Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Acinoptèrygiens du Stéphanien de Montceau-les-Mines (Saône-et-Loire, France).Daniel Heyler and Cécile PoplinKeywords: Aeduelliforms; Biogeography; Palaeonisciforms; paramblypteriforms; StephanienAbstract The study of new specimens from the Stephanian shales of Montceau-les-Mines confirms and enlarges the number of groups already known in this area. Among the Palaeonisciforms, “form A" is now known more completely, although no diagnosis or name can yet be given for it. “Form B" is redescribed and its relationships with “Elonichthys robisoni" are discussed. A palaeoniscid is recorded which resembles those from Bourbon l'Archambault. The paramblypteriforms occur rather frequently, but no genera can be determined. The aeduelliforms comprise some specimens close to Aeduella blainvíllei from Muse (Autun basin), and a new genus. Comparison of the latter with two fossils from Lally allows creation of two new species and a new family. This diversification of the aeduelliforms during this middle Stephanian leads to the hypothesis that the group originated at least as early the lower Stephanian. This material prooves again the characteristic endemism of this fauna, particularly of the aeduelliforms which are known only in the Massif Central where they diversified during the Permo-Carboniferous. Biogeographical consequences are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|

|
Crivadiatherium iliescui n. sp., nouvel Embrithopode (Mammalia) dans le Paléogène ancien de la dépression de Hateg (Roumanie).Constin Radulesco and Jean SudreKeywords: Embrithopods; Late Eocene; Paleobiogeography; RomaniaAbstract The investigations undertaken at Crivadia (Hateg Depression, Hunedoara District, Romania), the type locality of Crivadiatherium mackennai RADULESCO el al. (Radulesco, Iliesco et lliesco, 1976), led to the discovery of remains of a new Embrithopod. Close to the above mentioned species, but larger in size, this animal is here described as a new species of Crivadiatherium, C. iliescui. ln addition, the comparison made between the forms indicated above and Palaeaamasía kansui OZANSOY from the Eocene deposits of Anatolia (Ozansoy, 1966; Sen et Heintz, 1979) showed that the latter species included a heterogeneous material; this permitted us to distinguish the form in the Anatolian locality Ciçekdag-Arabin Kôyü under the name Palaeoamasia sp. The geographical distribution and diversity of the Embrithopod species under discussion (Balkan, Anatolia) support the idea of an eurasiatic origin of this group and seem to suggest the existence during the Eocene of a particular faunal province in south-eastern Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 3 (1985) |
|
|
|
A new species of hippopotamine (Cetartiodactyla, Hippopotamidae) from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation, Abu Dhabi, United Arab EmiratesJean-Renaud Boisserie, Mathieu Schuster, Mark J. Beech, Andrew Hill and Faysal BibiKeywords: Arab Peninsula; Hippopotamidae; Hippopotamine event; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.41.1.e2 Abstract The discovery of new hippopotamid material from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation (Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates) has prompted the revision of the existing material of this as yet unnamed fossil taxon. The Baynunah hippopotamid appears to be distinct from all other contemporary and later species in having a relatively more elongate symphysis, a feature similar to the earlier (and more primitive) Kenyapotamus. Yet, the Baynunah hippopotamid presents a dentition typical of the Hippopotaminae. It is therefore a distinct species attributed to the later subfamily, described and named in this contribution. This species provides further evidence for a ca. 8 Ma evolutionary event (termed “Hippopotamine Event”) that initiated the spread and ecological significance of the Hippopotaminae into wet habitats across Africa and Eurasia. The morphological affinities of the new species from Abu Dhabi suggest that the Arabian Peninsula was not a dispersal route from Africa toward southern Asia for the Hippopotamidae at ca. 7.5 Ma to 6.5 Ma. Article infos Published in Vol 41-1 (2018) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
Schmelzmikrostruktur in den inzisiven alt-und neuweltlicher histricognather nagetiereThomas MartinKeywords: Africa; Caviomorpha; Ctenodactyloidea; Deseadan; Enamel microstructure; Hunter-Schreger bands; Hystricognathi; Incisors; Ischyromyoidea; multiserial; Paleobiogeography; pauciserial; Phiomorpha; Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract Enamel microstructure in the incisors of Old- and New World hystricognath rodents: Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Ext (1992) |
|
|
|
Les Ischyrictis de la transition Vindobonien-VallésienMiquel Crusafont i PairóKeywords: Ischyrictis; MustelidaeAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|

|
Evolution de la lignée Megacricetodon collongensis-Megacricetotodon roussillonensis (Cricetidae, Rodentia, mammalia) au cours du Midocène inférieur et moyen dans le Sud de la France.Jean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Cricetids rodents; Evolutionary lineage; Lower and Middle Miocene; Mammalian biochronology; Megacricetodon new species; Southern FranceAbstract New populations of the genus Megacricetodon have recently been discovered in Southern France.Two new species are defined: M. lemartineli n. sp. and M. fournasi n. sp., their stages of evolution are intermediate between those of M. gersii and M. roussillonensis. Morphological and biometrical analysis indicate the presence of only one lineage: M. collongensis--M. collongensis-gersii--M. gersii--M.lemartineli nov. sp.--M. fournasi nov. sp. and M. roussillonensis. This observation allows to refine the chronology based on rodents, for the Late Early Miocene and the Middle Miocene in the Southern France. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|

|
Relations phylétiques de Bachitherium filhol, ruminant de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Denis Geraads, Geneviève Bouvrain and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Bachitherium; Cladistic analysis; France; Mammalia; Oligocene; RuminantiaAbstract A detailed comparative study of a complete skeleton of Bachitherium and a cladistic analysis of the sub-order Neoselenodontia lead us to propose a cladogram and a new classification of this group. The Tylopoda are the sister-group of the Ruminantia, which are chiefly defined by the fusion of the cuboid and navicular. Within this infra-order, Amphimeryx is the sister genus of a tetraselenodont group, in which the Hypertragulidae are well-separated group from a monophyletic group defined by the loss of trapezium, fusion of capitatum and trapezoid, and the isolation of the hypoconid on lower molars. The most primitive genera of this group, Lophiomeryx and Iberomeryx still have an open trigonid on the lower molars, but this is lingually closed in Archaeomeryx, sister-genus of the higher Ruminantia which have fused metatarsals and more evolved milk teeth. We divide them into two pan/orders : Tragulina (including the recent and miocene Tragulidae, and the North-American Leptomerycidae), and Pecora, with reduced lateral metacarpals and a new crest (telocristid) on the lower premolars. Within the Pecora, the upper molars of Gelocus are more primitive than those of Bachitherium (a genus with many autapomorphies in the dentition) itself more primitive than the group Prodremotherium + Eupecora, with fused metacarpals. We consider the Eupecora (including several genera without frontal appendages) to be monophyletic. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 2 (1987) |
|
|
|
Révision des Artiodactyles de l'Eocène moyen de Lissieu (Rhône)Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyles; Dichodon; FranceAbstract The object of this work is the study of the artiodactyls of the karstic locality of Lissieu near Lyon. Among the sixteen species counted, five (Hyperdichobune nobilis, Hyperdichobune sp., Haplabunodon mulleri, Tapirulus depereti and Pseudamphimeryx schlosseri) are cited for the first time in this fauna. The description of part of the anterior dentition of «Dichobune» langi permits the referal of this species to the genus Hyperdichobune. The new selenodont species Dichodon lugdunensis described in this work belongs, with its ancestor Dichodon simplex, to a lineage distinct from that of Dichodan cartieri and Dichodon ruetimeyeri. Finally, the taxonomic reality of the Lissieu species, Lophiobunodon rhodanicum Deperet, is justified. All the other species have been compared with those of Egerkingen. Even though with most of them no difference in age can be shown between the two deposits, some however indicate clearly by their degree of evolution that Lissieu is slightly more recent than Egerkingen. ln the history of Eocene mammals, the Lissieu fauna, because of its homogeneity, can be considered as a sure reference fauna of the Auversian period. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 4 (1972) |
|
|
|
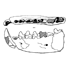
Pantolestidae nouveaux (Mammalia, Insectivora) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller (Alsace).Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Bouxwiller; Insectivora; Mammalia; Middle Eocene; Pantolestidaedoi: 10.18563/pv.3.3.63-82 Abstract The Pantolestidae from the middle eocene of Bouxwiller are the subject of a detailed study. Buxolestes hammeli (n. g., n. sp.) is not closely related to any other European or North American form described until now; it presents, however, some characters in common with Pantolestes, a form of the same age from North America. A parallel evolution from a common ancestral form could explain this ressemblance. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 3 (1970) |
|
|

|
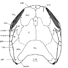
Revision of the historical collections of Pliocene-Pleistocene large mammals from Le Riège and Saint-Palais localities, near Pézenas (Southern France)Federica Mulè, Luca Pandolfi, Anne-Lise Charruault, Jean-Yves Crochet, Jérôme Ivorra, Fabrice Lihoreau, Laurent Marivaux, Mehdi Mouana, Félix Nesme, Céline Robinet, Philippe Münch and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: Hérault; Mammalia; Montpellier; Neogene; Quaternarydoi: 10.18563/pv.48.1.e2 Abstract Numerous “Quaternary” large-mammal fossils have been collected since the 1830s along the Le Riège stream, near Pézenas (Southern France). More than 120 specimens are stored in the collections of the Université de Montpellier (UM) under the name “Le Riège”. A major operation aiming at relocating the palaeontological collections of the University has made it possible to group together all the specimens of interest and launch their systematic revision for the first time. The fossils belong to the Reboul (1839; 51 samples) and de Christol (1865; 18 samples) Collections and 17 samples compose the Crochet & Ivorra Collection (1998). The remaining 38 samples have no mention about the exact time and location of their finding. We provide a critical inventory with literal transcription of inscriptions on specimens and historical labels. This revision confirms the presence of two distinct faunal assemblages under the name of “Le Riège”: Saint-Palais (Early Pliocene, MN14–15) and Le Riège sensu stricto (late Early Pleistocene, most likely MNQ19). The former assemblage, with coastal affinities, is composed of the ruminants Alephis sp. and Procapreolus cf. pyrenaicus, the rhinocerotid Pliorhinus megarhinus, the gomphotheriid Anancus arvernensis and marine mammals, all emblematic taxa for the Early Pliocene of Montpellier and Perpignan. The latter assemblage documents a late Early Pleistocene fluvio-volcanic sequence, yielding the bovid Bison (Eobison) spp., the cervid Eucladoceros cf. giulii, the hippopotamid Hippopotamus antiquus, the rhinocerotid Stephanorhinus etruscus, the equid Equus cf. altidens, and the elephantid Mammuthus cf. meridionalis, plus a few specimens of uncertain taxonomic affinities. This revision underscores the interest of revisiting historical collections and further provides a starting point for future research. Article infos in press |
|
S.I. Data |
|
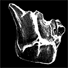
Les vertébres dévoniens de la Montagne Noire (Sud de la France) et leur apport à la phylogénie des pachyosteomorphes (Placodermes Arthrodires).Hervé Lelièvre, Raimund Feist, Daniel Goujet and Alain BlieckKeywords: Devonian; Montagne Noire; New taxon; PHYLOGENY; Placoderms; Stratigraphy; VertebrateAbstract Several different taxa of jawed vertebrates are reported for the first time from the Devonian of south-eastern Montagne Noire, France. Besides some undeterminable fragments of placoderm fishes from the Pragian and Lower Emsian, the material from the Upper Devonian is mainly represented by Melanosteus occitanus gen. and sp. nov. (Frasnian) and Thoralodus cabrieri LEHMAN, 1952 ("Famennian"). The good state of preservation of Melanosteus allows a detailed anatomical study leading to a phylogenetic analysis of the selenosteid pachyosteomorphs. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 1 (1987) |
|
|
|
Insectivores pliocènes du Sud de la France (Languedoc-Roussillon) et du Nord-Est de l'Espagne.Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Insectivora; Languedoc; Pliocene; Spain; SystematicsAbstract The first lists of Insectivores (Erinaceidae, Talpidae and Soricidae) from the Pliocene beds of Southern France and North-East Spain are given in this paper. The material from twelve localities is studied. These localities are geographically situated in Languedoc (Celleneuve, Vendargues, Nîmes, Sète, Balaruc 2 and Seynes), in Roussillon (Terrats, Serrats-d'en-Vacquer, Château d'eau and Mont-Hélène) and in North-East Spain (Layna, Medas Islands and Puebla de Valverde). These faunas correspond to the Early, Middle and Late Pliocene. 1 to 8 taxa are identified in these localities and 14 specific taxa are presently listed for this period in this area. Two new specific taxa are described as Galerix depereti nov. sp. from all the Early Pliocene localities in the North-Pyrenean area and as Desmanella gardiolensis nov. sp. from Balaruc 2. For this small mammals, two faunal assemblages are recognized. The first one is dated from the Early Pliocene (F 1, 2 and 3 zones in Aguilar et Michaux) and is characterized by Galerix depereti and rare and little diversified Soricids. The second one is Late Pliocene in age (zones G 2 and G 3). The fossils of the genus Talpa are relatively abundant and the Soricids are diversified and very abundant. The Middle Pliocene (zone G 1) is a transitional period. ln these faunas, most of the insectivore genera are known from the European Late Miocene beds (8 on 10). This fact demonstrates a relative continuity between the invectivore faunas from the Late Miocene to the Early Pliocene. In conclusion, somme paleoecological considerations are suggested. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|

|
Préface au mémoire jubilaire en hommage à René LavocatJacques MichauxKeywords: EditorialAbstract Monsieur René Lavocat, Directeur du Laboratoire de Paléontologie des Vertébrés de la troisième section de l'Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes, quittait le service actif en l'année 1979. View editorial Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
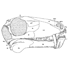
Reflections on some Russian eotheriodonts (Reptilia, Synapsida, Therapsida)Denise Sigogneau-Russell and P. K. TchudinovKeywords: Reptilia; Russia; Synapsida; Therapsidadoi: 10.18563/pv.5.3.79-109 Abstract As a result of the enrichment of eotheriodont material by one of us (P.K.T.), these specimens (essentially Biarmosuchur and Eotitanosuchur) are reexamined and refigured. A reevaluation of their particularities supports the distinction of two families, for which new diagnoses are proposed. This leads us to discuss the affinities of these families, with respect to the sphenacodonts on one hand, and to the South African primitive theriodonts on the other (gorgonopsids and ictidorhinids). This study contains inherent paleogeographic consequences which are considered in conclusion. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 3 (1972) |
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
A new Ardynomys (Rodentia,Cylindrodontidae) from the Eocene of the eastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia.Demberelyin DashzevegKeywords: Ardynomys; Eocene; Mongolia; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract A partial skull of Ardynomys russelli sp. nov. (Rodentia, Cylindrodontidae) is described. This was collected in the late Eocene of Alag Tsab locality in the eastem Gobi Desert, Mongolia. Ardynomys russelli sp. nov. is characterized by small size, brachyodont molars, and retention of P3. It represents the earliest record of the genus Ardynomys MATTHEW & GRANGER, 1925, in Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Une faunule de vertébrés sous la base de grès de Celas (Eocène supérieur) à ST Dresery (Gard)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Artiodactyla; Biostratigraphy; Eocene; MammalsAbstract The St-Dézéry local fauna (3 reptile-, 4 mammal species) is approximately of the same age as the La Débruge or the Ste-Néboule faunas. It conduces to a better dating of the limestones underlying the Célas sandstones. A large part of a mandible of Amphimeryx was found there, which documents the record of this family of small artiodactyls Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Les traces de pas d'amphibiens, de dinosaures et autres reptiles du Mesozoïque Français : inventaire et interprétations.Georges Gand, Georges Demathieu and Christian MontenatKeywords: Footprints; France; Inventory; Mesozoic; palaeontology; palaeovenvironments; Stratigraphydoi: 10.18563/pv.35.1-4.1-149 Abstract Since the 19th century, thousands of footprints were observed in the geological series of the French Mesozoic. All are located in the Triassic and Jurassic. After a promising beginning, in France, it is only a few papers which will be published in the first half 20th century, unlike the USA and of others countries of Western Europe. One ought to wait about 1950 for a revival and now they are nearly 200 papers which were devoted to the ichnofossils. The literature abundance and the renewed interest of the naturalists for the palichnologic studies decided to us to write a synthesis work. This one begins with a stratigraphic inventory in which, localisation, age and paleontological contents of about 180 fossiliferous sites are specified. After having pointed out the followed methods, the footprints paleontological interpretation is then approached in detail and the results obtained are replaced in stratigraphy to deduce the fauna evolution during the Mesozoic. So, it appears that Ichnologic data, more varied and rich in the Triassic and Liassic than those relating to the bones, very rare for the considered periods, are very informative. The middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian), thus reveals Cotylosauria, Lepidosauria, Crurotarsi with Rauisuchia, Ornithosuchidae, Crocodylia and Dinosauromorpha more the "Prodinosauria": Dinosamiforme whose skeletons are known in Argentina but only in Ladinian. The rather fast domination of Dinosaurs during Norian is also as well shown. The almost exclusive presence of their footprints, up to fifty cm long, in the Lower Hettangian indicates their supremacy in the environments. Footprints characterise not very deep life places located between inter-supratidal limits and often out of water. Sedimentologic and Palaeontologic studies showed that they were great coastal spaces during Middle Triassic, flood-plain with sebkhas while Upper Triassic, and a large !!coastal marsh!! in Grands-Causses during Liassic in which, mainly, fine stromatolithic layers were deposited. During the same periad, bay beaches spread in Vendée. During the Middle Jurassic, they are also brackish to lacustrine environments and recifallagoons in- the Upper Jurassic. Numerous measurements of the footprints and trackways directions showed that the animaIs moved there in weil defined directions, for long periods. They seem due to the palaeotopography of the life environments relatively stable. Also, the discovery of vegetal radicular networks and small footprints far away from the continental borderlands has suggested that the animals continuously lived in these palaeoenvironnements, belonging to large ecosystems, where the sedimentation rate was weak. This explains that thebadies could not fossilize there but only their footprints through the cyanobacterian action in main cases. From the vertical distribution of different ichnospecies, defined with adapted statistical methods, explained in this work, a palichnostratigraphy was established for the Middle Triassic. Although the footprints are also abundant in Hettango-Sinemurian of "Grands-Causses" and the Vendée, it was not possible, up to now, to establish any zonation in this series; Probably because the palichnofauna is too little diversified there, currently reduced to a majority of Theropods II-IV tridactyl traces. Article infos Published in Vol. 35, Fasc. 1-4 (2007) |
|
|
|
Muridae (Rodentia) du Pliocène supérieur d'Espagne et du midi de la France.Jacques MichauxKeywords: Anthracomys meini; Castillomys crusafonti; Pliocene; Rodents; Valerymys ellenbergeridoi: 10.18563/pv.3.1.1-25 Abstract The murid fauna of the terminal Pliocene of southwest Europe is rich in at least eight genera and ten species. With the species belonging to the genera Apodemus, Rhagapodemus, and Stephanomys not being studied here, the study of the other murids resulted for one thing in the description of three new genera and three new species: Castillomys crusafonti n. g., n. sp., Occitanomys brailloni n. g., n. sp., Anthracomys meini n. sp., Valerymys ellenbergerí (THALER) n. g., and for another thing in the recognition of a form hitherto unknown in this region, Micromys praeminutus KRETZOI. Systematic study has shown that certain species of the terminal Pliocene fauna had their ancestors in the Turolian fauna presently known in Spain. The evolutionary lineages thereby recognized have been studied more in detail and a list of the evolutionary tendencies of the dendal characters has been given. A chart of the probable phyletic relationships between the different murids of the Pliocene faunas of southwest Europe (With the genus Rhagapodemus and Apodemus dominans being excluded) is given in conclusion of this work. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 1 (1969) |
|
|
|
Les serpents des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Claude RageKeywords: Grande Coupure; Quercy Phosphorites; SerpentsAbstract A short review of the genera and species of snakes from the Quercy's phosphorites described by former authors is followed by the study of specimens recently collected. Most of these latter specimens belong to the Aniliidae, Boidae, Colubridae and to the Scolecophidia; the precise systematic position of some of them is not defined yet. The following genera and species are described: Eonilius europae nov. gen. and nov. sp., Platyspondylia lepta nov. gen. and nov. sp., Coluber cadurci nov. sp. and Dunnophis cadurcensis nov. sp.; a species described by de Rochebrune (Palaeopython filholi) is revised. One of the most important conclusions of this study is that the Colubridae appear as early as the Upper Eocene. The stratigraphic repartition of these snakes shows that the rich Upper Eocene fauna is followed by the very reduced fauna of the Lower Oligocene; then the oligocene «Grande Coupure» corresponds to a very important faunistic renewal. The fauna remains poor and little diversified during the beginning of the Middle Oligocene after which there is a new faunistic explosion. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|