Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Werneburg et al. New Permian Caseid from France
Field trip guides/EAVP Annual Conference/2023
Embrithopod from Croatia
Hypoplasia: CT-scan or naked eye?
Book of Abstracts/EAVP Annual Conference/2023
Eocene (57) , Quercy phosphorites (37) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (26)
|
Pantolestidae nouveaux (Mammalia, Insectivora) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller (Alsace).Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Bouxwiller; Insectivora; Mammalia; Middle Eocene; Pantolestidaedoi: 10.18563/pv.3.3.63-82 Abstract The Pantolestidae from the middle eocene of Bouxwiller are the subject of a detailed study. Buxolestes hammeli (n. g., n. sp.) is not closely related to any other European or North American form described until now; it presents, however, some characters in common with Pantolestes, a form of the same age from North America. A parallel evolution from a common ancestral form could explain this ressemblance. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 3 (1970) |
|
|

|
Cervus elaphus rossii (Mammalia, Artiodactyla), a new endemic sub-species from the Middle Pleistocene of CorsicaElisabeth PereiraKeywords: Cervus elaphus; Corsica; Endemism; PleistoceneAbstract Several endemic deer remains from the Middle Pleistocene deposits of the Castiglione cave (Oletta, Haute-Corse) are examined here. A morphometric analysis allows to relate them to a new insular subspecies Cervus elaphus rossii. The bones were compared with those of the mainland early Middle Pleistocene subspecies Cervus elaphus acoronatus Beninde and the European species Cervus elaphus Linné (Late Middle Pleistocene and Upper Pleistocene forms (continental and insular)). The Castiglione fossil shows peculiar morphofunctional features in its appendicular skeleton suggesting a morphological convergence with certain Bovidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 3-4 (2001) |
|
|
|
Données nouvelles sur le genre Stehlinia (Vespertilionoidea, Chiroptera) du Paléocène d'EuropeBernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Palaeocene; VespertilionoideaAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
Revision der Equoidea aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bel Halle (DDR).Jens L. Franzen and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Eocene; Europe; Mammalia; Perissodactyla; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The dentitions as well as one complete and several partial skeletons of Equoids from the Eocene lignite beds of the Geiseltal locality are revised. Instead of 13 species distinguished up to now 3 chronoclines with 5 species and 3 separate species are recognized (text. fig. 1). Propalaeotherium hassiacum HAUPT, 1925 is evolving into Propalaeotherium isselanum (CUVIER, 1824) between the levels of the « obere Unterkohle ›› and the « untere Mittelkohle ›› of the Geiseltal section. Propalaeotherium argentonicum GERVAIS, 1849 is shown to be present in the « untere Unterkohle ››, whereas Lophiotherium pygmaeum (DEPERET,1901) occurs in the « obere Mittelkohle ›› and in the « oberes Hauptmittel ››. Plagiolophus cartieri STEHLIN, 1904 appears during the transition from the « Mittelkohle ›› into the « Oberkohle ›› as the earliest true Palaeothere. Therefore the « Oberkohle ›› is already regarded as Upper Eocene. This is corroborated by the occurrence of a phyletic descendant of Propalaeatherium parvulum (Propalaeotherium n.sp.) in the middle and upper "Oberkohle " because this species appears otherwise for the first time at the mammal level of Lissieu. On the other hand Propachynolophus gaudryz (LEMOINE, 1878) described by Matthes (1977) from the « untere Unterkohle ›› turns out te be in fact a Phenacodont. Thus the decisive argument for classifying the « untere Unterkohle ›› as Lower Eocene has to be dropped. Biostratigraphically the « Unterkohle ›› and the «Basishauptrnittel ›› correspond with the lower Middle Eocene (mammal level of Messel), whereas the «unteres Hauptmittel ›› and the « untere Mittelkohle ›› are equivalent to the middle part of the middle Eocene (mammal level of lssel), and the « obere Mittelkohle ›› together with the « oberes Hauptmittel ›› coincide with the upper Middle Eocene (mammal level of Bouxwiller). Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
Révision des Rhombodontidae (Neoselachii Batomorphii) des bassins à phosphate du MarocAbdelmajid Noubhani and Henri CappettaKeywords: Batomorphii; Maastrichtian; Morocco; New taxa; Phosphate; RbombodontidaeAbstract The revision of the Rhombodontidae from the Maastrichtian of Morocco led us to the description of a new species: Rhombodus andriesi. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Les rongeurs de l'Eocène d'Afrique Nord-Occidentale [Glib Zegdou ( Algérie) et Chambi (Tunisie)] et l'origine des anomaluridae.Monique Vianey-Liaud, Jean-Jacques Jaeger, Jean-Louis Hartenberger and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Africa; Eocene; New taxa; Paleobiogeography; PHYLOGENY; RodentsAbstract This paper is about the oldest African rodents faunas, from the late Early Eocene, or early Middle Eocene, Glib Zegdou (Algeria) and Chambi (Tunisia) localities. Five species are described and figured, belonging to a new family here created, the Zegdoumyidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Nouvelles espèces de Dendromus (Rongeurs,Muriodea) à Langebaanweg (Pliocène,Afrique du Sud) conséquences stratigraphiques et PaléoecologiquesChristiane DenysKeywords: Dendromurinae; Paleoecology; Pliocene; Rodents; South Africa; StratigraphyAbstract New Dendromus species (Rodentia, Muroídea) from Langebaanweg (Pliocene, South Africa). Stratigraphical and paleoecological consequences. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Functional aspects of the evolution of rodent molarsPercy M. ButlerKeywords: Chewing; Muridae; Rodents; Wear facetsAbstract The wear facets of primitive rodents can be homologized with those of primitive primates and ungulates. As in primates, the jaw movement was ectental, with an increased anterior component in the lingual phase (phase ll). The buccal phase (phase I) in rodents approaches the horizontal and it tends to be reduced in importance in comparison with the lingual phase. ln more advanced rodents the efficiency of grinding is increased by the development of additional cutting edges of enamel (e.g. enlargement of hypocone, development of mesoloph and lingual sinus). The buccal phase movement becomes lined up with the lingual phase movement to form a single oblique chewing stroke,resulting in planation of the crown. As the stroke becomes more longitudinal (propalinal) the enamel edges become more transverse. In Muridae propalinal chewing evolved before the loss of cusps, facets were reorientated and additional cusps developed. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
New Late Miocene plecotine bats (Chiroptera, Vespertilionidae: Plecotini) from Gritsev, UkraineValentina V. Rosina, Sergei Kruskop and Yuriy SemenovKeywords: Barbastella; bats; late Neogene; Mammalia; Plecotusdoi: 10.18563/pv.42.1.e2 Abstract The Late Miocene site of Gritsev (MN 9, Ukraine) has yielded a very rich bat fauna, the remains of which are well preserved. Compared to other Neogene bat assemblages of Europe, the Gritsev bat community is unique in preserving plecotine bats, which are rare from Neogene sites. Some peculiar and new bat species, including a large plecotin Otonycteris, already were described from the Gritsev mammal site. Here we report new records of small plecotin bats from Gritsev, including a new taxon, Barbastella maxima nov. sp. This is the earliest reliable fossil record of this genus and it differs from more recent species of Barbastella in being considerably larger. The evolutionary patterns in the odontology within the tribe Plecotini, supported by biostratigraphical distribution of fossil records of Plecotus are discussed. The morphological peculiarities of the new fossils of plecotine bats from Gritsev are discussed in connection with its possible taxonomical affinity. Article infos Published in Vol 42-1 (2019) |
|
|

|
The Pleistocene vertebrate fauna of Robinson Cave, Overton County, TennesseeJ. E. Guilday, H. W. Hamilton and A. D. Mc CradyKeywords: Fauna; Mammalia; Pleistocene; Tennesseedoi: 10.18563/pv.2.2.25-75 Abstract A late Pleistocene deposit of 60 species of vertebrates and 12 of invertebrates is described from Robinson Cave, Overton County, Tennessee, U.S.A. Forty-eight species of mammals are represented by at least 2,483 individuals; 10 % are extinct, 10 % occur in the state only as boreal relicts in the Great Smoky Mountains; 23 % no longer occur as far south as Tennessee; 57 % occur at or near the site today. Nínety-one percent of the Recent mammal species can be found living today in the Minnesota-Wisconsin area, approximately 10 degrees farther north. Fluorine analysis suggests a long period of accumulation. The following 10 mammalian species are recorded from Tennessee for the first time. Sorex arcticus, Microsorex hoyi, Citellus tridecemlineatus, Clethrionomys gapperi, Microtus pennsylvanicus, Synaptomys cooperi, Synaptomys borealis, Zapus nudsonius, Napaeozapus insignis, Martes americana. Six additional species are present as boreal relicts in the Great Smoky Mountains of eastern Tennessee but not at the site today : Sorex cinereus, Sorex dispar, Sorex palustris, Parascalops breweri, Glaucomys sabrinus, Mustela nivalis. Six forms are extinct: Canis dirus, Ursus americanus amplidens, Sangamona furtiva, Dasypus bellus, Mammut americanus,Megalonyx jeffersoni. Twenty-six additional species of mammals, all of the snails, birds, reptiles, and amphibians recovered from the fauna still inhabit the area today: The fauna is indicative of a cold-temperate climatic episode associated with the Wisconsin glaciation, but may be chronologically mixed. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 2 (1969) |
|
|
|
First Neogene Otonycteris (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from Ukraine: its biostratigraphic and paleogeographic significance.Valentina V. RosinaKeywords: bats; East Europe; Gritsev; Late Miocene; Mammaliadoi: 10.18563/pv.39.1.e2 Abstract A new species, Otonycteris rummeli nov. sp., is described from the Late Miocene site Gritsev (MN 9) in the Ukraine. Otonycteris rummeli nov. sp. differs from those of most vespertilionids, except recent Otonycteris, Antrozous and Early Miocene Karstala silva, in having a well-developed entocingulid at the foot of the trigonid valley in the lower molars. The morphological resemblance of Otonycteris, Antrozous and Karstala is apparently a case of convergence in the evolution of the Old and New Worlds bat faunas. From at least the Middle Miocene the range of Otonycteris distribution spread to the whole of Central Europe and such a situation continued during the whole Late Miocene. This indicates a more arid climate in Europe during the Upper Miocene compared to the Quaternary. The reduction of the distribution range of Otonycteris and its extinction in most of the territory of Europe could have been caused by the global climatic cooling and increasing glacial cycle amplitude during the onset of the Quaternary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-1 (2015) |
|
|
|
Contribution à l'étude des genres Gliravus et Microparamys (Rodentia) de l'Eocène d'Europe.Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Eocene; Gliravus; Microparamys; Rodentiadoi: 10.18563/pv.4.4.97-135 Abstract Based on material found in about 15 localities the relationships of the genera Microparamys and Glirarus have been studied. One new genus, two subgenera and three species [Microparamys (Sparnacomys) chandoni n. subgen. and n. sp., Microparamys (Pantrogna) russelli n. subgen., Eoglirarus wildi n. gen. and n. sp., Gliravus meridionalis n. sp.] as well as the publication Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 4 (1971) |
|
|

|
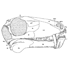
Etude du crâne de Pachynolophus lavocati n. sp. (Perissodactyla, Palaeotheriidae) des Phosphorites du QuercyJean-Albert RemyKeywords: Perissodactyla; Quercy phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.5.2.45-78 Abstract The genus Pachynolophus, one of the poorest known of the Palaeotheriidae, includes the brachyodont forms with reduced and non-molariform premolars and with upper molars lacking a mesostyle. Quantitative characters (divers surface indications and elongation of the teeth), while demonstrating a close relationship to Hyracotherium, permit a better differentiation of the genus, confirm its specific splitting, and permit the distinction of three lineages. The skull from Memerlein is taken as the type of a new species, P. Iavocati, of which the dentition is extremely characterized by its lophiodonty, the strong reduction of the premolars and the reduction of the cingula. This characterization testifies to a late age which extends the existence of the genus quite near to the Eocene-Oligocene limit. Compared with the only two skulls known of related species (Hyracotheríum vulpiceps and Pachynolophus Iivinierensis), that from Memerlein is distinguished by progressive characters affecting diferent regions but most particularly the braincase; it is not possible, however, to isolate within this evolution the part which leads to a systematic differentiation. Modernization is translated by a considerable increase in size of the braincase, principally in the frontal region, a development of the facial region with anterior displacement of the dental series and a greater specialization of the masticatory apparatus. This evolution parallels the history of the Equidae of the North American early Tertiary, but certain particularities, the form of the alisphenoid, the presence of an anterior frontal foramen, and the structure of the paroccipital apophysis, testifies to the independance of the European forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 2 (1972) |
|
|
|
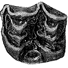
Reflections on some Russian eotheriodonts (Reptilia, Synapsida, Therapsida)Denise Sigogneau-Russell and P. K. TchudinovKeywords: Reptilia; Russia; Synapsida; Therapsidadoi: 10.18563/pv.5.3.79-109 Abstract As a result of the enrichment of eotheriodont material by one of us (P.K.T.), these specimens (essentially Biarmosuchur and Eotitanosuchur) are reexamined and refigured. A reevaluation of their particularities supports the distinction of two families, for which new diagnoses are proposed. This leads us to discuss the affinities of these families, with respect to the sphenacodonts on one hand, and to the South African primitive theriodonts on the other (gorgonopsids and ictidorhinids). This study contains inherent paleogeographic consequences which are considered in conclusion. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 3 (1972) |
|
|
|
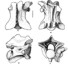
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 5 - Les périssodactyles EquidaeVéra EisenmannKeywords: Equidae; Hipparion; Late Vallesian; Mammalia; Montredon; PerissodactylaAbstract Revision of the hipparion material from Montredon, including newly excavated and other unpublished specimens brings evidence of specific heterogeneity. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Les Amphibiens et les reptiles du Pliocène supérieur de Balaruc II (Herault, France)Salvador BailonKeywords: amphibians; Europe; France; Pliocene; ReptilesAbstract The late Pliocene site (MN 16) of Balaruc II (Hérault, France) has provided remains of the following amphibians and reptiles: Chelotriton pliocenicus nov. sp. and Triturus marmoratus (Salamandridae), cf. Rana (Ranidae), cf. Blanus (Amphisbaenidae), cf. Agama (Agamidae), Gekkonidae indet., Lacerta s.l. (Lacertidae), "Ophisaurus" sp. (Anguidae), Michauxophis occitanus (Aniliidae), Erycinae indet. (Boidae), Elaphe cf. E. longissima and Malpolon sp. (Colubridae), cf. Naja (Elapidae) and Vipera sp. (Viperidae). The salamandrid Chelotriton pliocenicus and the aniliid Michauxophis occitanus constitute, up to now, the only records of these groups in the European Pliocene. The fauna is indicative of a warm, dry Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|

|
Relations phylétiques de Bachitherium filhol, ruminant de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Denis Geraads, Geneviève Bouvrain and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Bachitherium; Cladistic analysis; France; Mammalia; Oligocene; RuminantiaAbstract A detailed comparative study of a complete skeleton of Bachitherium and a cladistic analysis of the sub-order Neoselenodontia lead us to propose a cladogram and a new classification of this group. The Tylopoda are the sister-group of the Ruminantia, which are chiefly defined by the fusion of the cuboid and navicular. Within this infra-order, Amphimeryx is the sister genus of a tetraselenodont group, in which the Hypertragulidae are well-separated group from a monophyletic group defined by the loss of trapezium, fusion of capitatum and trapezoid, and the isolation of the hypoconid on lower molars. The most primitive genera of this group, Lophiomeryx and Iberomeryx still have an open trigonid on the lower molars, but this is lingually closed in Archaeomeryx, sister-genus of the higher Ruminantia which have fused metatarsals and more evolved milk teeth. We divide them into two pan/orders : Tragulina (including the recent and miocene Tragulidae, and the North-American Leptomerycidae), and Pecora, with reduced lateral metacarpals and a new crest (telocristid) on the lower premolars. Within the Pecora, the upper molars of Gelocus are more primitive than those of Bachitherium (a genus with many autapomorphies in the dentition) itself more primitive than the group Prodremotherium + Eupecora, with fused metacarpals. We consider the Eupecora (including several genera without frontal appendages) to be monophyletic. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 2 (1987) |
|
|

|
Equus caballus antunesi, nouvelle sous-espèce Quaternaire du PortugalJoao L. Cardoso and Véra EisenmannKeywords: Equidae; Equus caballus; new subspecies; Perissodactyla; Portugal; WürmAbstract Equus caballus antunesi, nova subspecies, was a hypsodont, slender, and rather small horse (around 141cm at the withers), with narrow hooves and protocones longer on P3/-P4/ than on M1/-M2/. It does not fit in any of the different "types" of Pleistocene caballine horses previously recognized but may be related to the horse from the Acheulean of Solana del Zamborino. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 2 (1989) |
|
|
|
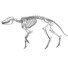
Artiodactyla aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bei Halle (DDR)Jorg Erfurt and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Artiodactyles; Eocene; Europe; Paleoecology; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The present study of Artiodactyla from the Middle Eocene of the Geiseltal lignite beds concems systematics, biostratigraphy, and palaeoecology on the basis of 174 specimens: isolated remains to more complete skeletons. Instead of the formerly known five species of two families are now recognized 14 species of the Diacodexeidae, Dichobunidae, Cebochoeridae, and Haplobunodontidae. New species are Aumelasia maniai, Anthracobunodon neumarkensis, Masillabune franzeni. Four species of the Geiseltalfauna are definitely known from elswere, and five species are closely related to those from other European localities. Evidently the faunal situation of artiodactyls during the Middle Eocene of Europe was largely uniform. The distribution of artiodactyls within the sequence of the Geiseltal strata corroborates the biostratigraphical concept of the land mammal age Geiseltalian (Franzen & Haubold l986b) as well as the mammalian reference levels MP 11-13 (Franzen 1987). Reconstructions of the skulls and skeletons allow conclusions on the functional morphology and palaeoecology of the artiodactyls of the European Middle Eocene Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|
|
On the genus Dikkomys (Geomyoidea, Mammalia)Morton Green and Philip R. BjorkKeywords: Dikkomys; Geomyoidae; North AmericaAbstract The geomyoid genus Dikkomys is well represented in a sample from the Black Bear Quarry Il local fauna of Early Hemingfordian age in Bennett County, South Dakota. Isolated unworn P/4's of Dikkomys matthewi WOOD have a prominent median cristid (sagicristid) with a connection to the metaconid and the hypolophid. With wear, P/4 does not become as molariform as P/4 because of this cristid. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|