Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
Palaeovertebrata Vol. 9, Ext:October 1980

|
Préface au mémoire jubilaire en hommage à René LavocatJacques MichauxKeywords: EditorialAbstract Monsieur René Lavocat, Directeur du Laboratoire de Paléontologie des Vertébrés de la troisième section de l'Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes, quittait le service actif en l'année 1979. View editorial |
|
|
Les crocodiliens paléogenes du Tilemsi (Mali): un aperçu systématiqueEric BuffetautKeywords: Crocodilians; Dyrosoridae; Eocene; Mali; PalaeoceneAbstract Abundant crocodilian fossil remains have been collected, mainly by R. Lavocat. from several levels of the Article infos |
|
|
|
Sur les empreintes de pas des gros mammifères de l'Eocène supérieur de Garrigues-ste-Eulalie (Gard)Paul EllenbergerKeywords: Eocene; Euzet; Footprints; IchnofaunaAbstract Is hereby described an impressive lchnoiauna belonging to the Lower to Middle Ludian of the Gard (S. France). The slab, already cleaned over a length of 18 m, is located near the top of the Potamides aporoschema lacustrine limestone (Lower Ludian, Euzet zone). It is therefore older than the Célas sandstone deposit, and still more than the Melanoides albigensis and M. acutus marly limestone corresponding to the Upper Levels of the Ludian stage. Although biostratigraphically older than the La Débruge and Montmartre zone, the biotope shows already a sampling of very tall Artiodactyles, Perissodactyles and Carnivorous. One of the most « majestic ›› Artiodactyles, Anopolotheriipus lavocati, nov., points out a huge size type. To mention also among the Ichnotypes described, 10, the big Perissodactyle Palaeotheriipus similimedius, nov., and the big Carnivorous Hyaenodontipus praedator, nov. Article infos |
|
|
|
L'occlusion dentaire chez Peradectes, Amphiperatherium et Peratherium, Marsupiaux du tertiaire d'Europe.Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Didelphidae; Eocene; Mastication; Oligocene; Wear facetsAbstract The general principles guiding the study of wear facets which develop during mastication in mammals possessing tribosphenic molars are named. The application of this method of study to the molars of European Tertiary Didelphidae shows that the lineage of this family as represented by the species Peratherium cuvieri (Upper Eocene), P. elegans (Lower-middle Oligocene) and P. antiquum (Upper Oligocene) has propessively evolved toward a more carnivorous diet. Article infos |
|
|

|
Compléments sur les Chiroptères de l'Eocène moyen d'Europe. Les genres Palaeochiropteryx et Cecilionycteris.Bernard Sigé and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Chiroptera; Geiseltal; Messel; Middle EoceneAbstract New dental and skeletal material referable to Palaeochiropteryx tupaiodon from the Middle Eocene locality of Article infos |
|
|
|
Sur les Condylarthres Cernaysiens Tricuspiodon et Landenodon (Paléocène supérieur de France)Donald E. RussellKeywords: Arctocyonidae; Condylarths; Late Paleocene; TricuspiodontidaeAbstract The numerical importance of the Condylarths in the Cernaysian fauna is discussed. The Condylarth family, Tricuspiodontidae, is reviewed in the light of new material and its close relationships to the Phenacodontidae is suggested ; one new species is recognized : Tricuspiodon sobrinus. European Arctocyonidae are reviewed and the recentclassification of Van Valen is briefly commented on. Also, the arctocyonine Landenodon is described for the first time in Thanetian (Late Paleocene) sediments ; two new species are proposed : T. lavocati and T. phelizoni. Article infos |
|
|
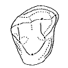
|
La variabilité morphologique dentaire du Landenodon (Condylarthra) de Dormaal, (Eocène,Belgique)Marc GodinotKeywords: Condylarths; Dormaal; Early Eocene; LandenodonAbstract The study of dental variations in Landenodon from Dormaal (early Eocene, Belgium) shows that only one Article infos |
|
|
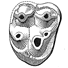
|
Nouveau Dichobunidae (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) du gisement d'Aumelas (Hérault) d'âge Lutétien terminalJean SudreKeywords: Aumelas; Dichobunidae; Hérault; Middle Eocene; Upper LutetianAbstract The faunal list of the mammals collected at the locality of Aumelas (Hérault, France) is revised. For the first Article infos |
|
|

|
Le genre Microstonyx en Espagne et ses relations avec les autres espèces du même genre hors d'EspagneJuana M. Golpe-PosseKeywords: Microstonyx; Spain; SuidaeAbstract The genus Microstonyx was found only in the north eastern part of Spain : M. antiquus, referable to the Article infos |
|
|
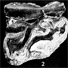
|
Prospection paléontologique de la région de Torralba de Ribota (Burdigalien du bassin de Calatayud, prov. de Zaragoza, Espagne)Edouard Boné, Maria T. Alberdi, Manuel Hoyos and Nieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Faunal assemblage; Macromammals; Spain; Zaragoza prov.Abstract The study of another faunal assemblage (mostly macromammals) from Torralba de Ribota (Calatayud, Zara- Article infos |
|
|
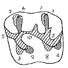
|
Functional aspects of the evolution of rodent molarsPercy M. ButlerKeywords: Chewing; Muridae; Rodents; Wear facetsAbstract The wear facets of primitive rodents can be homologized with those of primitive primates and ungulates. As in primates, the jaw movement was ectental, with an increased anterior component in the lingual phase (phase ll). The buccal phase (phase I) in rodents approaches the horizontal and it tends to be reduced in importance in comparison with the lingual phase. ln more advanced rodents the efficiency of grinding is increased by the development of additional cutting edges of enamel (e.g. enlargement of hypocone, development of mesoloph and lingual sinus). The buccal phase movement becomes lined up with the lingual phase movement to form a single oblique chewing stroke,resulting in planation of the crown. As the stroke becomes more longitudinal (propalinal) the enamel edges become more transverse. In Muridae propalinal chewing evolved before the loss of cusps, facets were reorientated and additional cusps developed. Article infos |
|
|

|
Problems of classification as applied to the RodentiaAlbert E. WoodKeywords:Abstract A classification should be both usable and useful,not too complex either in the amount of splitting or in the number of hierarchies involved, and not so simple as to give a false assurance of knowledge of relationships. Classifications are only possible because we do not have complete knowledge of the evolution of the organisms concerned because gaps in the record are necessary to allow the separation of the various taxa. Rodent classification is complicated by the large number of organisms involved and by the geat amount of parallelism that has taken place in the evolution of any and all features. If several independent features are characteristic of a certain taxon, should an effort be made to define the group on the basis of all the features, or should only one be selected as the determinant ? Unless the evolution of the several features was closely linked, the former solution will sooner or later lead to insurmountable problems. Article infos |
|
|

|
The stratigraphic sequence of North American rodent faunasRobert W. WilsonKeywords: North America; Rodents; Stratigraphic sequenceAbstract Rodents first appear in the latest Paleocene or earliest Eocene as very fragmentary specimens (Family Paramyidae) known largely from a single locality. After this sparse beginning, rodents are usually abundant in the North American record if proper recovery methods are used. Utilization of rodents for biostratigraphic purposes depends on 1/ extinction, and 2/ replacement by evolution of endemic groups and/or incursions of Old World rodents, and rarely and late by South American kinds. These incursions are separated by relatively long periods of isolation in the Paleogene, but more episodic in the Neogene. At least 10 rodent zones can be characterized by major distinctions, and these zones can be amplified into as many as 16 with little trouble. In general, rodent genera permit as refined a zonation as do genera of large mammals. Distinction at a specific level has not been attempted herein except in the Blancan and Post-Blancan. Article infos |
|
|

|
Données et hypothèses sur la radiation initiale des rongeurs.Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Diversification scheme; Radiation; RodentsAbstract About the early radiation of Rodents, we have now from the early tertiary of Asia, a new fossil record, and Article infos |
|
|
|
Les Dipodidae (Mammalia, Rodentia) d'Europe occidentale au Paléogène et au Néogène inférieur: origine et évolution.Marguerite Hugueney and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Dipodidae; Late Oligocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The study of three new populations of Plesiosminthuspromyarion from the "phosphorites du Quercy" and of material from "Auvergne" brings new data on european oligocene Dipodidae. They appear in Western Europe at the beginning of late Oligocene. Evolutionary trends of the group are drawn and particularly the emergence of morphotypes announcing P. schaubi, from the Coderet level, is revealed among the most recent populations of P. promyarion. Differences are attempted to be drawn between the three species : P. promyarion, P. myarion and P. schaubi by restudying the type-population of P. myarion from the aquitanian deposits of Chavroches (Allier) in comparison with two other populations from the same age and the same region. Relationships between early european, american and asiatic Dipodidae are discussed. Article infos |
|
|
|
On the genus Dikkomys (Geomyoidea, Mammalia)Morton Green and Philip R. BjorkKeywords: Dikkomys; Geomyoidae; North AmericaAbstract The geomyoid genus Dikkomys is well represented in a sample from the Black Bear Quarry Il local fauna of Early Hemingfordian age in Bennett County, South Dakota. Isolated unworn P/4's of Dikkomys matthewi WOOD have a prominent median cristid (sagicristid) with a connection to the metaconid and the hypolophid. With wear, P/4 does not become as molariform as P/4 because of this cristid. Article infos |
|
|

|
Nouvelle interprétation de l'évolution du genre Megacricetodon au cours du MiocèneJean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Megacricetodon; Micromammals; MioceneAbstract La découverte de nouveaux gisements à micromammifères dans le Miocène du Sud de la France et d'Espagne montre que, s'il n'est plus possible d'accepter dans son intégralité le schéma phylétique de Fahlbusch du genre Megacricetodon, il existe toutefois des segments de lignées à l'intérieur de provinces géographiques différentes (Péninsule Ibérique, France, Europe Centrale), avec lesquels on peut établir une biochronologie locale, segments qu'il est aussi possible de placer les uns par rapport aux autres, en utilisant les corrélations que l'on peut reconnaître entre certains niveaux repères des mammalogistes et l'échelle stratigraphique marine. Article infos |
|
|

|
Premières données sur les rongeurs de la formation de Ch'orora (Ethiopie) d'âge Miocène supérieur. I: ThryonomyidésJean-Jacques Jaeger, Jacques Michaux and Maurice SabatierKeywords: Ethiopia; Paraulacodus; Rodents; Upper MioceneAbstract The genus Paraulacodus has been collected in the Ch'orora formation of Upper Miocene age, in Ethiopia. The new species, P. johanesi n. sp.. is more evolved than the previously described indian species P. indicus HINTON of the Siwalik Hills area. The morphological gap between P. johanesi and the present Thryonomys is still important. Article infos |
|
|

|
Essai de filiation des campagnols et des lemmings (Arvicolidae, Rodentia) en zone holartique d'après la morphologie dentaire.Jean ChalineKeywords: Arvicolidae; Dental morphology; Paleogeography; phyletic relationshipsAbstract The Arvicolid evolution results in an increase of the dental structure complexity. The M3/ differenciation seems to characterise the tribe subdivisions, that of M/1 being variable from one to another lineage. The phyletic relationships of fossil lineages are discussed from a paleogeographic point of view. Article infos |
|