Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 2 - les carnivoresGérard de BeaumontKeywords: anatomy; Carnivora; France; Montredon; Systematics; Upper MioceneAbstract The locality of Montredon has provided 8 species of camivores, often little documented, that are discribed and depicted. All the remains are fragmentary and generally badly preserved which lowers very much the possible precision of the taxonomic study; this one has however allowed the creation of a new subspecies. The most richlypdocumented forms are an ursid (Indarctos) and a felid (Machairodus). Issuing often from a westem Europe evolution, the carnivores are well inserted between those of the better known faunas of the "Classical Pontian" and of the lower Vallesian and this situation fits also well with their stratigraphic level, that cannot however be more accurately defined with them alone. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
La poche à Phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien supérieur. 5-SquamatesJean-Claude RageKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The Squamates from Sainte-Néboule are charateristic of the Upper Eocene from the Phosphorites du Quercy. Most genera known from this locality do not survive the « Grande Coupure ». Cadurcoboa insolita gen. nov., sp. nov. is a small Boidae very characteristic of the Upper Eocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
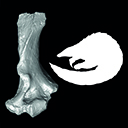
A pangolin (Manidae, Pholidota, Mammalia) from the French Quercy phosphorites (Pech du Fraysse, Saint-Projet, Tarn-et-Garonne, late Oligocene, MP 28)Jean-Yves Crochet, Lionel Hautier and Thomas LehmannKeywords: Oligocene; Pangolin; Pech du Fraysse; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e4 Abstract Pangolins have never shown a high taxic diversity and their fossil record is scarce. We report here the first discovery of a partial humerus from late Oligocene deposits in Pech du Fraysse (MP28, France). The new specimen from Pech du Fraysse is described and compared to various extant and extinct species of pangolins. It shows a suite of morphological features very similar to the humeri discovered in Saint-André (MP 26), Solnhofen (Burdigalien), and Saulcet (Aquitanian), attributed here to Necromanis franconica. The description of the specimen from Pech du Fraysse allowed us to discuss the systematics of Paleogene and Neogene pholidotans. The differences between PFY 4051 and N. franconica on the one side, and N. quercyi on the other side, might be sufficiently important to justify a generic distinction. A comparison with extant species showed that N. franconica was likely terrestrial and fossorial based on its humeral morphology. Related dataset Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|
|
Révision des Rhombodontidae (Neoselachii Batomorphii) des bassins à phosphate du MarocAbdelmajid Noubhani and Henri CappettaKeywords: Batomorphii; Maastrichtian; Morocco; New taxa; Phosphate; RbombodontidaeAbstract The revision of the Rhombodontidae from the Maastrichtian of Morocco led us to the description of a new species: Rhombodus andriesi. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Sur le plus ancien Lagomorphe Européen et la "Grande Coupure" Oligocène de StehlinNieves Lopez-Martinez and Louis ThalerKeywords: Grande Coupure; Lagomorphe; OligoceneAbstract Pour la première fois un spécimen de lagomorphe a été récolté en Quercy. L'intérêt de ce fossile tient surtout à son âge géologique inattendu, qui recule considérablement la date de première apparition en Europe de cet ordre de mammifère, Ceci nous paraît justifier une nouvelle réflexion sur la « grande coupure» oligocène, Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
Etude de la Variabilité chez Lophiodon lautricense NouletJean SudreKeywords: Cheek teeth; Eocene; Lophiodon; variabilitydoi: 10.18563/pv.4.3.67-95 Abstract The biometric and morphologie variability of the cheek teeth in the end-of-the-phylum species Lophiodon lautricense Noulet studied in this note, reposes on the observation of about 800 teeth. These were revealed to be little variable in absolute dimensions. The considerable morphologie variability in the upper premolars permitted the problem of the molarization process to be taken up. An hypothesis concerning the order of eruption of the cheek teeth is formulated based on an examination of a large number of milk dentitions. In conclusion, it is suggested that reservations be held on the value of dental characters classically used in systematics for the group under consideration. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 3 (1971) |
|
|

|
Un gisement à mammifères dans la formation lacustre d'âge Miocène moyen du Collet Redon près de St-Cannat (Bouches-du-Rhone). Implications stratigaphiquesJean-Pierre Aguilar and G. ClauzonKeywords: France; Neogene; RodentiaAbstract The new fauna of Collet Redon (Bouches-du-Rhône, France) is dated by three rodents: Megacricetodon aff. bavaricus, Democricetodon affinis mutilus and Peridyromys cf. hamadryas. They correlate this locality with Oggenhof and Ohningen in Bavaria (Western Germany). As the radiometric age of Ohningen is estimated between 14 and 13 M.Y., these three localities are of Serravallian age. This datation brings a complete readjusment of the stratigraphy of the section of Collet Redon formerly described by Collot and Combaluzier. The marine deposits with underly the continental formation with the mammal fauna, are Burdigalian. The angular unconformity between the marine and the continental deposits gives evidence of an episode of emersion on the margin of a sedimentary basin, with deformation and erosion. Owing to the newly discovered fauna, this geodynamical event is clearly settled within the regional geographical and chronological context. Lacustrine and continental deposits of such an age were up to now unsuspected in this area. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 5 (1979) |
|
|
|
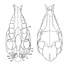
Le genre Leptolophus (Perissodactyla, Mammalia): morphologie et histologie dentaires, anatomie cranienne, implications fonctionnelles.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: dental histology; Eocene; functional anatomy; Palaeotheriidae; skull anatomy; Southern France; SystematicsAbstract A strong lophodonty, an extreme heterodonty, some hypsodonty and regular overlayings of coronal cement are prominent features of the genus Leptolophus (Palaeotheriinae = Palaeotheriidae s.s.). The histological pattern of the teeth unusually joins type II enamel prisms, characteristic of advanced ungulates, together with archaic features, such as an almost complete lack of Hunter-Schreger zonation and a weak expanse of peritubular dentine. The skull is narrow and slender, with an elongated ante-orbital facial region, a moderately notched nasal aperture, a rather elongated post-canine diastem, parallel zygornatic arches and a fairly dorsally located squamoso-mandibular joint.The functional analysis brings to light "ectolophodont" masticatory cycles with two phases, in which maximum power was applied, contrary to equíds, on hindmost teeth; likewise, skull accomodations to increasing height of the teeth are quite different. This study leads to the assumption that Leptolophus may have been light mammals, living in rather open surroundings, browsing on herbaceous plants or leaves cropped close to the ground. Moreover, it appears that it could have been some inadequacy of dental structures to the dietary, which leaded to quick wear of the teeth and to many enamel notches, but had been somewhat balanced by the early increase of hypsodonty, not induced in such a case by a biotop deterioration (as it will happen at the end of the Eocene). This ínadaptation might account for the short duration of the genus Leptolophus, whose the 3 species, L. stehlini, L. nouletí and L. magnus n. sp. are indeed confined in the level MP 16. Its geographical spreading (as far as known, South of western Europe) and the morphological pattern of its dentition suggest that this genus would have been related to early upper Eocene endemic spanish forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 1-2 (1998) |
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
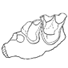
The new Algerian locality of Bir el Ater 3: validity of Libycosaurus algeriensis (Mammalia, Hippopotamoidea) and the age of the Nementcha FormationFabrice Lihoreau, Lionel Hautier and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Dispersal event; Miocene; North Africa; Tetralophodondoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e1 Abstract The description of original material of anthracothere and proboscidean in the new locality of Bir el Ater 3 from East Algeria, and a thorough review of early Libycosaurus remains of Bir el Ater 2 allows us validating L. algeriensis as the smallest and earliest species of Libycosaurus and probably the earliest migrant of the genus from Asia. The presence of a Tetralophodon in the Neogene Nementcha formation might represent the earliest occurrence of the genus in Africa. These original fossil remains allow us to discuss the age of the Neogene part of the Nementcha formation close to the Serravalian/Tortonian boundary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|
|
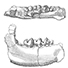
Un nouveau chiroptère vespertilionide de l'Oligocène d'EuropeBernard Sigé and Henri MenuKeywords: bats; Europe; nov. sp.; Oligocene; VespertilionidAbstract A fossil species of the extant genus Leuconoe, L. lavocati n. sp. from Le Garouillas Oligocene locality, Quercy phosphorites, SW-France, is established in nomenclatural standards. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|
|
|
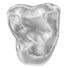
Les mammifères de Rians (Eocène inférieur, Provence)Marc GodinotKeywords: Eocene; Mammals; Provence; RiansAbstract The fossil mammals discovered in the quarry of Rians (Sparnacian, Provence) are described. Among these forms, Hyracotherium is interesting because of the little molarization of the lower premolars and its small size, and Diacodexis by its small size and very primitive astragalus ; they may be the most primitive representatives of their respective orders. Also, Proviverra eisenmanni n. sp. is the smallest and most primitive hyaenodontid yet described. Hyopsodus itinerans is the first species of this genus described France. Among other rare fossils is a new species of bat, a small palaeoryctid, and other forms not yet identified. Marsupials are varied. Several new species are present among the rodents. The fauna is well-balanced and rich in small hyopsodontid condylarths. It is stratigraphically situated at the Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 2 (1981) |
|
|
|
The eosimiid and amphipithecid primates (Anthropoidea) from the Oligocene of the Bugti hills (Balochistan, Pakistan): new insight into early higher primate evolution in South Asia.Laurent MarivauxKeywords: Amphipithecidae; anthropoid phylogney; Bugti Hills; Early Oligocene; Eosimiidae; PakistanAbstract Eosimiid and amphipithecid primates document a long and significant history of primate evolution throughout the Eocene in Southeast Asia. Despite the absence of a comprehensive post-Eocene fossil record, it was generally hypothesized that both families left no descendant in Asia. Recently, two new small-bodied taxa, Bugtipithecus and Phileosimias, have been recovered in early Oligocene coastal deposits from the Bugti Hills (Balochistan, central Pakistan) and referred to the families Amphipithecidae and Eosimiidae, respectively, on the basis of dental fossil remains. In this paper, we provide more exhaustive description, comparison, and discussion of these taxa. As for tarsiid and sivaladapid primates, the persistence of eosimiids and amphipithecids into the Oligocene clearly demonstrates that low latitudes of South Asia provided a continuous access to tropical refugia during the climatic deterioration characterizing the late Eocene-early Oligocene interval, which was seemingly lethal for primate communities elsewhere across the Holarctic continents. As a contribution to the ongoing phylogenetic debates regarding the position of eosimiids and amphipithecids on the primate family tree, we have performed a cladistic analysis in a high-level primate systematic context in order to assess the position and the role of these new taxa in that phylogenetic issue. Our results support the view according to which eosimiids and amphipithecids (and by extension Phileosimias and Bugtipithecus, respectively) are stem anthropoids. These fossils from Pakistan document an unsuspected Oligocene phase of the evolutionary history of anthropoid primates in southern Asia, which clearly enhances the extent of the anthropoid radiation in this province during the Paleogene. Several phylogenetic and paleobiogeographic aspects are discussed, notably the intra- and inter-relationships between Paleogene Asian and Afro-Arabian anthropoids, and the resulting potential dispersal models between both land-masses during the Paleogene. Article infos Published in Vol. 34, Fasc. 1-2 (2006) |
|
|
|
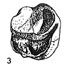
Un giraffidae dans le pliocène de Montpellier ?Claude GuérinKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Giraffidae; Mammalia; Montpellier; RuscinianAbstract An upper giraffid premolar without any indication about its origin is preserved at the Montpellier University among numerous fossils from the ruscinian formation of Montpellier. It can be related to Samotherium, of the Upper Miocene in Eastern Europe, North Africa and Asia, or more probably to Bramatherium or Hydaspitherium of the Pliocene of South East Asia. The sedimentological study of the matrix shows a calcareous background, which may indicate that this tooth does not come from the Montpellier formation. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|
|
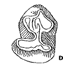
On the genus Dikkomys (Geomyoidea, Mammalia)Morton Green and Philip R. BjorkKeywords: Dikkomys; Geomyoidae; North AmericaAbstract The geomyoid genus Dikkomys is well represented in a sample from the Black Bear Quarry Il local fauna of Early Hemingfordian age in Bennett County, South Dakota. Isolated unworn P/4's of Dikkomys matthewi WOOD have a prominent median cristid (sagicristid) with a connection to the metaconid and the hypolophid. With wear, P/4 does not become as molariform as P/4 because of this cristid. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
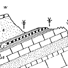
Les crocodiliens paléogenes du Tilemsi (Mali): un aperçu systématiqueEric BuffetautKeywords: Crocodilians; Dyrosoridae; Eocene; Mali; PalaeoceneAbstract Abundant crocodilian fossil remains have been collected, mainly by R. Lavocat. from several levels of the Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
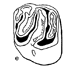
Pairomys et Ectropomys : la fin d'une ambiguïté ; mise au point sur les Oltinomyinae et Remyinae (Rodenia, Theridomyidae).Monique Vianey-Liaud, Norbert Schmidt-Kittler and Pablo Pelaez-CampomanesKeywords: PHYLOGENY; taxonomy; Theridomyidae; Upper EoceneAbstract The description of new material of the Upper Eoœne of France, Southem Germany and Spain together with the restudy of the material described by Thaler (1966b) as Pairomys allows to confirm the validity of the genus Ectropomys up to know controversally discussed. As a consequence the subfamily Remyinae and Oltinomyinae can be defined precisely. The study of the dental characters shows that the Remyinae in fact belong to the Theridomyidae and represent a derived evolutionary unit within this family. The Oltinomyinae together with the Theridomyinae and Issiodoromyinae very probably form a monophyletic unit. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Les sélaciens du Miocène de la région de MontpellierHenri CappettaKeywords: Ichtyofauna; Miocene; Montpellierdoi: 10.18563/pv.3.ext.1-139 Abstract The utilization of screen-washing and attack by dilute acetic acid has permitted the collecting, in the Miocene of the department of Hérault (France), of a very rich ichthyofauna. This fauna is presently comprised of about 60 studied species, of which 11 are new, and represents, in the present state of knowledge, the most varied Miocene selachian fauna described in the world. Article infos Published in Vol. 3, Ext (1970) |
|
|
|
Un crane de Chalicothere (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) du Miocène supérieur de Macédoine (Grèce) : remarque sur la phylogénie des ChalicotheiinaeLouis de Bonis, Geneviève Bouvrain, George D. Koufos and Pascal TassyKeywords: Chalicotheriidae; Cladistics; Greece; Miocene; Perissodactyla; PHYLOGENYAbstract The discovery in the Turolian (Late Miocene) of Dytiko 3 (Macedonia, Greece) of a complete skull with mandibles and cervical vertebrae, atlas and epistropheus, is a very important contribution to the knowledge of the subfarnily Chalicotheríinae. After the description, the comparison with other specimens of Miocene chalicotheres permits the revival of the generic name Macrotherium with a new species M. macedonicum. This genus is mainly characterized by a short snout and an inflated cerebral skull. It coexists during the Miocene with Chalicotherium. A cladistic analysis leads to conclusion that the species which has been described from the Early Middle Miocene of Rusinga must be identified as the type-species of a new genus: Butleria. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
Une faune du niveau d'Egerkinger (MP 14; Bartonien inférieur) dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Sud de la France)Jean Sudre, Bernard Sigé, Jean-Albert Remy, Bernard Marandat, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Marc Godinot and Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Biochronology; Early Bartonian; Eocene; evolution; Mammals; New taxa; QuercyAbstract The Laprade fauna is chronologically situated between those from Egerkingen and Lissieu and consequently, is close to the MP 14 reference-level of the European mammalian biochronological scale (Symposium of Mainz, 1987). Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 1 (1990) |
|