Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
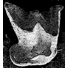
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 7- Didelphides (Marsupiaux)Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The family Didelphidae is represented by three species in the Sainte-Néboule site, phosphorites of Quercy (lower Oligocene, San Cugat's nivel): Amphiperatherium minutum (Aymard), Amphiperatherium sp. and Peratherium cuvieri (Fischer). Only the first and third species are abundant (88 and 97 pieces). This two populations are described. The marsupial fauna of the european lower Oligocene is not recognized in its entirety in this site. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Origins of avian reproduction: answers and questionsfrom dinosaurs.David J. Varricchio and Frankie D. JacksonKeywords: Avian reproduction; clutch; dinosaurs; egg size; nests; oviducts; parental careAbstract The reproductive biology of living birds differs dramatically from that of other extant vertebrates. Distinctive features common to most birds include a single ovary and oviduct, production of one egg at daily or greater intervals, incubation by brooding and extensive parental care. The prevalence of male parental care is most exceptional among living amniotes. A variety of hypotheses exist to explain the origin of avian reproduction. Central to these models are proposed transitions from a condition of no care to maternal, paternal or biparental care systems. These evolutionary models incorporate a number of features potentially preservable or inferable from the fossil record (integument, skeletal adaptations for flight, egg and clutch size, nest form, hatchling developmental stage, the number and function of oviducts, and the mode of egg incubation). Increasing availability of data on dinosaur reproduction provides a means of assessing these hypotheses with fossil evidence. We compare dinosaur data to a selection of models that emphasize maternal, paternal or biparental care. Despite some congruence with dinosaur features, no single model on the evolution of avian reproduction conforms fully to the fossil record, and the ancestral parental care system of birds remains ambiguous. Further investigation into dinosaur parental care, nest structures, clutch geometry, egg-pairing, eggshell porosity, and embryo identification may eventually resolve these issues. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
|
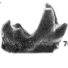
First record of the genus Megaderma Geoffroy (Microchiroptera: Megadermatidae) from Australia.Suzanne J. HandKeywords: Australia; Chiroptera; Megaderma; Megadermatidae; Pliocene; Rackham's Roost Site; RiversleighAbstract A new Tertiary megadermatid is described from Rackham's Roost Site, a Pliocene limestone cave deposit on Riversleigh Station, northwestern Queensland, Australia. It appears to represent the first Australian record of Megaderma GEOFFROY, 1810, a genus otherwise known from Tertiary African and European taxa and the living Asian species M. spasma (LINNAEUS, 1758) and M. (Lyroderma) lyra PETERS, 1872. Megademza richardsi n. sp. is one of the smallest megademiatids known. It exhibits a mixture of plesiomorphic and autapomorphic features, the latter appearing to exclude it from being ancestral to any living megadermatid. The new species is one of eight megadermatids identified from the Australian fossil record, most of which are referable to Macroderma MILLER, 1906. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|
|
Leptacodon nascimentoi n,sp., un nouveau Nyctitheriidae (Mammalia,Lipotyphla) de l'Eocène inférieur de Silveirinha (Baixo Mondego, Portugal)Carmen EstravisKeywords: Eocene; Leptacodon; Lipotyphla; Mammals; Nyctitheriidae; Portugal; SilveirinhaAbstract In this article is described a new species of Nyctitheriidae with primitive characters: Leptacodon nascimentoi n. sp. from the early Eocene of Silveirinha (Portugal). Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères post-glaciaires de Corse. Etude Archéozoologique.Jacques MichauxKeywords: Book reviewAbstract Les mammifères post-glaciaires de Corse. Etude Archéozoologique, par Jean-Denis Vigne, 1988. XXVle suppléments à "Gallia Préhistoire". Editions du C.N.R.S., Paris, 337 p. FRF 300. ISSN 0072-0100, ISBN 2-222-04130-9. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Neboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. 1 La poche et son remplissageBernard GèzeKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract La poche de Ste-Néboule, commune de Béduer (Lot), 15 km environ à l'WSW de Figeac, fait partie du groupe le plus septentrional des gouffres creusés par les ruissellements du Paléogène dans les calcaires jurassiques de la bordure sud-ouest du Massif Central et qui furent comblés à la même époque par des argiles sidérolithiques accompagnées de phosphate de chaux concrétionné ainsi que des restes de la célèbre faune dite «des phosphorites du Quercy» . Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
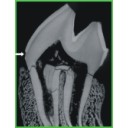
Enamel hypoplasia on rhinocerotoid teeth: Does CT-scan imaging detect the defects better than the naked eye?Manon Hullot and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: fossil teeth; method; micro-CT imaging; Rhinocerotoideadoi: 10.18563/pv.45.1.e2 Abstract Micro-CT imaging is an increasingly popular method in paleontology giving access to internal structures with a high resolution and without destroying precious specimens. However, its potential for the study of hypoplasia defects has only recently been investigated. Here, we propose a preliminary study to test whether hypoplastic defects can be detected with micro-CT (μCT) scan and we assess the costs and benefits of using this method instead of naked eye. To do so, we studied 13 fossil rhinocerotid teeth bearing hypoplasia from Béon 1 (late early Miocene, Southwestern France) as positive control and 11 teeth of the amynodontid Cadurcotherium (Oligocene, Phosphorites du Quercy, Southwestern France), for which enamel was partly or totally obscured by cement. We showed that all macroscopically-spotted defects were retrieved on 3D reconstructions and selected virtual slices. We also detected additional defects using μCT scan compared to naked eye identification. The number of defects detected using μCT was greater in the Cadurcotherium dataset (paired-sample Wilcoxon test, p-value = 0.02724) but not for our control sample (paired-sample Wilcoxon test, p-value = 0.1171). Moreover, it allowed for measuring width and depth of the defects on virtual slices (sometimes linked to stress duration and severity, respectively), which we could not do macroscopically. As μCT imaging is both expensive and time consuming while not drastically improving the results, we recommend a moderate and thoughtful use of this method for hypoplasia investigations, restricted for instance to teeth for which enamel surface is obscured (presence of cement, uncomplete preparation, or unerupted germs). Article infos Published in 45-1 (2022) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
Nouvelles espèces de Dendromus (Rongeurs,Muriodea) à Langebaanweg (Pliocène,Afrique du Sud) conséquences stratigraphiques et PaléoecologiquesChristiane DenysKeywords: Dendromurinae; Paleoecology; Pliocene; Rodents; South Africa; StratigraphyAbstract New Dendromus species (Rodentia, Muroídea) from Langebaanweg (Pliocene, South Africa). Stratigraphical and paleoecological consequences. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. 2- Amphibiens. Etude PreliminaireJean-Claude Rage and Colette Vergnaud-GrazziniKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The Caudata are known by two Salamandridae ; one of them is attributed to the genus Megalotriton. The Pelobatidae form the major part of the Anura ; a few bones indicate also the presence of Neobatrachia. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien supérieur. 4- CrocodiliensEric BuffetautKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Crocodilians are represented in the Upper Eocene of Sainte·Néboule (Lot) by an isolated parietal and a dorsal scute, bath from young individuals. They are refferred to Diplocynodon sp. Predators (mammals and birds) are probably responsible for the occurrence of remains of small crocodilians (belonging to the genera Allognathosuchus and Diplocynodon) in the phosphorltes of Quercy. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 9- Primates et ArtiodactylesJean SudreKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract La faune d'artiodactyles de Ste-Néboule, qui comprend neuf espèces, présente de nombreux Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Les Gruiformes (Aves) des phosphorites du Quercy (France). 1. sous-ordre cariamae (Cariamidae et Phorusrhacidae), systématique et biostratigraphie.Cécile Mourer-ChauviréKeywords: Aves; Biostratigraphy; Birds; Cariamae; gruiformes; Quercy Phosphorites; SystematicsAbstract The revision of the old collections of fossil birds from the “Phosphorites du Quercy” and the study of new material give the following results (Gruiformes, Cariamae) : The humeri and most of the carpometacarpi described under the name Filholornis belong in Elaphrocnemus. The ulnae ascribed to Fïlholornis belong in Idiornis. Most of the post-cranial elements of the genera Elaphrocnemus and Idiornis are described and show great similarities with recent Cariamidae and Opisthocomidae, and fossil Bathornithinae. A new genus and a new species, Oblitavis insolitus, are created in the sub-family Idiornithinae; two new species are described in the genera Elaphrocnemus (E. brodkorbz) and Idiornis (I. itardiensis), and the species Elaphrocnemus gracilis is transferred to the genus Idiornis. The genus Propelargus Lydekker is transferred from the family Ciconiidae to Cariamidae. A new generic name, Occitaniavis, is created for the species Geranopsis elatus, which belong in Cariamidae, while the type-species of the genus, Geranopsis hastingsiae, is a member of the Gruidae. The affinities between the Quercy avifauna and the Neotropical one is emphasized by the occurrence of Phorusrhacidae, previously known only from the Cenozoic of South America and the Late Pliocene or Early Pleistocene of North America. Thanks to the material collected during the new excavations, the stratigraphical position of most of the species is stated precisely, and evolutionary lineages are outlined. This study shows that the suborder Cariamae, presently restricted to two South American genera, was already extremely diversified during the Eocene, and widespread in Europe and North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 4 (1983) |
|
|

|
Morphotypes dentaires actuels et fossiles des Chiroptères Vespertilioninés. 1e partie: Etude des morphologies dentairesHenri MenuKeywords: bats; Dental morphology; fossils; PHYLOGENY; recent; SystematicsAbstract The classifications of the recent vespertilionine bats were made wihtout taking in account the teeth morphology; this resulted in a reduction of the possibilities of comparison with the available fossils. The generalized use of dental formulae was abusive: this contributed to the admission of artificial genera. These conditions have long delayed the consideration of characters able to frame the phylogeny of the sub-family. In the first part of the study, the teeth morphologies are described and analysed. morphological reference types are established for each upper and lower tooth: they should make an easier elaboration of criteria for the differentiation at generic level. The position of the species in view of these criteria allows one to group them into homogeneous genera, and to appreciate the degree of relationship that the latter have between them. The second part of the study (next publicationà will develop inferences dealing with systematics and phylogeny Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 2 (1985) |
|
|

|
Analyse d'ouvrage: “J.J. THOMASON (Ed.): Functional morphology invertebrate paleontology (1995)”Jacques MichauxKeywords: Book review; Functional morphologyAbstract Functional morphology invertebrate paleontology, édité par Jeffrey J. THOMASON, 1995. Cambridge University Press, xi + 277 p. ISBN 0-521-44095-5, f. 45,00 ($ 69,95). Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 1 (1996) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 6 - Les périssodactyles RhinocerotidaeClaude GuérinKeywords: Aceratherium; anatomy; Biostratigraphy; Dicerorhinus; Miocene; Montredon; Paleoecology; Upper VallesianAbstract The Montredon site has yielded about hundred rhinoceros remains: Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 12- Fissipèdes (Carnivores)Louis de BonisKeywords: Carnivora; Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Les Carnivores Fissipèdes de Sainte-Néboule appartiennent tous au genre Cynodictis et semblent constituer une population homogène. Celle-ci se distingue suffisamment des espèces déjà décrites pour constituer un taxon particulier : Cynodictis lacustris neboulensis n. s. sp. . L'étude des variations à l'intérieur de cette population nous a conduit à reconsidérer les critères utilisés pour définir les espèces existantes et à regrouper certaines d'entre elles. Il semble qu'il demeure cependant trois lignées distinctes dans le genre Cynodictis mais le matériel nous paraît encore insuffisant pour traduire cette remarque en termes de systématique. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
Données nouvelles sur le genre Stehlinia (Vespertilionoidea, Chiroptera) du Paléocène d'EuropeBernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Palaeocene; VespertilionoideaAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
The microfauna of the Djebel Qafze CaveG. HaasKeywords: Micromammals; RodentsAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|
|
Rates of evolution in divergent species lineages as a test of character displacement in the fossil record : tooth size in Paleocene Plesiadapis (Mammalia, Proprimates)Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: character displacement; character divergence; fractal time series; Plesiadapis; Rates of evolutionAbstract Two species lineages of North American late Paleocene Plesiadapis exhibit a pattern of size divergence from a common ancestral lineage. Time series of fossils in each of these lineages are analyzed to test the idea that size divergence represents competitive character displacement. The critical factor in a test of character divergence is showing that divergent lineages evolved directionally rather than randomly (multifactorially). Analysis of evolutionary rates and their temporal scaling in Plesiadapis shows that both divergent species lineages have the scaling slope expected for lineages evolving randomly rather than directionally, and size divergence in Plesíadapis does not represent character displacement. Rates of evolution commonly observed on a per-generation time scale are high enough to produce character displacement within a few generations. Thus character displacement is not likely to be visible on scales of time that can be studied in the fossil record. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Neue Beobachtungen zum Schädel-und Gebiss-Bau der Paulchoffatiidae (Multituberculata,Ober-Jura).Gerhard HahnKeywords: Dentition; Paulchoffatiidae; Portugal; Skull structure; Upper JurassicAbstract The ventral face of the Paulchoffatiinae skull (Multituberculata, Lower Kimmeridgian, Portugal) is new reconstructed. Some details hitherto unknown are added, as the presence of jugals, the structure of the palatine and the extension of the pterygoids. The situation of the m2/ is discussed. Kielanodon hopsoni n. g., n. sp. is erected, known by its upper p3-5/. From Guimarotodon leiriensis the mandible with its dentition is made known. New informations concerning the milk-dentition and the replacement of teeth are also added. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 4 (1987) |
|