Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Werneburg et al. New Permian Caseid from France
Field trip guides/EAVP Annual Conference/2023
Embrithopod from Croatia
Hypoplasia: CT-scan or naked eye?
Book of Abstracts/EAVP Annual Conference/2023
Eocene (57) , Quercy phosphorites (37) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (26)
|
Un nouveau type de coquille d'oeuf présumé Dinosaurien dans la Campanien et le Maestrichtien continental de Provence.Philippe KerourioKeywords: Campanian/Maastrichtian; eggshell microstructure; ProvenceAbstract The discovery of eggshells of ornithoid type is signaled for the first time in the continental Campanian and Maastrichtían of Provence. The taxonomie relationship of these eggshells and their interest in the biostratigraphical study of Upper Cretaceous of Provence are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 4 (1982) |
|
|
|
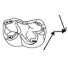
Eurodexeinae, eine neue unterfamilie der Artiodactyla (Mammalia) aus dem unter- und mitteleozän europasJorg Erfurt and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyls; Eocene; evolution; Germany; Lutetian; new genus; New subfamilyAbstract Dichobunoid artiodactyls are described in this paper from the middle Eocene Geiseltal lignite deposits near Halle (Sachsen-Anhalt, Germany). The genera Eurodexis and Parahexacodus are established based on odontologica1 studies. The type-species are E. ceciliensis (FRANZEN & KRUMBIEGEL, 1981) and P. germanicus n. sp. from the "obere Mittelkohle" (see text), MP 13. The genera are referred to the new subfamily Eurodexeinae (Dichobunidae, Artiodactyla, Mammalia), which also contains the monospecific genus Eygalayodon SUDRE & MARANDAT, 1993. These new genera show many features similar to North American homacodontids and antiacodontids. They exemplify a high degree of diversity in European dichobunids. Moreover, the family Dichobunidae includes the Dichobuninae and the Hyperdichobuninae. The connection of the posthypocristid with the postentocristid, the shift of a medial to a lingual position of the hypoconulid on the lower molars and the development of a large, caniniform P1 are regarded as the principal tendencies of the eurodexeines. The entoconid is larger and more mesially situated compared to that of Diacodexis. The hypoconulid has a lingual position on a broad postcingulid. The elongation of the premolars and the presence of diastemata are considered associated with extension of the muzzle. This and the acute tubercles of the molars could indicate a limited degree of insectivory. Protodichobune cf. oweni and Diacodexis cf. varleli, first reported here from the "untere Unterkohle" (MP 11) of the Geiseltal, demonstrate the existence of forms in the basal part of the middle Eocene, that are direct descendants of lower Eocene ones. Eurodexis russelli n. sp. from MP 10 of Premontre is the most primitive representative of Eurodexis. A further part of this lineage could be Messelobunodon sp. from MP 11 of Messel (Germany). Another form from Premontre, referred to Eurodexeinae indet., represents the origin of the lineage to Parahexacodus germanicus n. sp. from the Geiseltal (MP 13). The identification of several lineages in MP 10 is evidence of an adaptive radiation during this time. Unfortunately the history of the earlier species of Diacodexis is not known well enough to exclude earlier diversifications. Our study shows the independent development of artiodactyls at the end of the lower Eocene in Europe, North America (and maybe in Asia) with much convergence. The question of the geographic origin of the genus Diacodexis is still open. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Neboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. 1 La poche et son remplissageBernard GèzeKeywords: Eocene; Quercy phosphoritesAbstract La poche de Ste-Néboule, commune de Béduer (Lot), 15 km environ à l'WSW de Figeac, fait partie du groupe le plus septentrional des gouffres creusés par les ruissellements du Paléogène dans les calcaires jurassiques de la bordure sud-ouest du Massif Central et qui furent comblés à la même époque par des argiles sidérolithiques accompagnées de phosphate de chaux concrétionné ainsi que des restes de la célèbre faune dite «des phosphorites du Quercy» . Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Compléments sur les Chiroptères de l'Eocène moyen d'Europe. Les genres Palaeochiropteryx et Cecilionycteris.Bernard Sigé and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Chiroptera; Geiseltal; Messel; Middle EoceneAbstract New dental and skeletal material referable to Palaeochiropteryx tupaiodon from the Middle Eocene locality of Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
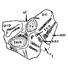
Die Ohr-Region der Paulchoffatiidae (Multituberculata, Ober-Jura).Gerhard HahnKeywords: Multituberculata; Ober-Jura; Paulchoffatiidae; Petrosum; PortugalAbstract The petrosal of the Paulchoffatiidae HAHN, 1969 is described and compared with that of younger multituberculates and of other Mesozoic mammals. The "Morrison petrosal", described by Prothero (1983), is also discussed; it probably belongs to the multituberculates. The reconstruction of the ventral side of the Paulchoffatiinae-skull, given by Hahn in 1987, is completed by addition of the otic and the occipital region. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 3 (1988) |
|
|
|
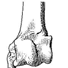
Anatomie du membre antérieur chez un chiroptère Molossidé (Tadarida sp.) du Stampien de Cereste (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence).Bernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Molossidae; Oligocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.4.1.1-38 Abstract The present study describes in detail the anterior limb osteology of a molossid chiropteran of the genus Tadarida, from Céreste, a Stampian locality in the Apt-Forcalquier Oligocene basin already known for its fishes, plants and insects. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 1 (1971) |
|
|

|
Préface au mémoire jubilaire en hommage à René LavocatJacques MichauxKeywords: EditorialAbstract Monsieur René Lavocat, Directeur du Laboratoire de Paléontologie des Vertébrés de la troisième section de l'Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes, quittait le service actif en l'année 1979. View editorial Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Rongeurs du Miocène inférieur et moyen en Languedoc. Leur apport pour les correlations Marin-Continental et la Stratigraphie.Jean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Languedoc; Miocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract The rodents (Cricetidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) found in lacustrine, brackish marine and karstic sediments of Miocene age in Languedoc, assign the position of the different localities in the scale of "niveaux repères" used by mammalogists. Some detailed stratigraphical studies bring several correlations between this continental biochronological scale and the marine scale ; the most important results are the Aquitanian age of the "niveaux repères" of Coderet and Paulhiac, the Burdigalian age of Laugnac, Estrepouy, Vieux-Collonges, La Romieu and Sansan and the Langhian or Lower Serravallian age of La Grive M. The correlations between the Tethys and the Central Paratethys for the Lower Neogene profit also of these results, since the locality of Neudorf Spalte 1, 2 (Czechoslovakia) is shown to be younger than Sansan (France). The paleontological study has also several geological inferences for the Miocene of Languedoc ; with the calibration of this Miocene, we know quite precisely that the Lower Miocene is chiefly a time lacustrine sedimentation, and also that the marine Miocene sedimentation ends early in the Miocene Period, in Langhian or lower Serravallian times. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 6 (1980) |
|
|

|
Les Bovidae (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) du Miocène moyen de la formation Hofuf (Province du Hasa, Arabie Saoudite).Herbert ThomasKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Bovidae; Middle Miocene; Palaeogeography; Saudi ArabiaAbstract The study of the bovids from Al Jadidah (Hofuf Formation, Saudi Arabia) confirms that the fauna comes from a pre-Hipparion level. The Al Jadidah age is close to that of Fort Ternan (14 m.y.) and Beni Mellal, but cannot be older than that of Fort Ternan. The age of the Hofuf Formation is close to but slightly older than the oldest deposits of the Ngorora Formation (Kenya). 7 to 9 species have been recorded, of which 2 to 4 remain indeterminate. If the great specific diversity of te bovids from this locality gives evidence of immigrations from anterior Asia (Turkey) (e.g. Pachytragus Iigabuei sp. nov.), the bovid assemblage of Al Jadidah results in fact from a double influence: from the anterior Asia and mainly from Africa (e.g. the Caprotragoides lineage and the Neotragini? Homoiodorcas). The Al Jadidah bovids reflect, on the whole, the predominant character of open to very open environment, which supports the conclusions drawn from our two preliminary studies. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 5 (1983) |
|
|

|
New records of the pantodont Archaeolambda from the Paléocène of southern ChinaSuyin Ting, Judith A. Schiebout and Jianjian ZhengKeywords: Archaeolambda; China; Paleocene; PantodontAbstract Two new finds of pantodont materials from southern China, assigned to Archaeolambda, are described in this paper. One, a new species from the Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong Province, is similar to Alcidedorbignya inopinata from the early Paleocene of Tiupampa, Bolivia in size. It provides reliable evidence of the occurrence of Archaeolambda in the early-middle Paleocene of southern China. The second find includes specimens of Archaeolambda sp. cf. A. planicanina from the ?late Paleocene of Hengyang Basin, Hunan Province, which are the first record of a fossil mammal from the area near Hengyang city. The only vertebrate fossils previously found here were two genera of crocodiles discovered in 1938. This find sheds new light on the local biostratigraphy. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Présence de Palaeobatrachidae (Anura) dans des gisements tertiaires Français caractérisation, distribution et affinités de la familleColette Vergnaud-Grazzini and Robert HoffstetterKeywords: Anura; Palaeogeography; SystematicsAbstract The Palaeobatrachidae until now have not been reported from France. The present note makes known the discovery of very significant remains in three Tertiary localities of France: Cernay (late Paleocene), Laugnac (late Aquitanian) and Sansan (middle Helvetian). The osteologic characters, as well as the geographic and stratigraphic distribution of the family are re-stated with added details. The Palaeobatrachidae are a European family known from the late Jurassic of Catalonia (publication in course by J. Seiffert) to the Plio-Pleistocene (pre-Mindel) of Poland and Rumania. By their way of life and certain osteologic characters they are similar to the Pipidae, but they are distinguished by profound differences. It would be rash to include them in the Pipoidea or even in the Aglossa. They are apparently an independant group, essentially holarctic, which held in Europe a role equivalent to that played by the Pipidae south of Tethys. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 4 (1972) |
|
|
|
Les Tayassuidés des phosphorites du QuercyLéonard GinsburgKeywords: Quercy phosphorites; TayassuidaeAbstract Revision of the Tayassuidae from the old collections of the Quercy leads to interesting facts about taxonomic and phylogenetic problems. It could not have been well done without constant comparison with contemporaneous Tayassuidae from stratified series, as well as with European Miocene Tayassuidae and Hyotheriinae. The result is that only three species are present in the Phosphorites of Quercy: Doliochoerus quercyi FiLHOL (represented by two sub-species: the older, D. quercyi quercyi and the more recent, D. quercyi aquensis), Palaeochoerus gergorianus CROIZET et BLAINVILLE and Palaeochoerus purillus nov. sp. The two former species disappeared with Stampian time, while the third is the direct ancestor of the Aquitanian Palaeochoerus typus POMEL, which became extinct before the beginning of Burdigalian. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
Neue Beobachtungen zum Schädel-und Gebiss-Bau der Paulchoffatiidae (Multituberculata,Ober-Jura).Gerhard HahnKeywords: Dentition; Paulchoffatiidae; Portugal; Skull structure; Upper JurassicAbstract The ventral face of the Paulchoffatiinae skull (Multituberculata, Lower Kimmeridgian, Portugal) is new reconstructed. Some details hitherto unknown are added, as the presence of jugals, the structure of the palatine and the extension of the pterygoids. The situation of the m2/ is discussed. Kielanodon hopsoni n. g., n. sp. is erected, known by its upper p3-5/. From Guimarotodon leiriensis the mandible with its dentition is made known. New informations concerning the milk-dentition and the replacement of teeth are also added. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 4 (1987) |
|
|

|
Agriotherium intermedium (Stach 1957) from a Pliocene fissure filling of Xiaoxian County (Anhuei Province, China) and the phylogenetic position of the genus.Zhanxiang Qiu and Norbert Schmidt-KittlerKeywords: Carnivora; China; PHYLOGENY; Pliocene; skull anatomy; UrsidaeAbstract A fragmentary mandible and maxilla of a small sized Agriotherium of a young individual discovered from a Pliocene fissure filling in Xiaoxian county (Anhuei Province, China) are described. Judging from the morphology of the dentition and its dimensions the new material can be identified as Agriotherium inlermedium (STACH l957). Hendey's proposition (1980) that the Agriotherium species are derived from Indarctos is reconsídered on the basis of the new documents. As a result of a more general phylogenetic discussion it can be stated, that: 1. the supposed size increase as well as other trends, leading from Indarctos to Agriotherium are untenable ; 2. there are no positive indications to assume a phylogenetic transition of these two genera. 3. there are no real arguments in favor of an adaptational reversal in the evolution of Agriotherium. Hence, many features of that genus supposed by Hendey to be derived are plesiomorphic ; 4. regardless of the previous points it is methodologícally impossible to establish direct ancestor - descendant relationships between Indarctos and Agriotherium species, as Hendey did. Based on the data available and especially on the characters of the new material from China it is more likely that Agriotherium and Indarctos are two genera which developed independently. While advanced Agriotherium species, e.g. A. africanum, resemble in some respects Indarctos by adaptational analogies, more primitive species, e.g. Agriotherium intermedium, are quite dissimilar to lndarctos. While Indarctos might be derived from an Ursavus like forerunner, Agriotherium has its roots more likely somewhere in between Ursavus and the Hemicyon-group. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|

|
Les nouvelles faunes de rongeurs proches de la limite mio-pliocène en Roussillon. Implications biostratigraphiques et biogéographiquesJean-Pierre Aguilar, Jacques Michaux, Bernadette Bachelet, Marc Calvet and Jean-Pierre FaillatKeywords: Arvicolidae; Cricetidae; Gliridae; Miocene; Muridae; Pliocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract Three new fossiliferous localities, two of karstic origin, Castelnou 3 and Font Estramar, respectively Late Upper Miocene and Lower Pliocene, and one of lacustrine origin, Thuir, Lower Pliocene, add data about the transition between Miocene and Pliocene faunas of rodents in southern France. An unexpected association of taxa was present in the late Upper Miocene, including between others, Myocricetodon, Hispanomys, Ruscinomys, Cricetus barrierei, Promimomys and a new species of Stephanomys, S. dubari nov. sp. Myocricetodon is still known in the Lower Pliocene. It is shown that the large field-mice known since the Late Upper Miocene belong to two different lineages, on one side, A. jeanteti, on the other side, A. gudrunae followed by A. gorafensis. Biochronological and biogeographical implications are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 4 (1991) |
|
|
|
Sur les Condylarthres Cernaysiens Tricuspiodon et Landenodon (Paléocène supérieur de France)Donald E. RussellKeywords: Arctocyonidae; Condylarths; Late Paleocene; TricuspiodontidaeAbstract The numerical importance of the Condylarths in the Cernaysian fauna is discussed. The Condylarth family, Tricuspiodontidae, is reviewed in the light of new material and its close relationships to the Phenacodontidae is suggested ; one new species is recognized : Tricuspiodon sobrinus. European Arctocyonidae are reviewed and the recentclassification of Van Valen is briefly commented on. Also, the arctocyonine Landenodon is described for the first time in Thanetian (Late Paleocene) sediments ; two new species are proposed : T. lavocati and T. phelizoni. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Eléments nouveaux sur l'évolution des genres Eucricetodon et Pseudocricetodon (Eucricetodontinae, Rodentia,Mammalia, de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Bernard ComteKeywords: evolution; Occidental Europe; Oligocene; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract The review of material recently collected in the new localities from the “Phosphorites du Quercy", and different localities from the South of France, bring new informations on the genus Eucricetodon THALER. 1966, and Pseudocricetodon THALER, I969 (Middle and Upper Oligocene. Western Europe). Thanks to Eucricetodon huerzeleri VIANEY-LIAUD, 1972, which were unsufficiently known until now, is proposed. During the middle Oligocene Eucricetodon atavus MISONNE, 1957 seems to give rise to two lineages. One of them led to Eucricetodon huberi,which however exhibits a larger size and a development of progressive characters on the teeth. The other would be Eucricetodon huerzeleri well differentiated at the “Mas de Pauffié" standard level (beginning of the upper Oligocene). The ornementation of lower incisors is described, when possible. Though the fossils are not abundant, it seems that the ancestral lineage, Eucriretodon atavus, remains in the upper Oligocene (Boningen standard level). evolving into Eucricetodon praecursor SCHAUB, 1925 (Rickenbach standard level). The characters of Eucricetodon dubius (SCHAUB. 1925), represented by a numerous population in Pech Desse and Pech du Fraysse (Quercy). confirm that this species and Eucricetodon praecursor belong to two different lineages. As Eucricetodon dubius shows more primitive features, this species could not originale from Eucricetodon atavus -Eucricetodon huberi. The appearance of this species at the level of Mas de Pauffié could be the result of an immigration. A new definition of Pseudocricetodon incertus (SCHLOSSER. 1884) is given. This species has been found in several localities, where it had not been identified until now. lts comparison with Pseudocricetodon moguntiacus (BAHLO. l975), found at several localities from the standard level of Antoingt (end of middle Oligocene). shows a parallel evolution to that of Pseudocetodon incertus, which is of larger size and with a less complicated pattern of teeth. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 1 (1985) |
|
|
|
Rongeurs Miocènes dans le Valles-Penedes 2 : Les rongeurs de Castell de BarberaJean-Pierre Aguilar, Jordi Agusti and J. GibertKeywords: Castell de Barbera; Miocene; Rodents; Valles-PenedesAbstract The rodent-fauna (Cricetidae and Gliridae) recently found at Castell de Barbera (Spain) is similar to those from the other locslities of the Valles - Penedes - Can Ponsic 1 and Can Llobateres - : same composition and similar evolutionary level of the different species. On the other hand this fauna is different from those of Upper Vindobonian and Vallesian localities of the Calatayud - Teruel area. Castell de Barbera has an intermediate chronological position between the localities of Anwil (Switzerland) and Can Ponsic 1. It is still not possible to validate or invalidate the initial attribution based on absence of Hipparion of Castell de Barbera to the Upper Vindobonian. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 1 (1979) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères Montiens de Hainin (Paléocène moyen de Belgique) Part1: Multituberculés.Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Belgium; Hainin; Mammals; multituberculates; PaleoceneAbstract The Montian locality of Hainin (Hainaut, Belgium) yielded about twenty teeth of Multituberculates. They are very peculiar forms, showing no affinities, at the generic level, with those hitherto known from North America, Asia and Europe. They are referred to the new taxa Boffius splendidus nov. gen., nov. sp., Hainina belgica nov. gen., nov. sp., and H. godfriauxi nov. gen., nov. sp. They expose some common features, such as the advanced type of first upper molar. possessing at least three complete rows of cusps. Because of this, and also of the upper premolar reduction, Boffius splendidus appears as the most specialized form within the Ptilodontoidea suborder. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 4 (1979) |
|
|
|
Deux nouveaux primates dans l'Oligocène inférieur de Taqah (Sultanat d'Oman): premiers Adapiformes (?Anchomomyini) de la péninsule arabique?Emmanuel Gheerbrant, Herbert Thomas, Jack . Roger, Sevket Sen and Zaher Al-SulaimaniKeywords: Adapids; Afro-Arabian plate; Early Oligocene; New taxa; Primates; Trans-Tethyan dispersalsAbstract Two new species, Omanodon minor n. g., n. sp. and Shizarodon dhofarensis n. g., n. sp., known from fifteen isolated teeth, are described here as the first adapiform primates (?Anchomomyini) recognizable to date in the Taqah material (early Oligocene of Sultanate of Oman). Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 4 (1993) |
|