Saxon-Anhalt, Germany). Its stratigraphic range is restricted to the MP 13 ("obere Mittelkohle") of the Geiseltalian. The material consists of seven fragments, representing both upper and lower jaws. It is indicated, that H. krumbiegeli was a small bunodont herbivore. The size and primitive character of the teeth suggest that the genus possibly is directly derived from Diacodexeidae.The new material forms the basis for reinterpreting the haplobunodontid phylogeny. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
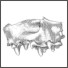
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 8- Insectivores et Chiroptères.Bernard SigéKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The small insectivorous placental mammals from Ste-Néboule are poorly varied. Two orders of insectivores are documented : the Proteutheria by Pseudorhyncocyon cayluxi (leptictids), the Lipotyphla by Saturninia gracilis and S. beata (nyctitheriids). The bats are only rhinolophoids and mostly hipposiderids. Sufficient populations allow us to restrict the original definitions of three previous species (Hipposideros schlosseri, Palaeophyllophora quercyi, P. oltina). From now, these species can be regarded as monophyletíc. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Terrestrial vertebrate paleocommunities from the Cerro del Pueblo Formation (Late Cretaceous; Late Campanian) at Las Aguilas, Coahuila, MexicoHéctor E. Rivera-Sylva, Eberhard Frey, Wolfgang . Stinnesbeck, Natalia Amezcua Torres and Diana Flores HuertaKeywords: Campanian; Coahuila; dinosaurs; Mexico.; Vertebratesdoi: 10.18563/pv.42.2.e1 Abstract The Las Águilas site near Porvenir de Jalpa, Coahuila, Mexico, is extremely rich in tetrapod remains comprising both bones and trackways of several dinosaur taxa of late Campanian age. Within a 50 m thick section we identified at least nine layers with dinosaur bone assemblages. In one of these the dinosaur bones are associated with remnants of eusuchian crocodilians, turtles, plesiosaurs, pterosaurs, tyrannosaurids, dromaeosaurids, parksosaurid, hadrosaurids, ceratopsids, and ankylosaurs. This layer is also rich in coprolites of turtles, crocodilians and likely theropods, thus providing evidence for the wealth of Late Cretaceous vertebrate life in the area. Article infos Published in Vol 42-2 (2019) |
|
|
|
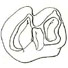
Rongeurs de l'Oligocène moyen provenant de nouvelles fouilles dans les phosphorites du QuercyMonique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Oligocene; Quercy Phosphorites; Rodents; Theridomysdoi: 10.18563/pv.2.5.209-239 Abstract A recent campaign of excavations (1965-68) undertaken by the Laboratoire de Paléontologie of Montpellier in pockets of the Quercy phosphorites, has permitted the dating of several localities thanks to the analysis of their micromammalian fauna. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 5 (1969) |
|
|

|
Une faunule de vertébrés sous la base de grès de Celas (Eocène supérieur) à ST Dresery (Gard)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Artiodactyla; Biostratigraphy; Eocene; MammalsAbstract The St-Dézéry local fauna (3 reptile-, 4 mammal species) is approximately of the same age as the La Débruge or the Ste-Néboule faunas. It conduces to a better dating of the limestones underlying the Célas sandstones. A large part of a mandible of Amphimeryx was found there, which documents the record of this family of small artiodactyls Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Long-term fidelity of megaoolithid dinosaurs to a large breeding-ground in the Upper Cretaceous of Aix-en-Provence (southern France).Géraldine Garcia, Yves Dutour, Isabellle Cojan, Xavier Valentin and Gilles CheylanKeywords: Large nesting ground; megaloolithid eggs; Southern France; Upper CretaceousAbstract We present here the preliminary results from a new nesting site "Sextius-Mirabeau", discovered close to the historical centre of Aix-en-Provence in Upper Cretaceous deposits. This extensive megaloolithid nesting ground, the first large scale excavation (3225 m²) in France, yielded more than 530 eggs, some organized in clusters. Their study reveals the reproductive strategy of the megaloolithid egglayer group which indicates nesting fidelity and gregarious behaviour. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
|
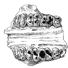
Les Tayassuidés des phosphorites du QuercyLéonard GinsburgKeywords: Quercy Phosphorites; TayassuidaeAbstract Revision of the Tayassuidae from the old collections of the Quercy leads to interesting facts about taxonomic and phylogenetic problems. It could not have been well done without constant comparison with contemporaneous Tayassuidae from stratified series, as well as with European Miocene Tayassuidae and Hyotheriinae. The result is that only three species are present in the Phosphorites of Quercy: Doliochoerus quercyi FiLHOL (represented by two sub-species: the older, D. quercyi quercyi and the more recent, D. quercyi aquensis), Palaeochoerus gergorianus CROIZET et BLAINVILLE and Palaeochoerus purillus nov. sp. The two former species disappeared with Stampian time, while the third is the direct ancestor of the Aquitanian Palaeochoerus typus POMEL, which became extinct before the beginning of Burdigalian. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
The fossil rabbit from Valdemino cave (Borgio Verezzi,Savona) in the context of western Europe Oryctolagini of Quaternary.Giulia Nocchi and Benedetto SalaKeywords: Lagomorpha; Mammals; North-western Italy; Oryctolagus; Plio-Pleistocene; SavonaAbstract The present research deals with the remains of a lagomorph found at Valdemino cave and comes to the conclusion that it is a rabbit with peculiar characteristics in comparison with the other known species Oryctolagus laynensis, O. lacosti and 0. cuniculus. We studied other fossil remains of rabbit populations from Villafranchían and middle Pleistocene deposits and compared them with data from the literature and with recent material. The analysis leads us to maintain two phylogenetic hypotheses about the history of Oryctolagini. The ñrst one, already formulated by Lopez Martinez, suggests that 0. cuniculus derives from O. laynensis,while the origin of O. lacostí is unknown; according to the second hypothesis 0. laynensis would be the common ancestor of two phyletic lineages, 0. lacosti and 0. cuniculus. In both cases the lagomorph from Valdemino would be the form derived from 0. lacosti, from which however it differs in peculiar characteristics. Since the rabbit from Valdemino survives until the beginning of Postgalerian, its disappearance may coincide with the retreat of 0. cuniculus from western Europe in Spain and, perhaps, in south-western France, before the last glaciation. O. cuniculus survived in Spain, from where it spread once again over western Europe as a result of man. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
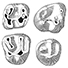
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 6 - Les périssodactyles RhinocerotidaeClaude GuérinKeywords: Aceratherium; anatomy; Biostratigraphy; Dicerorhinus; Miocene; Montredon; Paleoecology; Upper VallesianAbstract The Montredon site has yielded about hundred rhinoceros remains: Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
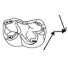
Rongeurs du Miocène inférieur et moyen en Languedoc. Leur apport pour les correlations Marin-Continental et la Stratigraphie.Jean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Languedoc; Miocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract The rodents (Cricetidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) found in lacustrine, brackish marine and karstic sediments of Miocene age in Languedoc, assign the position of the different localities in the scale of "niveaux repères" used by mammalogists. Some detailed stratigraphical studies bring several correlations between this continental biochronological scale and the marine scale ; the most important results are the Aquitanian age of the "niveaux repères" of Coderet and Paulhiac, the Burdigalian age of Laugnac, Estrepouy, Vieux-Collonges, La Romieu and Sansan and the Langhian or Lower Serravallian age of La Grive M. The correlations between the Tethys and the Central Paratethys for the Lower Neogene profit also of these results, since the locality of Neudorf Spalte 1, 2 (Czechoslovakia) is shown to be younger than Sansan (France). The paleontological study has also several geological inferences for the Miocene of Languedoc ; with the calibration of this Miocene, we know quite precisely that the Lower Miocene is chiefly a time lacustrine sedimentation, and also that the marine Miocene sedimentation ends early in the Miocene Period, in Langhian or lower Serravallian times. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 6 (1980) |
|
|
|
Eurodexeinae, eine neue unterfamilie der Artiodactyla (Mammalia) aus dem unter- und mitteleozän europasJorg Erfurt and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyls; Eocene; evolution; Germany; Lutetian; new genus; New subfamilyAbstract Dichobunoid artiodactyls are described in this paper from the middle Eocene Geiseltal lignite deposits near Halle (Sachsen-Anhalt, Germany). The genera Eurodexis and Parahexacodus are established based on odontologica1 studies. The type-species are E. ceciliensis (FRANZEN & KRUMBIEGEL, 1981) and P. germanicus n. sp. from the "obere Mittelkohle" (see text), MP 13. The genera are referred to the new subfamily Eurodexeinae (Dichobunidae, Artiodactyla, Mammalia), which also contains the monospecific genus Eygalayodon SUDRE & MARANDAT, 1993. These new genera show many features similar to North American homacodontids and antiacodontids. They exemplify a high degree of diversity in European dichobunids. Moreover, the family Dichobunidae includes the Dichobuninae and the Hyperdichobuninae. The connection of the posthypocristid with the postentocristid, the shift of a medial to a lingual position of the hypoconulid on the lower molars and the development of a large, caniniform P1 are regarded as the principal tendencies of the eurodexeines. The entoconid is larger and more mesially situated compared to that of Diacodexis. The hypoconulid has a lingual position on a broad postcingulid. The elongation of the premolars and the presence of diastemata are considered associated with extension of the muzzle. This and the acute tubercles of the molars could indicate a limited degree of insectivory. Protodichobune cf. oweni and Diacodexis cf. varleli, first reported here from the "untere Unterkohle" (MP 11) of the Geiseltal, demonstrate the existence of forms in the basal part of the middle Eocene, that are direct descendants of lower Eocene ones. Eurodexis russelli n. sp. from MP 10 of Premontre is the most primitive representative of Eurodexis. A further part of this lineage could be Messelobunodon sp. from MP 11 of Messel (Germany). Another form from Premontre, referred to Eurodexeinae indet., represents the origin of the lineage to Parahexacodus germanicus n. sp. from the Geiseltal (MP 13). The identification of several lineages in MP 10 is evidence of an adaptive radiation during this time. Unfortunately the history of the earlier species of Diacodexis is not known well enough to exclude earlier diversifications. Our study shows the independent development of artiodactyls at the end of the lower Eocene in Europe, North America (and maybe in Asia) with much convergence. The question of the geographic origin of the genus Diacodexis is still open. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
The lower Miocene artiodactyls of Tagai bay, Olhon island, lake Baikal (Russia)Inesa VislobokovaKeywords: Artiodactyls; Mammals; Miocene; SiberiaAbstract The mammalian fauna of the Tagai locality of Olhon Island in Lake Baikal contains six artiodactyls: Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
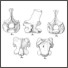
Die Referenzfauna des Geiseltalium, MP levels 11 bis 13 (Mitteleozan, Lutetium)Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Eocene; Geiseltal; Land mammal ages; Mammalian reference levelsAbstract The Middle Eocene Fossillägerstätte of the Geiseltal lignite beds near Halle/S. (German Democratic Republic) is the reference locality of the European land mammal age Geiseltalian and of the Mammalian Paleogene reference levels MP 11 - MP 13. Due to this importance a reinvestigation is given of the lithostratigraphical development of the Geiseltal beds and of their vertebrate sites. The last are genetically related to the southwest border of the Geiseltal depression and the influx of carbonate-rich waters. The geographical distribution and stratigraphical position of the fossiliferous sites depends on subrosive and tectonically controlled distribution of coal seams. The geological factors and the known stratigraphical guide of some mammalian species suggest corrections of the age of some sites. Four of the alltogether five coal bearing phases contain the 35 sites with mammalian remains. By the distribution of the around 69 mammal species are characterized, with 5 faunal steps ranging from MP 11 to MP 14 or over the Geiseltalian up to the Lower Robiacian. Well distant are the faunas of MP 11 and MP 12. Beginning with MP 12 up to MP 13/14, the fossil record is very frequent by 27 sites. This evidence coincides somewhat more with the concept of land mammal ages compared to that of the punctual mammalian reference levels. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|
|
La poche à Phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien supérieur. 5-SquamatesJean-Claude RageKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The Squamates from Sainte-Néboule are charateristic of the Upper Eocene from the Phosphorites du Quercy. Most genera known from this locality do not survive the « Grande Coupure ». Cadurcoboa insolita gen. nov., sp. nov. is a small Boidae very characteristic of the Upper Eocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Agriotherium intermedium (Stach 1957) from a Pliocene fissure filling of Xiaoxian County (Anhuei Province, China) and the phylogenetic position of the genus.Zhanxiang Qiu and Norbert Schmidt-KittlerKeywords: Carnivora; China; PHYLOGENY; Pliocene; skull anatomy; UrsidaeAbstract A fragmentary mandible and maxilla of a small sized Agriotherium of a young individual discovered from a Pliocene fissure filling in Xiaoxian county (Anhuei Province, China) are described. Judging from the morphology of the dentition and its dimensions the new material can be identified as Agriotherium inlermedium (STACH l957). Hendey's proposition (1980) that the Agriotherium species are derived from Indarctos is reconsídered on the basis of the new documents. As a result of a more general phylogenetic discussion it can be stated, that: 1. the supposed size increase as well as other trends, leading from Indarctos to Agriotherium are untenable ; 2. there are no positive indications to assume a phylogenetic transition of these two genera. 3. there are no real arguments in favor of an adaptational reversal in the evolution of Agriotherium. Hence, many features of that genus supposed by Hendey to be derived are plesiomorphic ; 4. regardless of the previous points it is methodologícally impossible to establish direct ancestor - descendant relationships between Indarctos and Agriotherium species, as Hendey did. Based on the data available and especially on the characters of the new material from China it is more likely that Agriotherium and Indarctos are two genera which developed independently. While advanced Agriotherium species, e.g. A. africanum, resemble in some respects Indarctos by adaptational analogies, more primitive species, e.g. Agriotherium intermedium, are quite dissimilar to lndarctos. While Indarctos might be derived from an Ursavus like forerunner, Agriotherium has its roots more likely somewhere in between Ursavus and the Hemicyon-group. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|

|
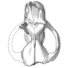
Sur la présence de dents de mammifères (Creodonta, Perissodactyla) près de la limite Paléocène-Eocène à Hoegaarden, BelgiqueRichard Smith and Jerry J. HookerKeywords: Belgium; Creodonta; Landenian; Mammals; PerissodactylaAbstract Amongst a collection of selachian teeth made at Hoegaarden in a marine level of Bruxellian (Lutetian) age, containing a reworked Landenian (Sparnacian) fauna mixed with a contemporaneous one, a few teeth of terrestrial mammals have been discovered. They comprise two rare European taxa: ? Hallensia sp. and Palaeonictis gigantea, both known from the Landenian. Even though the ?Hallensia has not been definitely identified, il differs from the only perissodactyl of this age previously recorded from Belgium (Cymbalophus cuniculus). Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
A new Ardynomys (Rodentia,Cylindrodontidae) from the Eocene of the eastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia.Demberelyin DashzevegKeywords: Ardynomys; Eocene; Mongolia; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract A partial skull of Ardynomys russelli sp. nov. (Rodentia, Cylindrodontidae) is described. This was collected in the late Eocene of Alag Tsab locality in the eastem Gobi Desert, Mongolia. Ardynomys russelli sp. nov. is characterized by small size, brachyodont molars, and retention of P3. It represents the earliest record of the genus Ardynomys MATTHEW & GRANGER, 1925, in Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Avant-proposMarc Godinot and Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: D.E.RussellAbstract Le présent volume est l'aboutissement d'un projet né il y a presque cinq ans. En décembre 1991, l'un d'entre nous (MG) prenait des contacts en vue de proposer un symposium sur les mammifères fossiles, dédié à D.E. Russell, dans le programme du 4e Congrès de la European Society for Evolutionary Biology. Ce congrès, baptisé "Evolution 93", devait se tenir à Montpellier en août 1993. Son Comité d'Organisation, animé par F. Catzeflis, recherchait des organisateurs de symposiums. L'idée fut acceptée avec enthousiasme par le second d'entre nous (PDG), et le titre de notre Symposium fut précisé: " Palaeobiology and Evolution of Early Cenozoic Mammals - A Symposium in Honor of D.E. Russell". Le projet fut formellement accepté par le Comité d'Organisation en avril 1992. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Les pantolestidés (Mammalia, Pantolesta) de l'Eocène inférieur de Prémontré (Aisne, France).Richard SmithKeywords: France; Mammals; Pantolestids; YpresianAbstract Study of pantolestid mammals from the late Ypresian locality of Prémontré (reference level MP 10) allows the recognition of three genera: Palaeosinopa. Pantolestes and Premontrelestes n. gen. Pantolestes, up to now only recorded from North America, is represented by P. sabatieri n. sp. Premontrelestes n. gen., represented by the type species P. duchaussoisi n. sp., is compared with Pantolestes and Buxolestes. The latter, known from middle Eocene sites in Europe, has not been recognized at Prémontré. Two other taxa, the first of which is close to Pantolestes and the second of Premontrelestes n. gen. are left in open nomenclature. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|
|
Pairomys et Ectropomys : la fin d'une ambiguïté ; mise au point sur les Oltinomyinae et Remyinae (Rodenia, Theridomyidae).Monique Vianey-Liaud, Norbert Schmidt-Kittler and Pablo Pelaez-CampomanesKeywords: PHYLOGENY; taxonomy; Theridomyidae; Upper EoceneAbstract The description of new material of the Upper Eoœne of France, Southem Germany and Spain together with the restudy of the material described by Thaler (1966b) as Pairomys allows to confirm the validity of the genus Ectropomys up to know controversally discussed. As a consequence the subfamily Remyinae and Oltinomyinae can be defined precisely. The study of the dental characters shows that the Remyinae in fact belong to the Theridomyidae and represent a derived evolutionary unit within this family. The Oltinomyinae together with the Theridomyinae and Issiodoromyinae very probably form a monophyletic unit. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|