Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
PalaeovertebrataVol. 27, Fasc. 3-4:145-154. 1998
<< prev. article next article >>
|
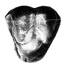
Carolocoutoia ferigoloi nov. and sp. (Protodidelphidae), a new Paleocene "opossum-like" marsupial from Brazil.Francisco J. Goin, Edison V. Oliveira and Adriana M. CandelaKeywords: Brazil; Didelphimorphia; Itaborai; Marsupialia; New taxa; Paleocene; Protodidelphidae; South AmericaCite this article: Goin F. J., Oliveira E. V., Candela A. M., 1998. Carolocoutoia ferigoloi nov. and sp. (Protodidelphidae), a new Paleocene "opossum-like" marsupial from Brazil. Palaeovertebrata 27 (3-4): 145-154. AbstractCarolocoutoia ferigoloi gen. et sp. nov. is the largest of protodidelphid marsupials, known from Middle Paleocene levels at Itaboraí Formation, southeastern Brazil. It differs from other members of this family in having molars with low cusps which are basally inflated, rounded crests without cutting edges, and a thick enamel layer which is wrinkled, specially at the labial half. A comparative analysis among representatives of this family led us to recognize only three genera undoubtely assignable to it: Protodidelphis PAULA COUTO, 1952, Robertbutleria MARSHALL, 1987, and Carolocoutoia gen. nov. Protodidelphids lack the basic derived features diagnostic of Polydolopimorphian marsupials, while most of its derived features agree with its belonging to the Didelphimorphia. Protodidelphids comprise a specialized clade of opossum-like marsupials adapted to frugivorous or frugivore-omnivorous feeding habits. They differ from other didelphimorphians in having very large, spire-like entoconids, reduced and antero-posteriorly compressed paraconids, absence of stylar cusp C and of para- and metaconules, large stylar cusps B and D which are proximate to each other, short postmetacristae, eccentric protocones, and molars that increase rapidly in size from M/ml to M/m3. Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 3-4 (1998) |
|